Molecular marker closely linked with oil content character of rapes and application
A molecular marker and oil content technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and genetic breeding, can solve the problems of poor repeatability, small effect value, difficult rapeseed breeding application, etc., and achieve the effect of clear selection target, high difficulty and high cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1. Construction and character determination of rapeseed oil content segregated population
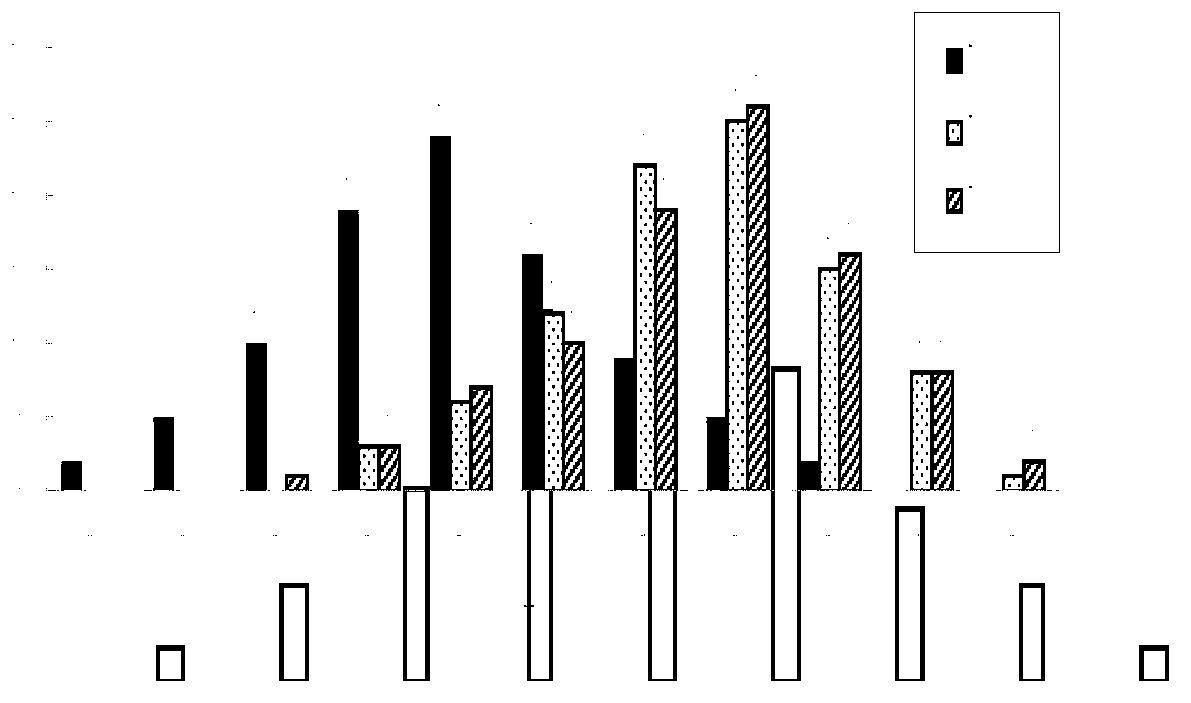
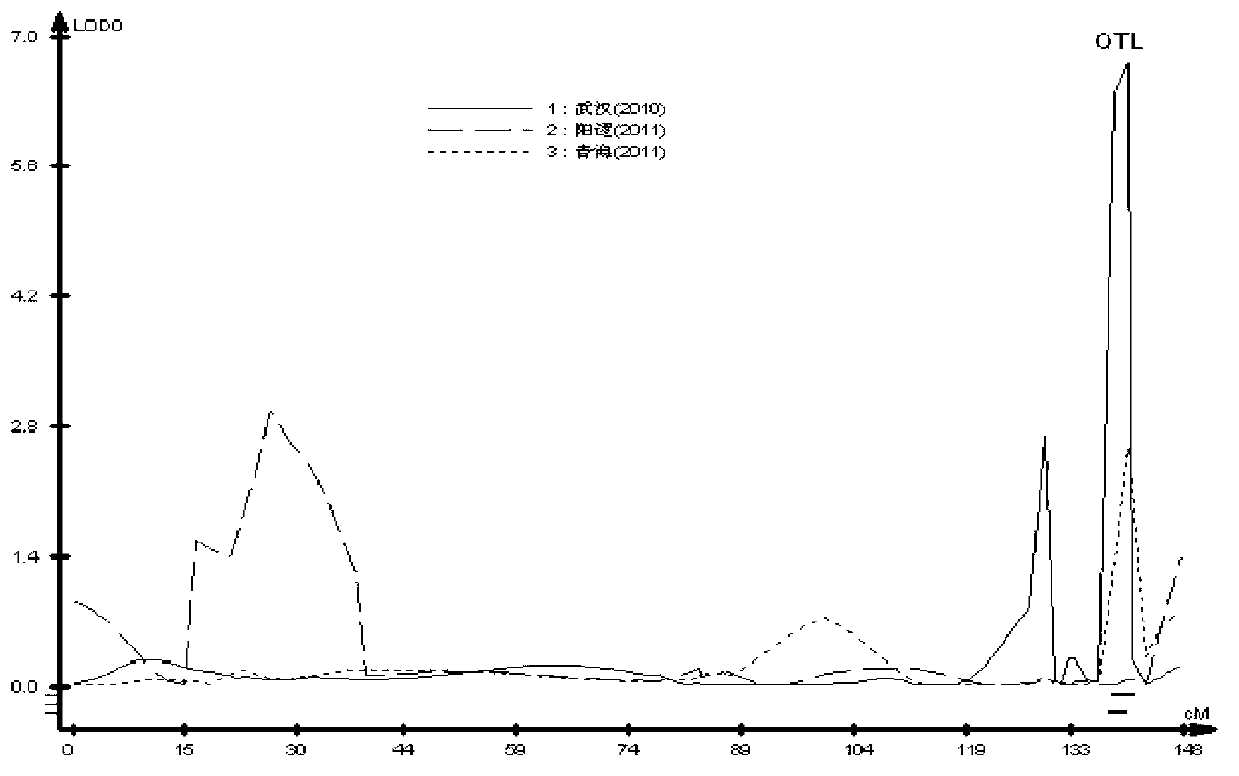
[0032] The population used in this example is the hybrid offspring of high and low oil content parents (zy036 with 50% oil content and 51070 with 36% oil content, respectively) - DH population. The DH isolates were harvested in Wuhan in 2010, Yangluo and Qinghai in 2011. The seed oil content of the parental and DH populations was determined by a near-infrared analyzer. The oil content data distribution results show that the oil content of the three experiments is a continuous normal distribution, and the variation range is very wide, which proves that the oil content is a quantitative trait ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2. Extraction of total DNA from leaves of parental zy036, 51070 and DH isolated populations
[0034] The total DNA of leaves was extracted by CTAB method. The specific steps are as follows:
[0035] A. Get 0.1 gram of leaf fresh sample and put it into grinding, add 700 microliters of extract and grind, then put into 1.5 milliliter centrifuge tube and place in 65 ℃ of constant temperature water baths for 60 minutes, mix 2-3 times in between;
[0036] b. Add an equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1, volume ratio), invert gently to mix thoroughly; centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes to separate the layers, gently pipette the supernatant and transfer it to another. 1.5 ml centrifuge tube; add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1, volume ratio) to re-extract once;
[0037] c. Add 1 ml of -20°C pre-cooled absolute ethanol, freeze at -20°C for no more than 30 minutes to allow DNA precipitation; centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3. Development of primers and screening of polymorphisms
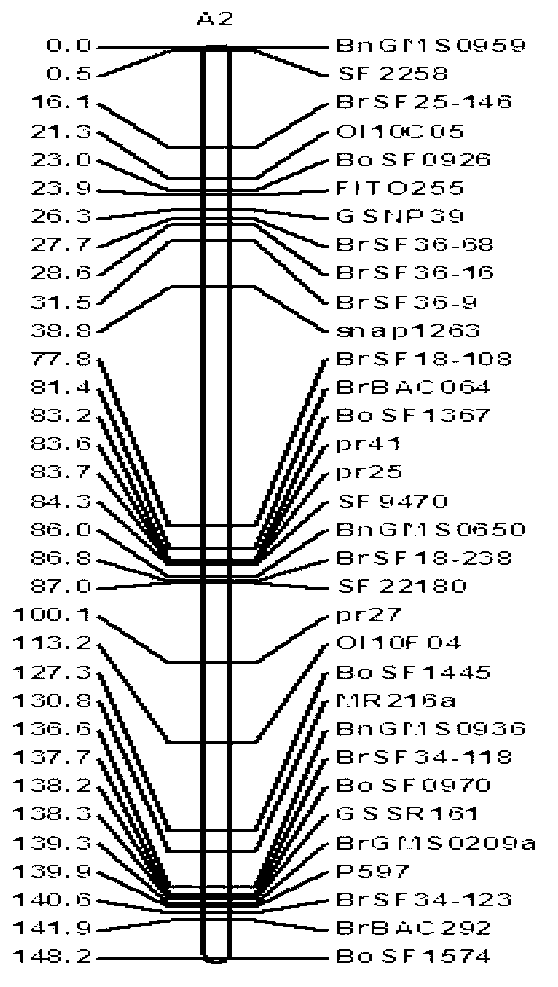
[0040] The primers used by the applicant include three categories: the first category is simple repeat sequence (SSR) primer sequences published in published articles and Brassica databases (http: / / www.brassica.info / resource / markers / ssr-exchange .php), including BN, BnEMS, BnGMS, BoGMS, BrGMS, BRAS, CB, CNU, EJU, ENA, FITO, IGF, MR, Na, Ni, Ol, Ra, niab, sN, sR and sS and many other series; The second category is based on the sequencing results of Chinese cabbage, cabbage and Brassica napus, the applicant uses MISA software to search for SSR sites on the whole genome sequences of Chinese cabbage, Brassica napus and Brassica napus, and develop simple repeat sequence (SSR) primers. Using the SNP function of SOAP software to predict SNP sites in the whole genome sequences of Chinese cabbage, cabbage and Brassica napus, and develop single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) primers named BrSF, BrBAC, P, BoSF, SF, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com