Hartman wave front detector with aperture alignment function
A detector and photodetector technology, applied in instruments, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of deviation of measurement results, inability to precisely control, access, etc., and achieve the effect of precise alignment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
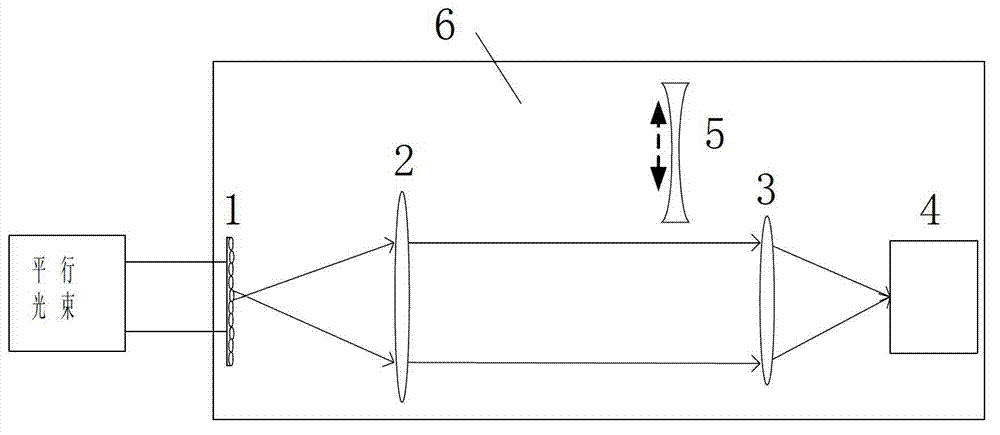
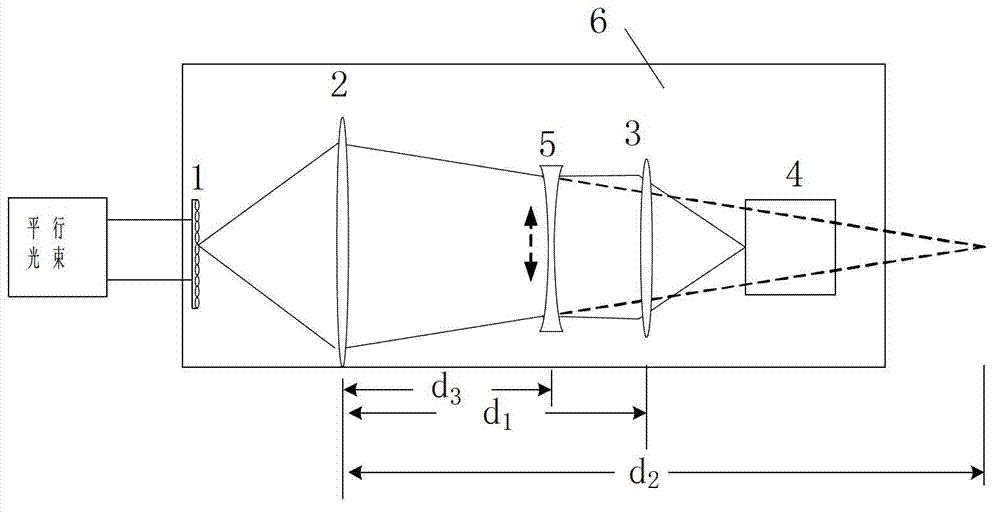
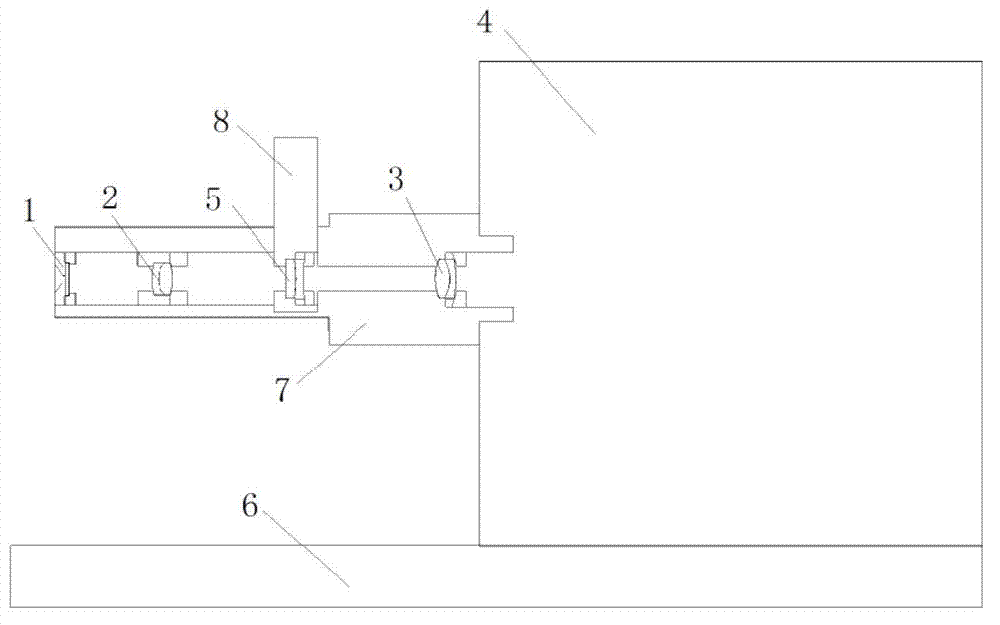
[0017] 1) The microlens array 1 is a circular plano-convex lens purchased from SUSS Company and a rectangularly arranged microlens array panel. The diameter of a single microlens is 150 μm, the radius of curvature is 3400 μm, and the focal length f 1 =4.40mm, the size of the entire panel is 10mm×10mm×1.20mm, attached to a 1.5mm aperture diaphragm, that is, the aperture D 1 =1.5mm.
[0018]2) The first lens 2, the second lens 3, and the switching concave lens 5 are double-cemented achromatic lenses, and the surface is coated with an anti-reflection coating. The diameters are 5mm, 6mm, and 5mm, and the thicknesses are 3.00mm, 3.00mm, and 2.00 mm, the focal lengths are 10.00mm, 12.80mm, -22.73mm respectively.
[0019] 3) The photodetector 4 is a high-sensitivity EMCCD (DV897 from ANDOR, UK), with a pixel count of 128×128, and a square light window of 1.9mm×1.9mm, namely the aperture D 4 =1.9mm, the number of pixels in the light window is 80×80, using 2×2 binning mode, the sampl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Caliber | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Focal length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com