Extracting method for active polysaccharide in higher plant or edible and medicinal fungi
A technology for edible and medicinal fungi and higher plants, which is applied in the field of high-efficiency extraction of active polysaccharides in plants or edible and medicinal fungi, can solve the problem of low extraction rate, achieve simple solvent recovery, increase polysaccharide content, and low average molecular weight Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
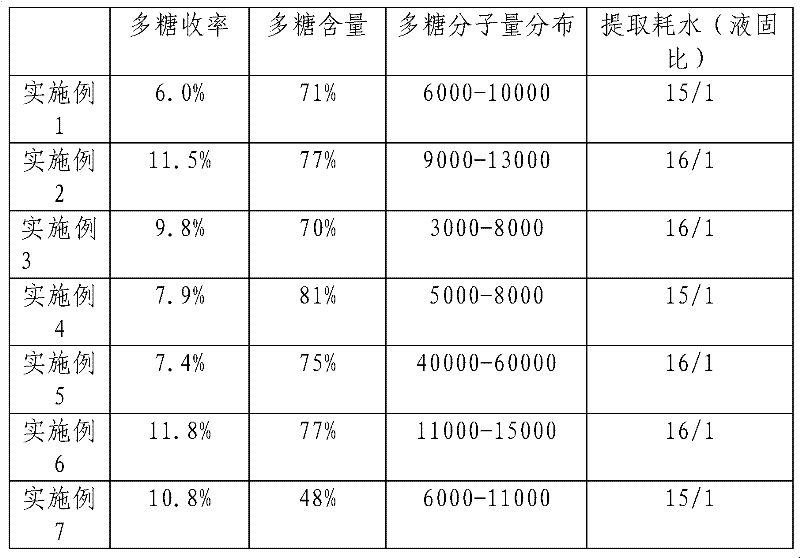
Examples
Embodiment 1
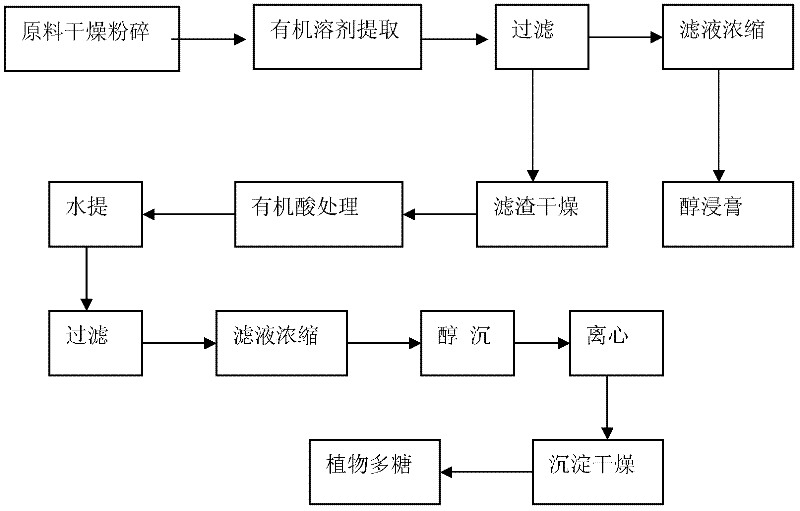
[0034] like figure 1 As shown in the schematic diagram of the technological process, the specific process is as follows:
[0035] 1) Take 1.5 kg of dried, impurity-removed, and mechanically crushed Astragalus membranaceus in a Chinese herbal medicine extraction container, add 10 L of ethanol, heat and reflux for extraction for 1 hour, and repeat the above process once;
[0036] 2) Filtrate, combine the two filtrates and recover ethanol by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain an alcoholic extract rich in fat-soluble active ingredients such as flavonoids, saponins, and coumarin, and partially dry the filter residue for subsequent use;
[0037] 3) taking the dried filter residue in step 2) and placing it in the extraction container;
[0038] 4) Take 180g of oxalic acid and add 2.0L of water to make an oxalic acid solution;
[0039] 5) Take 2L of the oxalic acid solution in the above step 4), add it to the extraction container in the step 3), stir fully to make the filt...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0049] 1) 1.5kg papaya is placed in the extraction container after drying, removing impurities, and mechanically pulverizing;
[0050] 2) Take 0.8L of anhydrous acetic acid, add 0.15L of water, add 0.05L of dilute hydrochloric acid with a mass percentage concentration of 5%, and make 1L of acetic acid\hydrochloric acid mixed acid solution;
[0051] 3) Take 1L of the mixed acid solution in step 2), add it to the extraction container in step 1), stir well to make it evenly wet to obtain the mixed material;
[0052] 4) Heat the mixed material in step 3) to 80° C., keep it warm for 60 minutes, and carry out vacuum distillation until there is no liquid in the extraction container.
[0053] 5) Add 5L of 95% ethanol solution in the extraction container in step 4), fully stir, filter, and distill the filtrate to recover ethanol to obtain the alcoholic extract rich in papaya flavonoids. After the filter residue is partially dried, it is organ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0061] 1) 1.5 kg of dried, impurity-removed, and pulverized Angelica sinensis was placed in an extraction container, 7 L of petroleum ether was added, heated and refluxed for extraction for 1 hour, and the above process was repeated once;
[0062] 2) Filtrate, combine the two filtrates and distill under reduced pressure to recover petroleum ether to obtain the volatile oil of Angelica sinensis, and dry the filter residue of Angelica sinensis for later use;
[0063] 3) Part of the dried angelica filter residue in step 2) is placed in an extraction container, 10L of ethanol is added, heated to reflux for extraction for 1 hour, and the above process is repeated once;
[0064] 4) Filtrate, combine two filtrates and recover ethanol by vacuum distillation to obtain an alcoholic extract rich in angelica flavonoids, and partly dry the filter residue for later use;
[0065] 5) get the Angelica sinensis filter residue that dries in step 4) and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com