Low-fat or fat-free yoghurt, and process for production thereof
A manufacturing method and yogurt technology, applied in milk preparations, biochemical equipment and methods, dairy products, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory requirements, lack of natural feeling, and affecting taste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
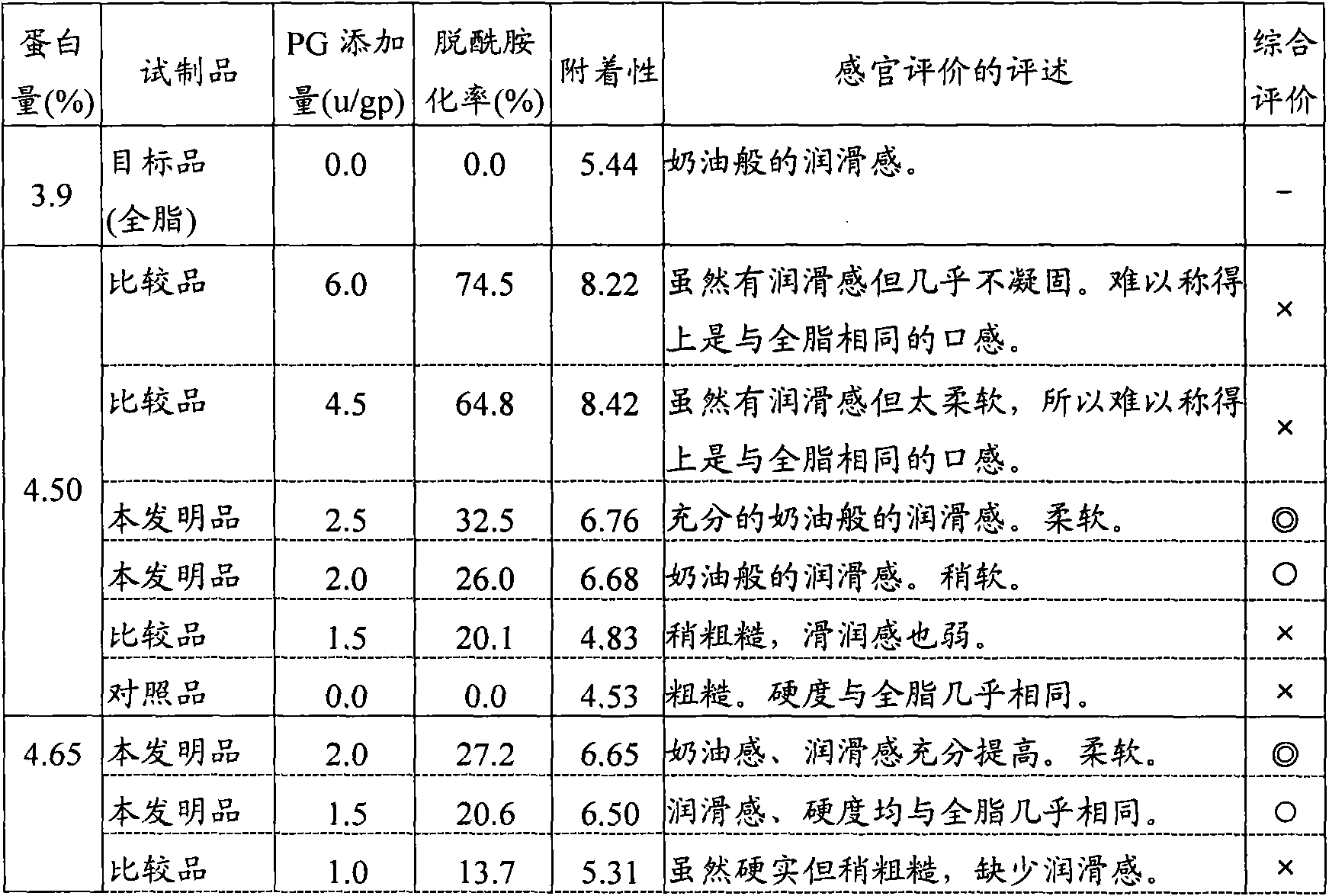
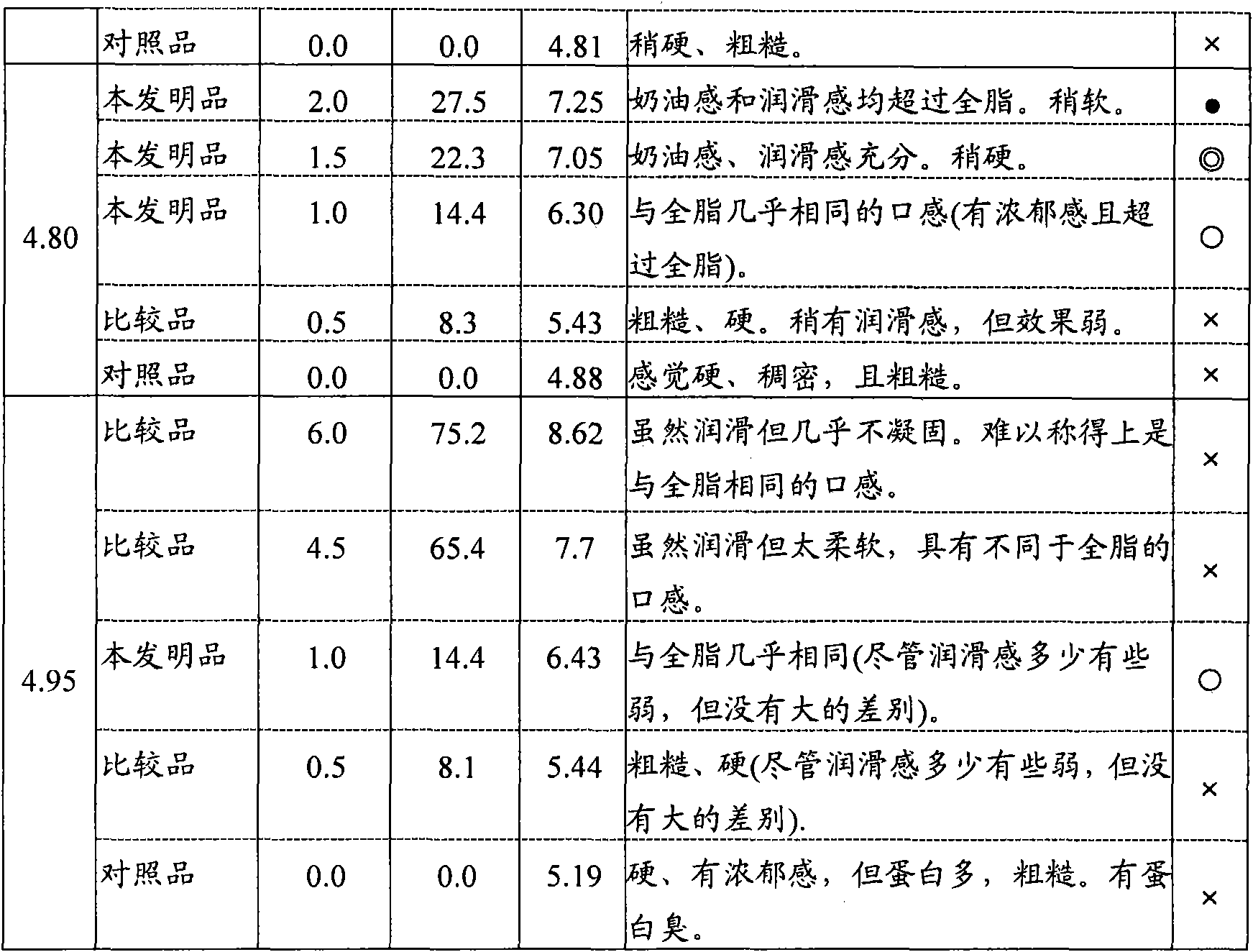
[0074] Add low-heat skimmed milk powder (35.6% protein from Yotsuba Dairy Company) to commercially available skim milk (Koiwai Skim Milk Koiwai Dairy Co., Ltd. milk fat content is 0.1%, protein is 3.5%), and the protein content is adjusted to 4.50%, 4.65%, 4.80% %, 4.95%, and then add 0.5 to 6.0 U, 60 U / ml protein glutaminase (manufactured by Amano Enzyme Co., Ltd., 500 U / g, from the genus Chryseobacterium; hereinafter abbreviated as PG) per 1 g of protein in milk. ) solution and allowed to react at 55°C for 60 minutes. Thereafter, the enzyme was inactivated by heating at 95° C. for 2 minutes in a boiling bath, and then cooled to obtain skim milk having different deamidation rates. Add 15U of PG to every 1g of protein in milk to make it work under the same conditions (react at 55°C for 60 minutes), measure the amount of ammonia when the deamidation reaction is almost saturated, and the deamidation rate is 100% . According to the method described in lines 1 to 14 on page 11 o...
Embodiment 2
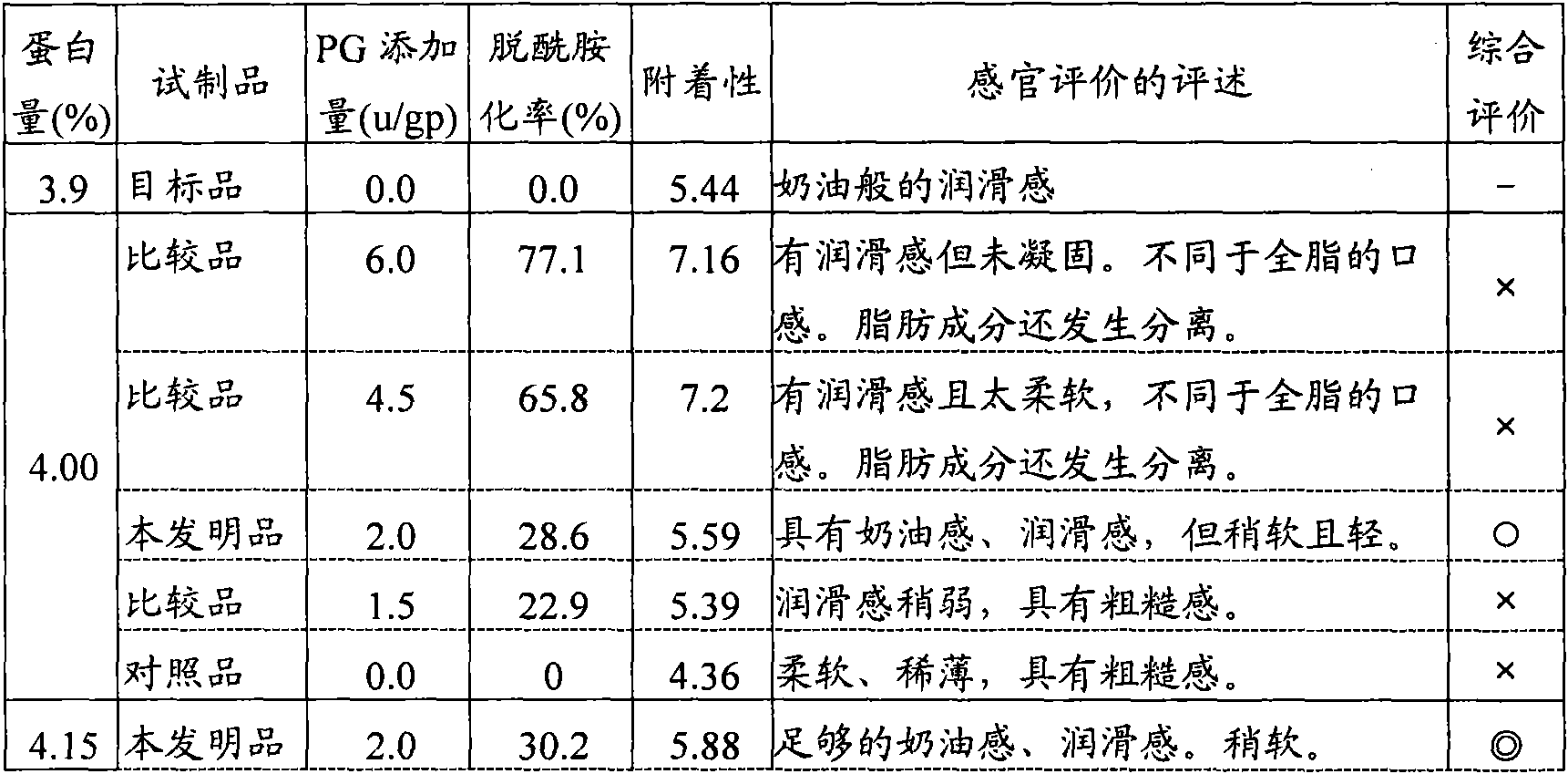
[0084] Low-calorie skimmed milk powder (Yotsuba Dairy Co., 35.6% protein) was added to commercially available low-fat milk (low-fat milk from fresh milk Takanashi Dairy Co., Ltd., 1.0% milk fat and 3.3% protein), and the protein content was adjusted to 4.0 %, 4.15%, 4.3%, 4.45%, 0.5-6.0U of PG solution (60U / ml) was added to each 1g of protein in milk, and reacted at 55°C for 60 minutes. Thereafter, the enzymes were inactivated by heating at 95° C. for 2 minutes in a boiling bath, and then cooled to obtain low-fat milks having different deamidation rates. The amidation rate of each PG-treated milk was obtained by the same method as in Example 1. As a result, when the protein content was 4.0%, each sample was a PG-treated low-fat milk with a deamidation rate of 28.6% and 22.9%. When the protein content is 4.15%, each sample has a deamidation rate of 30.2%, 24.8%, and 15.4% PG-treated low-fat milk; when the protein content is 4.3%, each sample has a deamidation rate of 30.4%, 23....
Embodiment 3
[0094] Add PG to a 10% (w / w) solution of low-heat skim milk powder (35.6% protein from Yotsuba Dairy Company) under the condition of sufficient deamidation, that is, add 12.5U of PG per 1g of protein, and make it cool at 55°C The reaction was carried out for 60 minutes. Afterwards, heat in a boiling bath until reaching 80° C. to inactivate the enzyme, followed by cooling. Next, in order to make a powder, it freeze-dried after freezing at -80 degreeC, and prepared the PG-processed skim milk powder whose deamidation rate was 100%. The PG-treated skim milk powder was dissolved in low-fat milk so that the protein content reached 4.4%, heated in a boiling bath at 95° C. for 2 minutes to sterilize, and then cooled to obtain low-fat milk powder added with PG-treated skim milk powder. Fat milk (deamidation rate: 27.6%) (deamidation treatment milk protein addition method).
[0095] Add low-calorie skimmed milk powder (35.6% protein from Yotsuba Dairy Company) to low-fat milk (1.0% mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com