Multiplex analysis of stacked transgenic protein
A protein, transgenic plant technology, applied in the field of high-throughput analysis, can solve the problem of time-consuming and hinder the use of mass spectrometry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
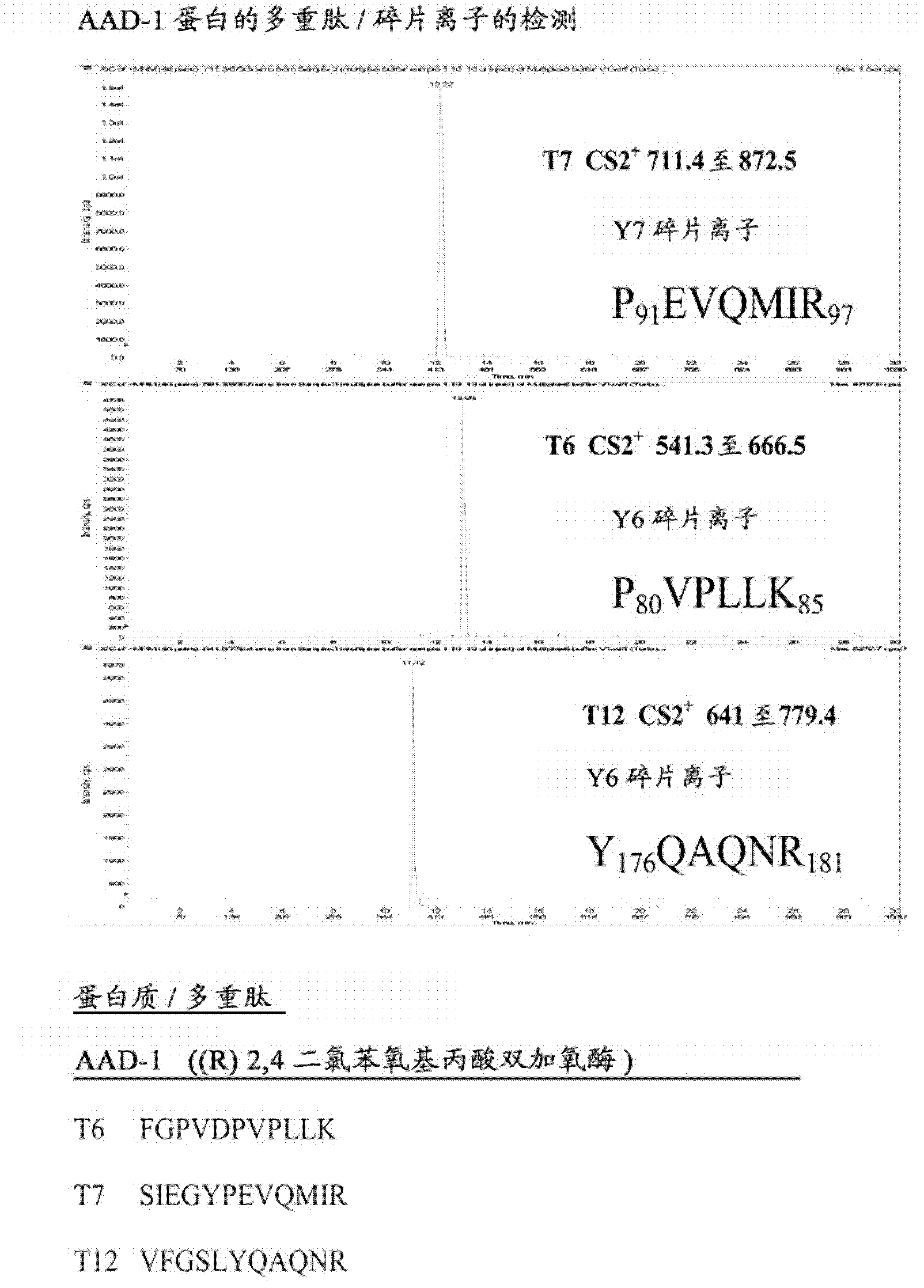
[0093] Six different transgenic proteins (Cry1F, Cry34, Cry35, AAD-1, AAD-12 and PAT) were selected for development of LC\MS\MS multiplex analysis. Detect and identify individual proteins in a single injection of a complex protein mixture by mass spectrometry.
[0094] The first format of the multiplex analysis was to proteolytically digest the six proteins separately, then enrich the resulting protein peptides into proteolytically digested plant tissue extracts and use LC\MS\MS for analysis in a single Injection was performed to detect specific precursor / fragment ions for each of the six proteins. The methodology developed during this first multiplex format was then applied to multiplex detection of four proteins expressed in current inbred maize breeding material.
Embodiment II
[0096] LC\MS\MS multiple detection in plants
[0097] Table 1 lists the concentration of each individual stock protein received, and the resulting dilution of each protein when subjected to trypsinization. Prior to digestion with the protease trypsin, all proteins were buffer exchanged to 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.9 (SIGMA) to ensure efficient digestion conditions. Aliquots from each stock protein (see Table 1) were transferred to sterile 1.5 mL eppendorf tubes and made up to 100 μL using 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.9. Zeba Desalt Spin Column (Pierce #89882) was used for buffer exchange of each protein according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Three spin washes of the Zeba column were performed, each wash using 300 μL of 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.9, and spinning at 1500 g for 1 min. A 100 μL aliquot of each sample protein was then applied to the surface of the Zeba column resin and spun at 1500g for 2 minutes. The buffer-exchanged material was then...
Embodiment III
[0109] A single LC\MS\MS multiplex targeted MRM analysis for all six DAS proteins was then constructed using the precursor / fragment ion data generated from the individual protein analyses. The peptides were first subjected to LC\MS\MS multiplex detection by fortifying ammonium bicarbonate buffer (25 mM, pH 7.9) with tryptic digested material from each of the six proteins. Approximately 5-20 fmol of each protein was injected onto the column for the initial multiplex-6 analysis of the boosted buffer.
[0110] Figure 1-6 Extracted ion chromatograms for each of the six proteins detected in a single injection are shown. in particular, figure 1 LC\MS\MS multiplex detection of AAD-1 is shown. The data are LC\MS\MS ion chromatograms for the extraction of AAD-1 ((R)-2,4-dichlorophenoxypropionate dioxygenase), which contains AAD in the corn seed extract -12, Cry1F, Cry34, Cry35 and PAT were detected in a single injection.
[0111] figure 2 LC\MS\MS multiplex detection of AAD-12 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com