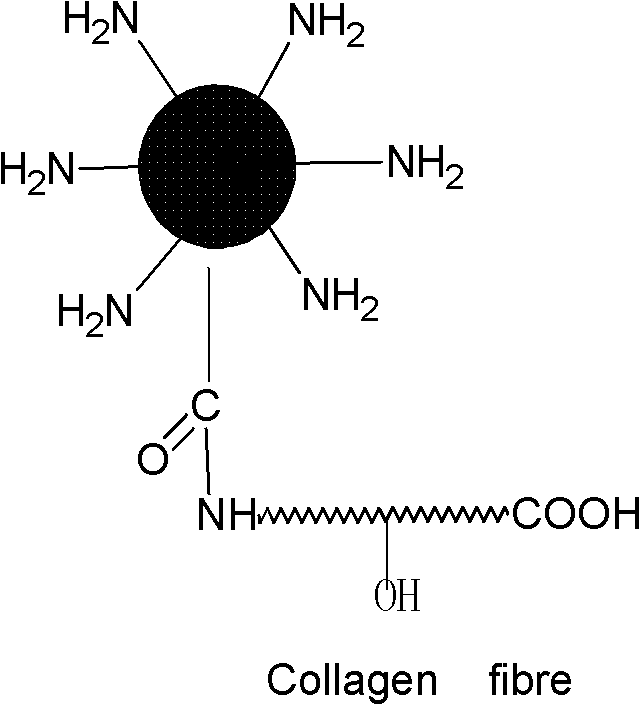
Preparation method of modified collagen fiber adsorbing material
A collagen fiber and adsorption material technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of modified collagen fiber adsorption materials, can solve the problems of high cost, complicated procedures, and difficult to recycle, and achieves the effects of strong adsorption performance, abundant resources, and no secondary pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Step 1: Preparation of Collagen Fibers
[0022] Collagen fibers are obtained by drying hides and skins after acid treatment, enzyme treatment, alkali treatment, dealkalization, and dehydration (see the preparation and performance characterization of pigskin acid-relaxed collagen fibers, Volume 39, Issue 3, May 2007);
[0023] Step 2: Preparation of hyperbranched polyamidoamine
[0024] The acetone solution of triethylenetetramine and vinyl acetate was reacted at room temperature for 4 hours, and then the temperature was raised to 130° C. to continue the reaction for 3 hours. Remove acetone under reduced pressure and vacuum at 60°C, extract and wash the crude product with acetone, and dry at 60°C to constant weight to obtain hyperbranched polyamidoamine;
[0025] Step 3: Weigh the hyperbranched polyamidoamine, collagen fibers and crosslinking agent glutaraldehyde at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.8, add 50 mL of water per mole of collagen fibers to add the collagen fibers to a ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Step 1: Preparation of Collagen Fibers
[0028] Collagen fibers are obtained by drying hides and skins after acid treatment, enzyme treatment, alkali treatment, dealkalization, and dehydration (see the preparation and performance characterization of pigskin acid-relaxed collagen fibers, Volume 39, Issue 3, May 2007);
[0029] Step 2: Preparation of hyperbranched polyamidoamine
[0030] Ethylenediamine and ethyl ether solution of vinyl propionate were reacted at room temperature for 5 hours, then the temperature was raised to 150°C and the reaction was continued for 4 hours. Ether was removed under reduced pressure at 80°C, the crude product was extracted and washed with acetone, and then dried at 60°C to constant weight to obtain hyperbranched polyamidoamine;
[0031] Step 3: Weigh the hyperbranched polyamidoamine, collagen fibers and crosslinking agent glyoxal at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.5, add 200 mL of water per mole of collagen fibers to add the collagen fibers to a ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Step 1: Preparation of Collagen Fibers
[0034] Collagen fibers are obtained by drying hides and skins after acid treatment, enzyme treatment, alkali treatment, dealkalization, and dehydration (see the preparation and performance characterization of pigskin acid-relaxed collagen fibers, Volume 39, Issue 3, May 2007);
[0035] Step 2: Preparation of hyperbranched polyamidoamine
[0036] 1,3-Propanediamine and chloroform solution of isopropenyl acetate were reacted at room temperature for 4 hours, and then the temperature was raised to 140° C. to continue the reaction for 3 hours. The chloroform was removed under reduced pressure at 100°C, the crude product was extracted and washed with acetone, and then dried at 60°C to constant weight to obtain hyperbranched polyamidoamine;
[0037] Step 3: Weigh the hyperbranched polyamidoamine, collagen fibers and crosslinking agent carbodiimide at a molar ratio of 1:1:1.0, add 150 mL of water per mole of collagen fibers, and add the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com