Bacterial strain capable of generating alginate lyase and fermentation method thereof
A technology of alginate lyase and bacterial strain, which is applied in the field of alginate lyase (ALG22) and its preparation, can solve the problems of lagging development of algae processing industry, few types of processed products, weak market competitiveness, etc., and achieve easy artificial cultivation and Effects of expanding cultivation, enriching diversity and selectivity, and highlighting salt tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: Strains Tamlana Isolation of sp. ZJU HZ22
[0041] Wild seaweed and surrounding seawater were collected from the Zhoushan area of the East my country Sea. The algae were crushed under aseptic conditions, and transferred to a 500 ml sterile shaker bottle together with 200 ml seawater samples, and a small amount of sterile fresh kelp pieces and peptone (finally Concentration 1 g / l) and yeast extract (final concentration 1 g / l), continued cultivation at 28°C, 120 rpm, and observed changes in the turbidity of the culture medium and residual kelp. Replace natural seawater with oligotrophic 2216 medium, add appropriate amount of fresh kelp pieces (200 g / l), sterilize at 121°C for 30 min, and take 10% inoculum from the above-mentioned shake flask with kelp degradation effect Transfer, cultivate under the same conditions until the kelp is degraded, and repeat the transfer for 2-3 generations to obtain a bacterial population with a stable degradation effect. The a...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Strains Tamlana Amplification, sequence determination and analysis of 16S rRNA gene of sp. ZJU HZ22 (CGMCC No. 5324)
[0045] Strain ZJU HZ22 was streaked on the 2216 slope and cultured at 28°C until a lawn was formed. Scrape a loop of bacteria from a sterile inoculation loop and place it in a 1.5 ml sterile centrifuge tube. Genomic DNA was extracted using the Bacterial Genome Rapid Extraction Kit (Dongsheng Biology) and used as a template for PCR. The general primers for amplifying the 16S rRNA gene are as follows:
[0046] Forward primer: 5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3';
[0047] Reverse primer: 5'- ACGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT -3';
[0048] The above primers correspond to bases 8-27 and bases 1510-1492 of the 16S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli respectively. 50 μl PCR reaction system: 5 μl 10×buffer, 1 μl 10 mM dNTPs, 1 μl each 4 μM primer, ddH 2 O 42 μL, Taq enzyme 0.5 μl (2.5 U), DNA template 0.5 μl (10-100 ng). The PCR reaction conditions were: denaturation at...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: Strains Tamlana Identification of morphological and physiological characteristics of sp. ZJU HZ22 (CGMCC No. 5324)
[0052] The strain ZJU HZ22 used for identification was all inoculated in 2216 medium, and 15 g / l agar could be added to prepare solid medium, and sterilized at 121°C for 30 min.
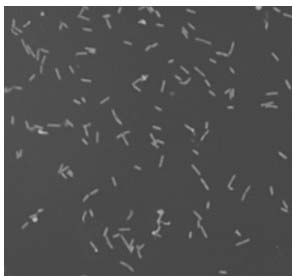
[0053] A single colony was obtained by streak culture on a plate, and at the same time, the colony was picked to prepare a bacterial suspension, and the microscopic examination was carried out on a glass slide. The results showed that the strain had the following morphological characteristics: (1) Colony morphology: the colony was round and the surface was smooth , waxy luster, raised, smooth-edged, translucent, bright yellow in color. (2) Cell morphology: Gram-negative bacteria, typical rod-shaped cells under the light microscope (Olympus, BX40), arranged singly, and split in the middle.
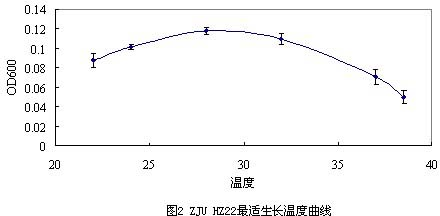
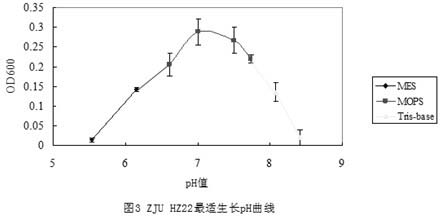
[0054] Using 2216 as the basal medium, the physiological characteristics we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com