Exon conserved sequence amplified polymophic molecular marker and its analysis method
A technology of conserved sequences and molecular markers, applied in the fields of genomics and bioinformatics, can solve the problems of being easily affected by experimental conditions, long process time, unable to provide complete information, etc., to improve repeatability and reliability, reduce time and The effect of low cost and primer design cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
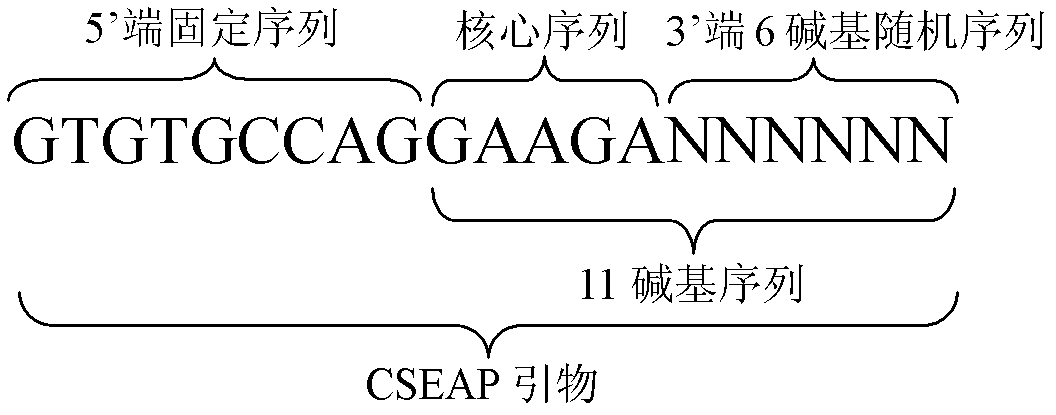
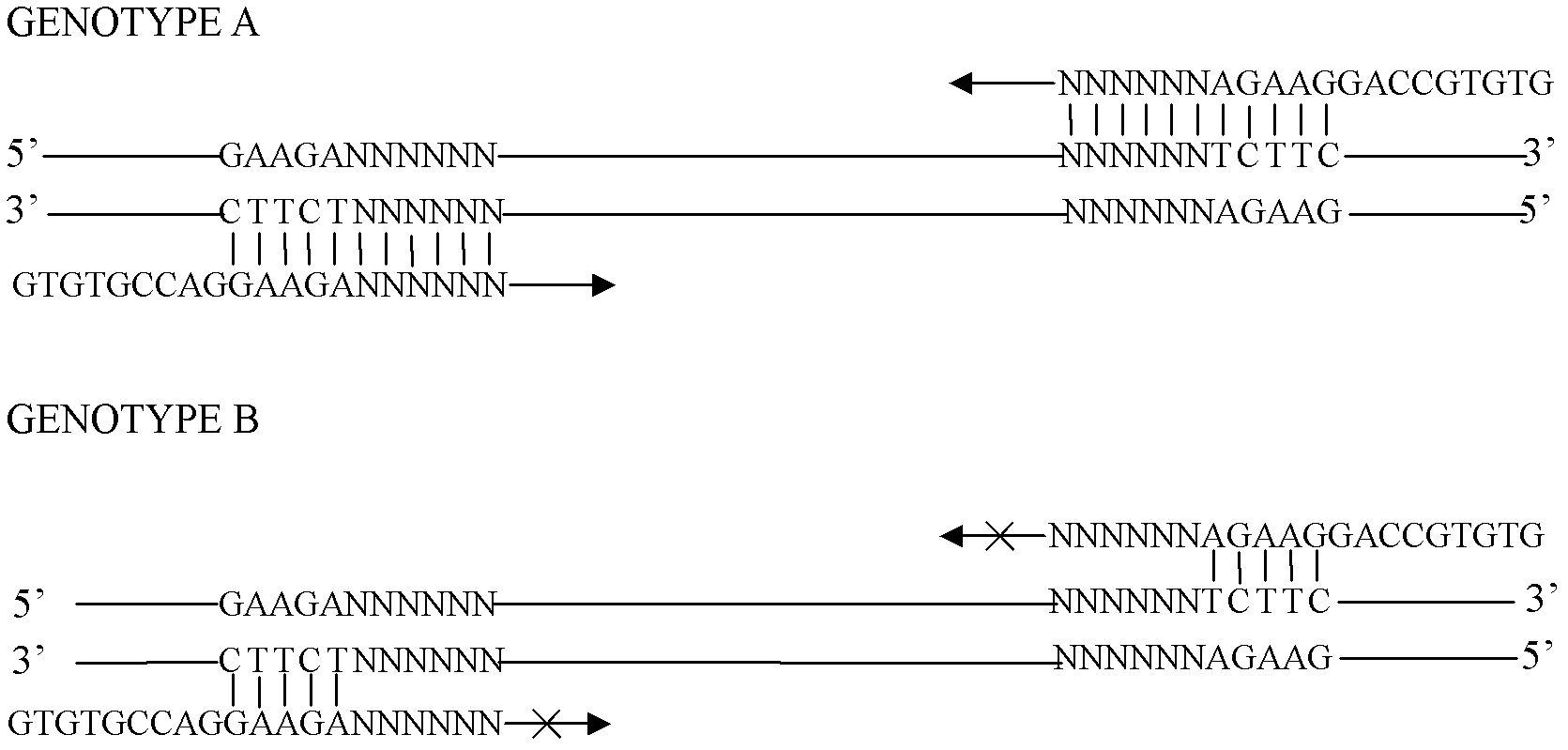
[0048] In this example, sugarcane variety resources were used as materials, and Arabidopsis thaliana and rice were used as close relatives to carry out molecular markers of exon conserved sequence amplification polymorphisms.
[0049] 1. Select 37 sugarcane variety resources as materials, take heart leaves from sugarcane plants, remove the midrib and cut the middle part for DNA extraction, and use the CTAB method to extract DNA.
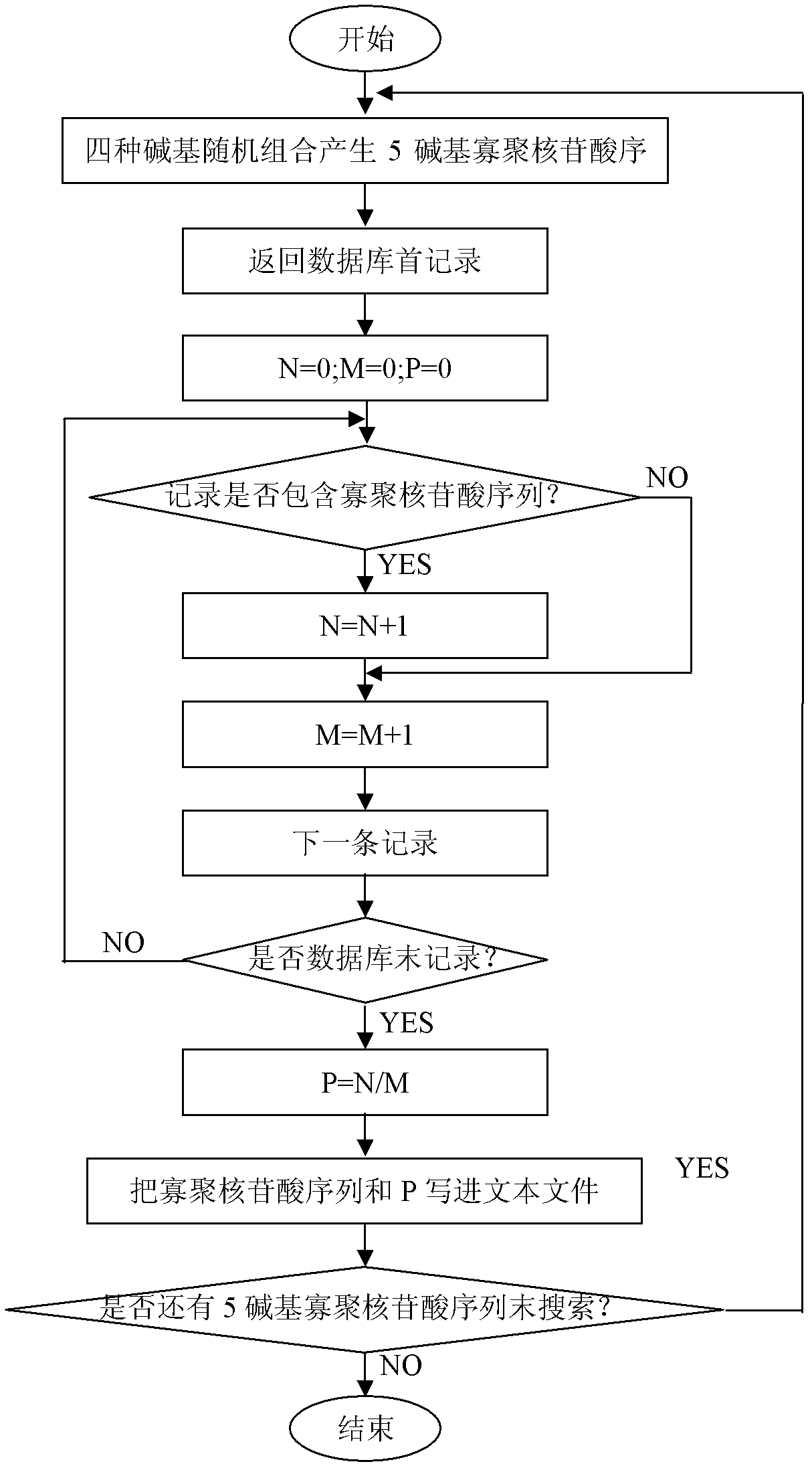
[0050] 2. Download the mRNA sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana, sugarcane and rice from the NCBI website, and construct the mRNA databases of these crops respectively. The Arabidopsis mRNA database contains 78,301 records, and the mRNA sequences include complete sequences and partial sequences. The mRNA databases of sugarcane and rice consisted of 75 and 3990 complete mRNA sequences, respectively. Programming software Delphi 7.0 (Borland Software Corporation, USA) was used to program, and four bases (A, T, C, G) were combined to generate 1024 5-base o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com