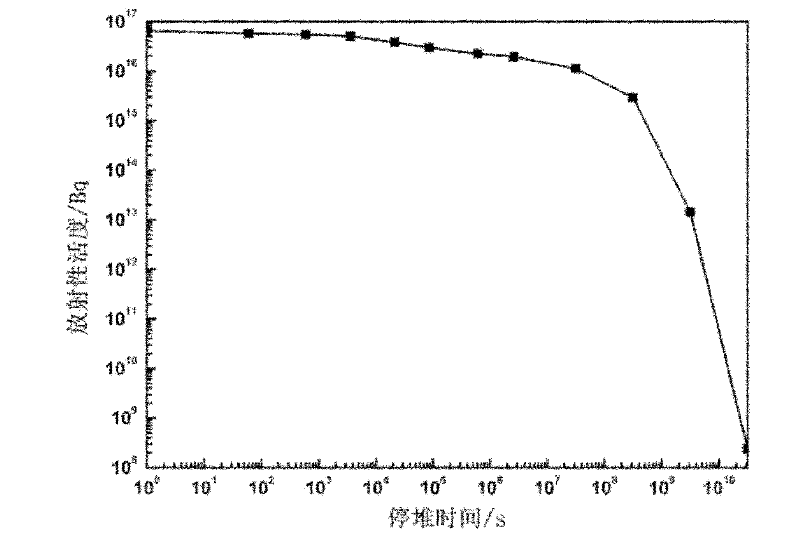
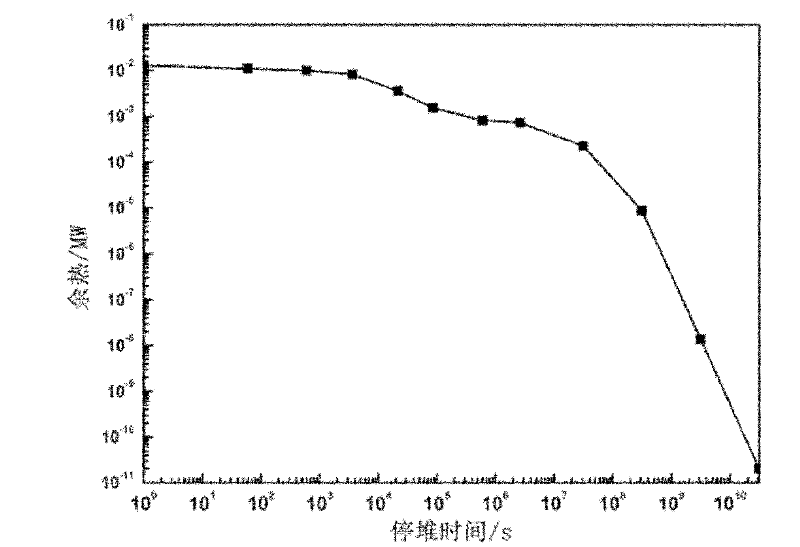
Method for producing nitrogen controlling low activity ferrite martensite steel for fusion reactor
A low-activity ferritic and martensitic steel technology is applied in the field of manufacturing nitrogen-controlled low-activity ferritic-martensitic steel for fusion reactors, and can solve problems such as low-activity characteristic requirements of fusion reactor materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0059] The method for preparing iron-tungsten alloy described in this step can be prepared by referring to any existing method. This step is the only step in which metal tungsten is added in the whole method, and metal iron can also be added in subsequent steps, so in this step As long as the mass percentage of tungsten is controlled not to exceed 20% of the iron-tungsten master alloy. The total amount of metal tungsten added is controlled at 1.45%-1.6% (mass percentage) of the nitrogen-controlling low-activity ferritic martensitic steel for fusion reactors.
[0060] The melting point of the iron-tungsten master alloy prepared in this step is lower than 1600° C., which is beneficial to the melting of tungsten in the subsequent smelting step.
[0061] Step 2: Proportionate ingredients according to the chemical composition of the alloy, chromium, manganese, vanadium, carbon, tantalum, etc. are all selected from high-purity materials. The primary melting of the alloy is carried ...
Embodiment 1
[0078] Embodiment 1: the method for manufacturing the nitrogen-controlling low-activity ferrite / martensitic steel of the ratio listed in the aforementioned experiment 2
[0079] First, the iron-tungsten master alloy is prepared by vacuum induction melting, and the mass percentage of tungsten is 10.6%. The alloy composition is 8.5% Cr, 1.55% W, 0.24% V, 0.10% C, 0.10% Ta, 0.5% Mn, 0.03% N, and the balance is iron (mass percentage). According to the alloy design composition distribution, considering the burning loss rate of different alloy elements, the preparation of each raw material should have different allowances, and the allowances are calculated according to the aforementioned percentages. Add the prepared pure iron, iron-tungsten master alloy, pure vanadium, pure chromium and pure carbon into the vacuum induction melting furnace. Turn on the furnace to vacuumize, when the vacuum degree reaches within 5Pa, start power transmission, heat up to 1500-1550°C, the raw materia...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2: the method for manufacturing the nitrogen-controlling low-activity ferrite / martensitic steel of the ratio listed in the aforementioned experiment 3
[0081] First, the iron-tungsten master alloy is prepared by vacuum induction melting, and the mass percentage of tungsten is 10.5%. The alloy composition is 8.3% Cr, 1.6% W, 0.27% V, 0.11% C, 0.09% Ta, 0.45% Mn, 0.035% N, and the balance is iron (mass percentage). According to the alloy design composition distribution, considering the burning loss rate of different alloy elements, the preparation of each raw material should have different allowances, and the allowances are calculated according to the aforementioned percentages. Add the prepared pure iron, iron-tungsten master alloy, pure vanadium, pure chromium and pure carbon into the vacuum induction melting furnace. Turn on the furnace to vacuumize, when the vacuum degree reaches within 5Pa, start power transmission, heat up to 1500-1550°C, the raw materi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com