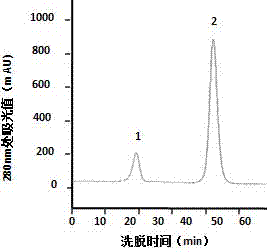
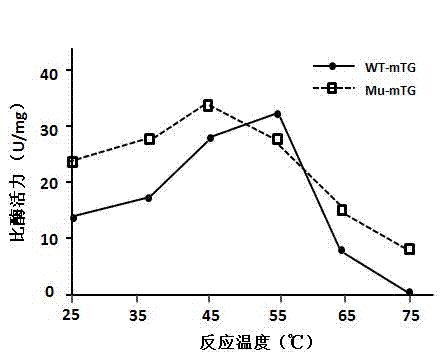
Method for separating and purifying microbial transglutaminase
A technology for separation and purification of transglutaminase, applied in the direction of transferase, etc., can solve the problems of low enzyme yield, purity and specific activity, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1 Fermentation of transglutaminase enzyme
[0045] The MTG production strain in this example is the Streptomyces mobaraensis mutant strain of Streptomyces mobaraensis, which is produced by the STK4 wild strain through ultraviolet irradiation mutagenesis, and the MTG secreted by the mutant strain is mutated. Amino acids at positions 10, 241 and 284 of the mutant MTG have been mutated, and the amino acid at position 10 is serine or threonine; the amino acid at position 241 is alanine or glycine; the amino acid at position 284 is valine Or tyrosine. The amino acids at positions 10, 241, and 284 of wild-type MTG are alanine, proline, and serine, respectively. The mutated MTG of the present invention has higher activity than wild MTG at 25°C and 37°C.
[0046] First, inoculate the strains on the slant medium and culture at 30°C for 5-7 days, collect all the microorganisms and inoculate them into the fermentation broth, cultivate them at 150rpm for 24 hours, then...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2 Determination method of transglutaminase enzyme activity
[0049] The enzyme activity was determined by the Grossowicz colorimetric method, with NA-CBZ-GLN-GLY and hydroxylamine as the substrates, and L-glutamic acid-γ-monohydroxamic acid as the standard curve. Put the substrate (NA-CBZ-GLN-GLY and hydroxylamine) and 40ul of the sample to be tested into water to preheat for 10-15min, add 100ul of substrate to the sample, act for 10min, then add 40ul of stop solution (trichloroacetic acid and FeCl3) to terminate the reaction. The sample was taken out, centrifuged at 8000×g for 5-10 min, and the enzyme activity was measured by a colorimetric method with a protein and nucleic acid quantification instrument at 562 nm. Definition of enzyme activity unit: the amount of enzyme required for the enzyme to catalyze the substrate to generate 1molL-glutamic acid-γ-monohydroxamic acid in 1min under the condition of 37°C.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Dispase treatment
[0051] Fermentation hydraulic filtration removes bacteria, and the filtrate is centrifuged at 4°C and 12,000rmp for 15 minutes to remove residual bacteria fragments and some macromolecular proteins; the supernatant is treated with dispase at 50-200 mg / L, and stirred slowly at room temperature for 30-60 minutes. The enzyme activity of the fermented supernatant after treatment was increased from 1.9U / ml to 2.4U / ml.
[0052] Table 1. Effect of dispase on active MTG in fermentation broth
[0053] volume Enzyme activity original fermentation broth 450ml 1.9U / ml Dispase-treated fermentation broth 400ml 2.4U / ml
[0054] Table 1 shows that dispase treatment can convert pro-MTG in the fermentation broth into active MTG, thereby increasing the yield of active MTG.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com