Preparation method of novel Mannich water-based epoxy curing agent
A water-based epoxy, Mannich-type technology, used in epoxy resin coatings, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of short pot life, low coating film hardness, and poor compatibility of water-based epoxy systems, and achieve long pot life. , The effect of high film hardness and good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
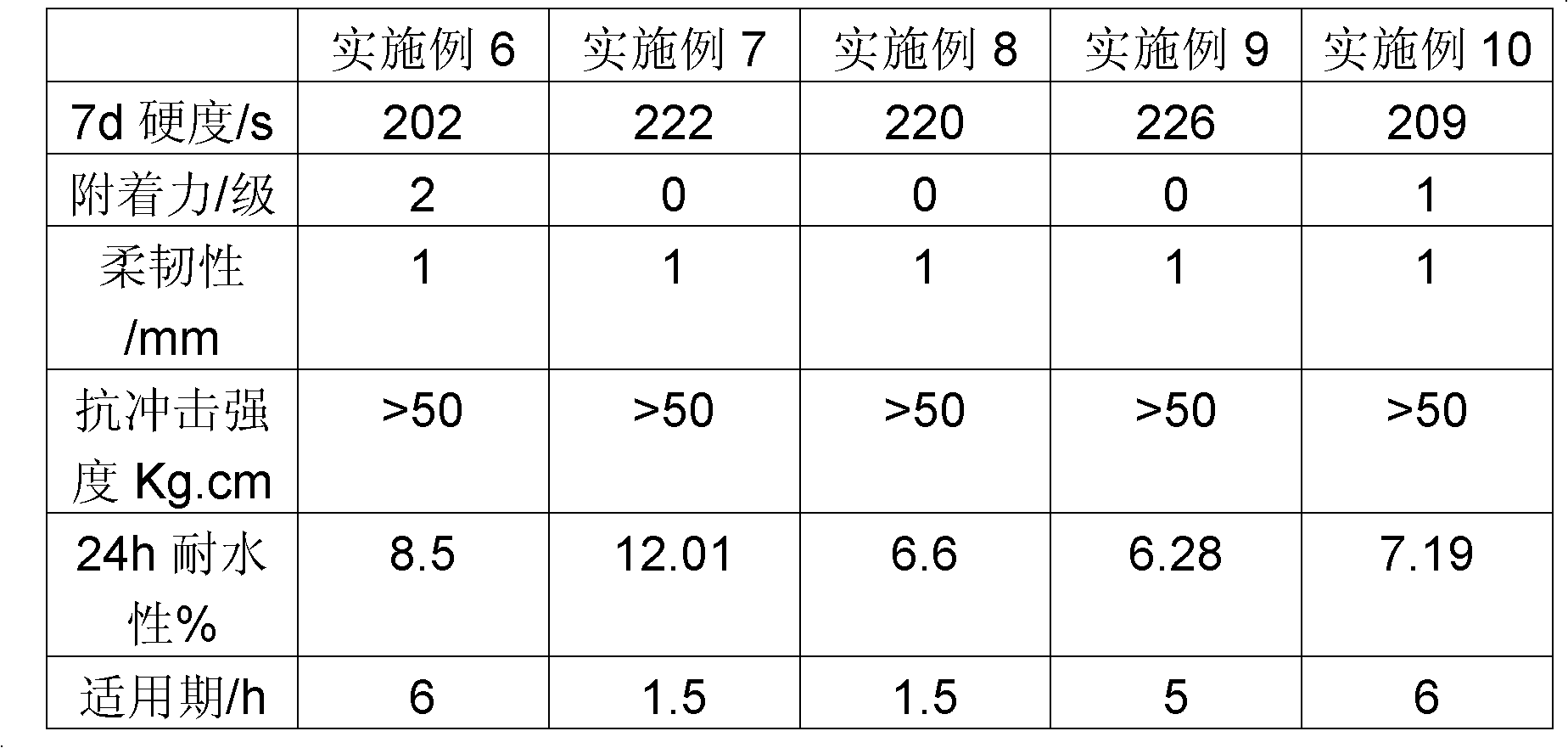
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Step 1: Mix 26.5g of 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol with 64g of polyetheramine, stir and heat up to 70°C, and react for 8h to obtain Mannich modified amine A1.
[0020] The second step: under nitrogen blanketing conditions, put 60g polyethylene glycol 6000 and 3.8g E-51 into a four-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser, a thermometer and a mechanical stirring device, stir, heat up, and heat the reactants When the temperature reaches about 60°C, the catalyst boron trifluoride diethyl ether is added, and the temperature is raised to 80°C, and the constant temperature reaction is maintained for 4 hours to obtain the terminal functional group epoxy prepolymer P.
[0021] Step 3: Add 2.5g of P and 15.5g of A1 into a three-necked flask, raise the temperature to 70°C, add 3.8g of E-51 into the reaction flask, and maintain a constant temperature for 3h. Then 4.5 g of phenyl glycidyl ether was added, and the temperature was raised to 80° C. for 2 h. The modified ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Step 1: Mix 26.5g of 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol with 31g of diethylenetriamine, stir and heat up to 70°C, and react for 8h to obtain Mannich modified amine A1.
[0024] The second step: under nitrogen blanketing conditions, put 60g polyethylene glycol 6000 and 3.8g E-51 into a four-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser, a thermometer and a mechanical stirring device, stir, heat up, and heat the reactants When the temperature reaches about 60°C, a catalyst, triphenylphosphine, is added, and the temperature is raised to 80°C, and the reaction is maintained at a constant temperature for 4 hours to obtain the terminal functional group epoxy prepolymer P.
[0025] Step 3: Add 5.5g of P and 15.5g of A1 into a three-necked flask, raise the temperature to 70°C, add 34g of E-51 into the reaction flask, and maintain a constant temperature for 3h. The modified Mannich amine A2 was obtained, the temperature was lowered, and the modified product A2 was emulsified ...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Step 1: Mix 26.5g of 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol with 31g of diethylenetriamine, stir and heat up to 70°C, and react for 8h to obtain Mannich modified amine A1.
[0028] Step 2: Add 15.5g of A1 into a three-necked flask, raise the temperature to 70°C, add 2.85g of E-51 into the reaction flask, and maintain a constant temperature for 3h. The modified Mannich amine A2 was obtained, the temperature was lowered, and the modified product A2 was emulsified when the temperature was lowered to 50° C. to obtain the nonionic water-based epoxy curing agent emulsion M3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com