Double-rail double-drive-based three-beat double-workpiece bench exchange apparatus and method thereof
A technology of double workpiece table and exchange device, which is applied in the direction of photolithography exposure device, microlithography exposure equipment, etc., can solve the problems of less movement beat, large reaction force of abutment, increased time for table change, etc., and achieves table change time Short, fast driving speed, small mass and inertia effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
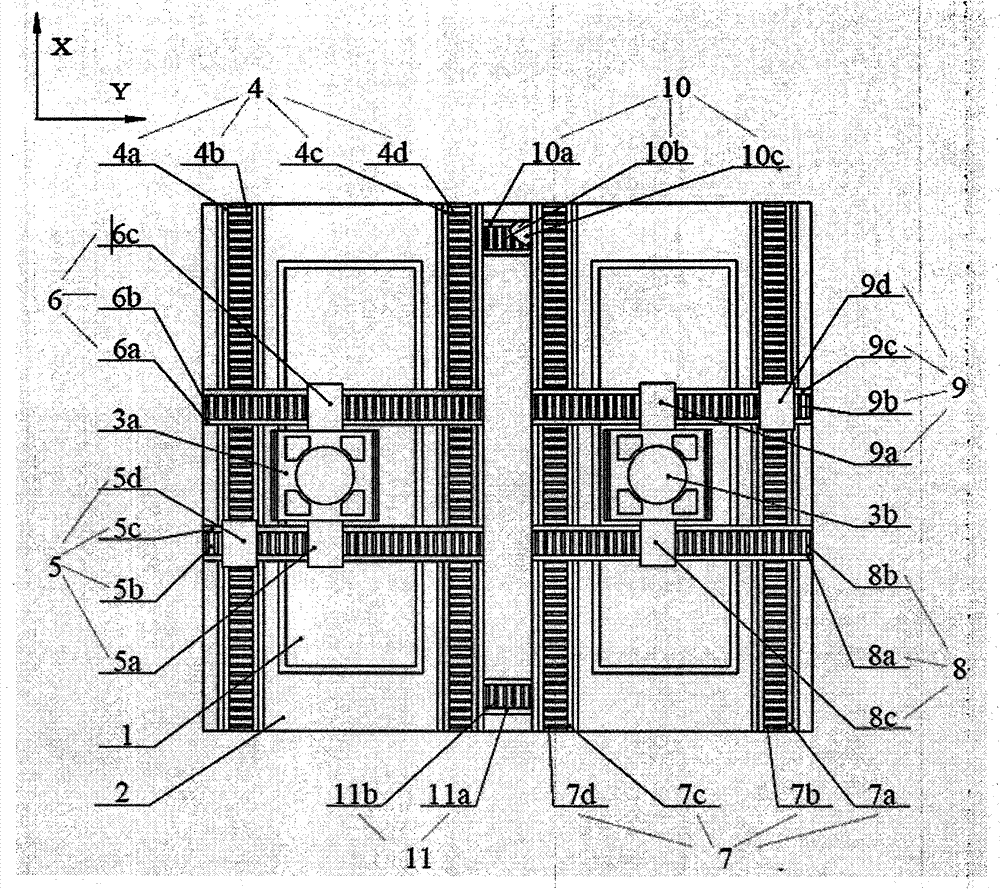
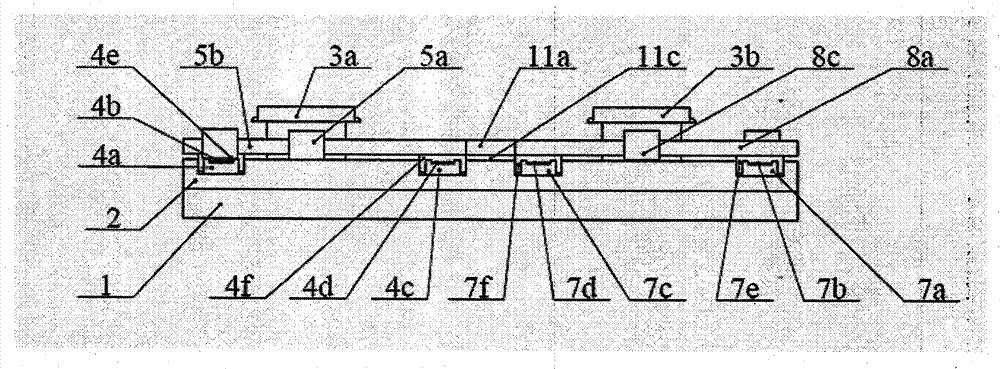
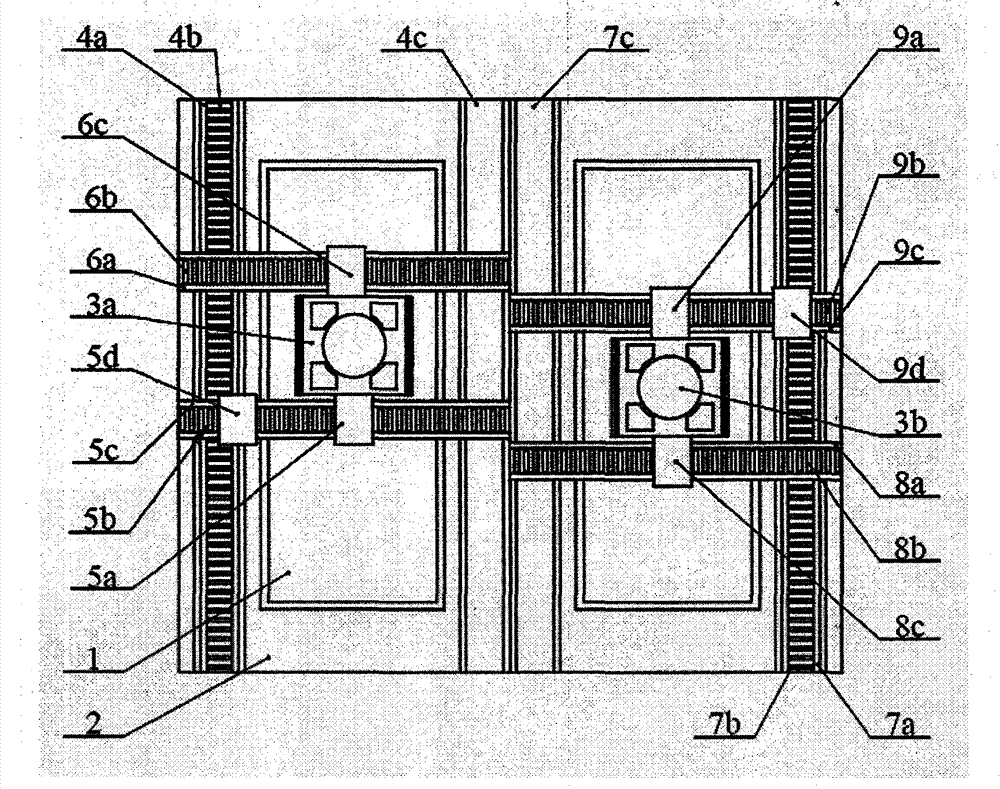
[0026] A three-beat double worktable exchange device based on double guide rails and double drives, the system includes a base 1, a first workbench 3a set on the base 1 and running on the exposure station and a pre-alignment station The second workpiece table 3b is characterized in that: the exposure station of the base 1 is provided with the first static pressure air bearing guide rail 4a in the X direction, the first linear motor stator 4b in the X direction, and the first linear motor mover in the X direction 4e, the X-direction second static pressure air bearing guide rail 4c, the X-direction second linear motor stator 4d, and the X-direction second linear motor mover 4f constitute the X-direction first linear motion unit 4, and the X-direction first linear motion unit 4 The unit 4 is provided with the first linear motor mover 5a in the Y direction, the first linear motor mover 2 5d in the Y direction, the first linear motor stator 5b in the Y direction, and the first stati...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Removing the X-direction second linear motor 4d, X-direction fourth linear motor 7d, Y-direction first transition linear motion unit 10 and Y-direction second linear motion unit 11 in the X-direction linear drive unit in Embodiment 1 can be implemented Example 2, such as Figure 7 shown. The station exchange process of the two workpiece platforms in embodiment 2 is exactly the same as in embodiment 1. The difference is that the X-direction driving form of the two workpiece tables is driven by a double guide rail and a single motor. Compared with Embodiment 1, the problem of inconsistency in driving the dual motors in the X direction can be avoided under the premise of ensuring the angular rigidity of the X direction movement. At the same time, due to the removal of the transitional linear motion unit, the range of motion of the double workpiece table increases, but the size of the X-direction linear motor increases.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Remove the X-direction second linear motor 4d, the X-direction second static pressure air bearing guide rail 4c, the X-direction fourth linear motor 7d, the X-direction fourth static pressure air bearing guide rail, and the X-direction linear drive unit in the first embodiment. The first transition linear motion unit 10 in Y direction and the second linear motion unit 11 in Y direction can obtain embodiment 3, such as Figure 8 shown. The station exchange process of the two workbenches in embodiment 3 is exactly the same as that in embodiment 1. Compared with Embodiment 1, Embodiment 3 reduces the number of the X-direction second linear motor 4d, the X-direction second static pressure air bearing guide rail 4c, the X-direction fourth linear motor 7d, and the X-direction fourth linear motor 7d in the X-direction linear drive unit. Four static pressure air bearing guide rails, the first transition linear motion unit 10 in the Y direction and the second linear motion unit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com