Test device and method for judging soil layer collapsibility
A test device and technology of collapsibility, which is applied in the field of test devices for determining the collapsibility of soil layers, and can solve problems such as the inability to determine the sampling depth, the failure to penetrate the soil exploration point, and the unpredictable thickness of the collapsible soil layer. , to achieve the effect of obvious superiority, small size and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
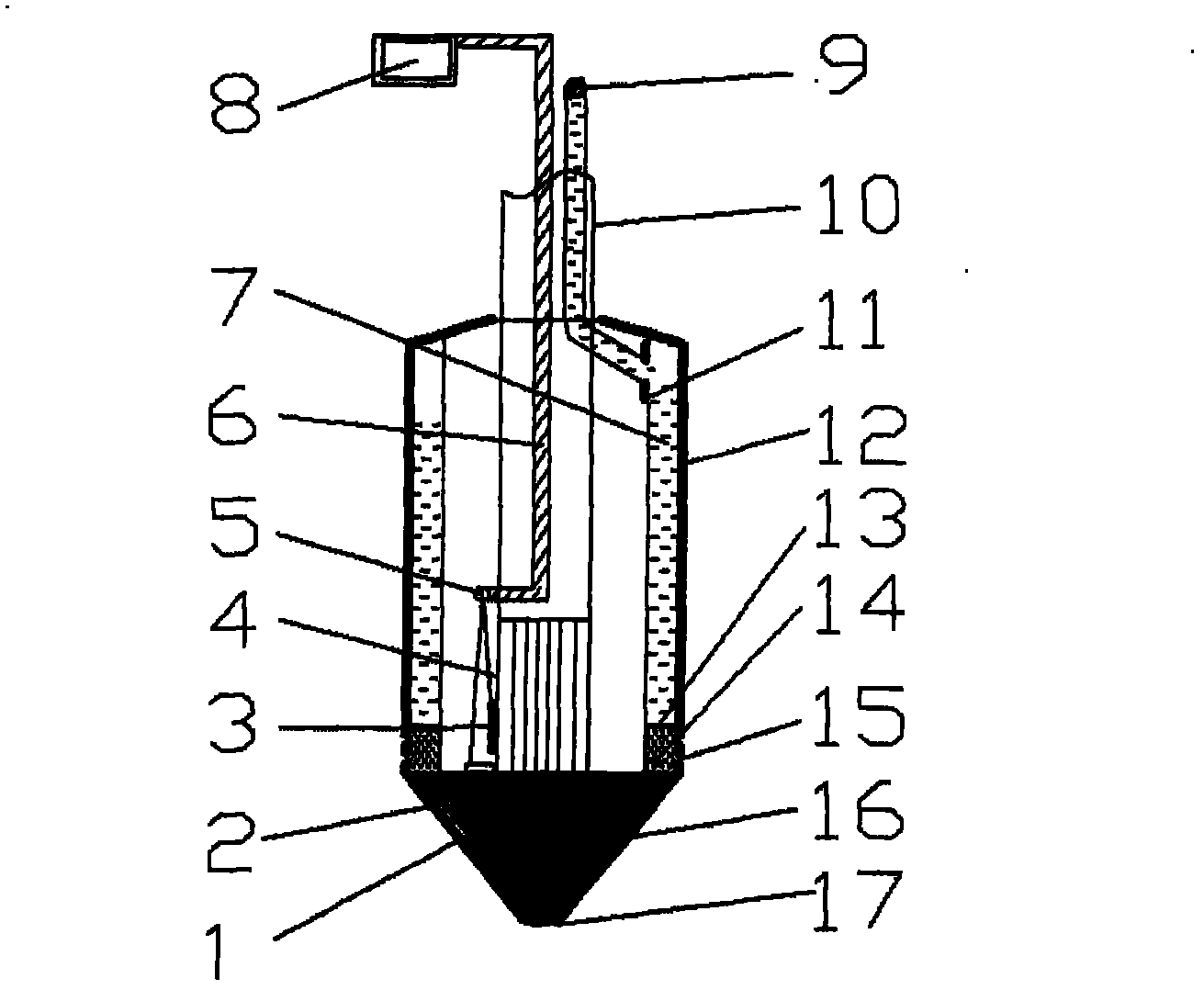
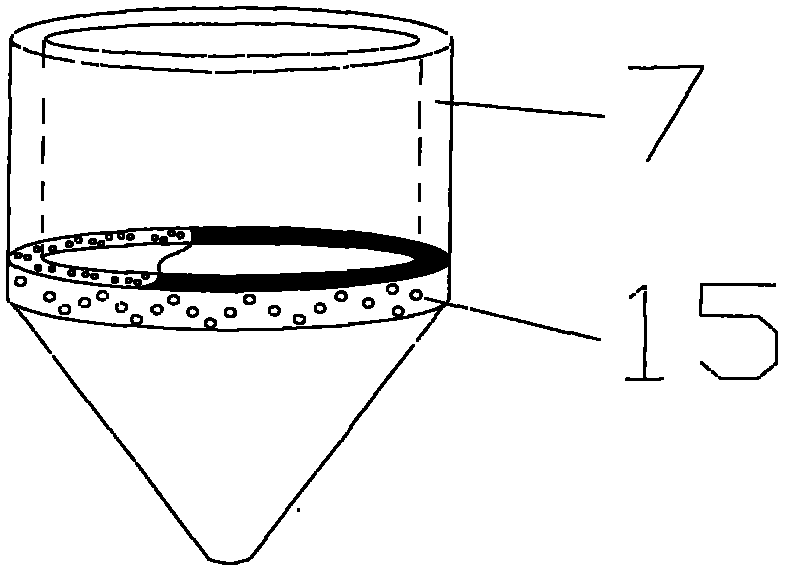
[0045] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, this example provides a test device for judging the collapsibility of the soil layer, including an outer sleeve 12, a push rod 10 and a data processor 8 connected sequentially from the conical probe 16, and the outer sleeve 12 is a hollow cylindrical metal The body is made of heat-treated stainless steel (40Cr) material with a thickness of 5mm, its diameter can be 3-5cm, preferably 4.5cm in diameter, and its height is 7-10cm, preferably 9cm; the push rod 10 is heat-treated A hollow circular tube made of stainless steel (40Cr) material, the external diameter of the circular tube is 1.5cm, and the internal diameter is 1cm. The push rod 10 can be connected end to end and continuously connected to continuously press the conical probe 16 into the soil layer; the conical probe 16 is a solid cone, which is made of heat-treated stainless steel (40Cr), and has electronic components such as a soil moisture detector and a stress sensor in...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This example provides a test method for judging the collapsibility of the soil layer. When the test device described in Example 1 is used in this example, the resistance of the undisturbed loess cone 17 at a certain depth can be measured first, and the natural water content can be calculated. Lower the strength of the loess, and then fill the soil around the cone tip 17 to saturation, then measure the resistance of the soil cone 17 at this time, and compare the strength change of the soil before and after saturation to determine whether the soil layer is collapsible loess.
[0055]The specific implementation process of the present invention is to apply a force to the push rod 10 at the tail of the test device, and press the conical probe 16 into the soil at a constant speed. The probe sensor generates a resistance change signal, which will be transmitted to the data processor 8 on the ground. Under different soil layer conditions, the penetration resistance is differen...
Embodiment 3
[0058] In this example, within the survey depth range of 40.00m, the main formation is composed of silty loess, as follows:
[0059] 1. When in use, use a certain penetration pressure to press the conical probe 16 into the soil at a constant speed, and the intrusion rate of the conical probe 16 is controlled between 0.015 and 0.025m / s. When the conical probe 16 is in contact with the soil during the penetration process, it will generate penetration resistance, and the probe sensor will generate a resistance change signal, which will be transmitted to the measuring instrument on the ground.
[0060] 2. The resistance strain gauge 2 and the sensor 3 in the conical probe 16 will transmit the changing resistance signal to the data collector through the cable 5 for automatic recording. The depth of each penetration is 20cm, and then the resistance and the resistance of the cone tip 17 are obtained. deep relationship.
[0061] 3. After measuring the resistance of the cone tip 17 at...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com