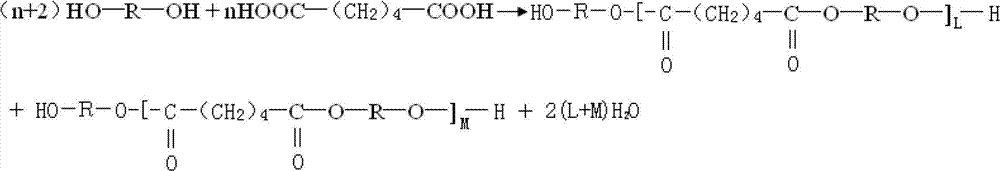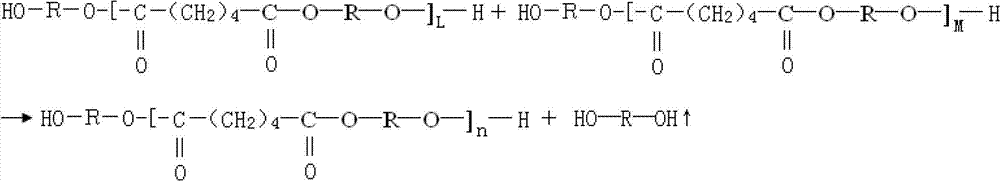Hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol and preparation process thereof
A polyester polyol and a preparation process technology, which are applied in the fields of ester polyol and its preparation, hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol and its preparation, can solve problems such as poor hydrolysis resistance, achieve high stability and reduce alcohol consumption. Loss, energy saving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol of this embodiment has the structural formula:
[0027]
[0028] Where R is (CH 2 ) 4
[0029] n represents the degree of polymerization, where the value range of n is 1-50;
[0030] A hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol and its preparation process, including the following steps:
[0031] 1. Add diols 1,4 butanediol, methyl propylene glycol, and adipic acid into the reactor, and then add the catalyst tetraisopropyl peptide ester, the mass ratio of the diols, adipic acid, and the catalyst It is 0.65:1:0.00004, turn on the stirrer, and pour nitrogen into it, stir evenly;
[0032] 2. Raise the temperature of the reactor. When the temperature of the materials in the reactor rises to 130°C, the esterification reaction starts, that is, glycols will generate low molecular weight polyester through the esterification reaction. The condensation water vapor produced by the reaction and its The entrained glycols are rectified through the rectific...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol of this embodiment has the structural formula:
[0041]
[0042] Where R is (CH 2 ) 4
[0043] n represents the degree of polymerization, where the value range of n is 1-100;
[0044] The preparation process of the hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0045] 1. Add glycols, ethylene glycol, methyl propylene glycol, and adipic acid to the reactor, and then add the catalyst tetraisopropyl peptide ester. The mass ratio of glycols, adipic acid, and catalyst is 0.70: 1:0.000045;
[0046] 2. Heat up the reactor. When the temperature of the materials in the reactor rises to 132°C, the esterification reaction starts, that is, glycols and adipic acid undergo esterification to generate low-molecular-weight polyester, and the condensation water produced by the reaction at this time The steam and its entrained glycols are rectified through the rectification tower. The glycols are recovered in the ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol of this embodiment has the structural formula:
[0055]
[0056] Where R is (CH 2 ) 4
[0057] n represents the degree of polymerization, where the value range of n is 1-150;
[0058] The preparation process of the hydrolysis-resistant polyester polyol of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0059] 1. Add the glycols methyl propylene glycol, 1,4 butanediol, and adipic acid into the reactor, and then add the catalyst tetraisopropyl peptide ester, the mass ratio of the three is 0.75:1:0.00005;
[0060] 2. Heat up the reactor. When the temperature of the materials in the reactor rises to 130°C, the esterification reaction begins, that is, glycols and adipic acid undergo esterification to generate low-molecular polyester, and the condensation water produced by the reaction at this time Steam and its entrained glycols are rectified through a rectification tower. The glycols are recovered in the tower and directly enter the reactor....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com