General band gap reference starting circuit
A technology for starting circuits and reference circuits, which is applied in the direction of adjusting electrical variables, control/regulating systems, instruments, etc., and can solve the problem of multiple degenerate points of current mode bandgap reference circuits, lack of versatility and practicability, and complex circuit structure. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
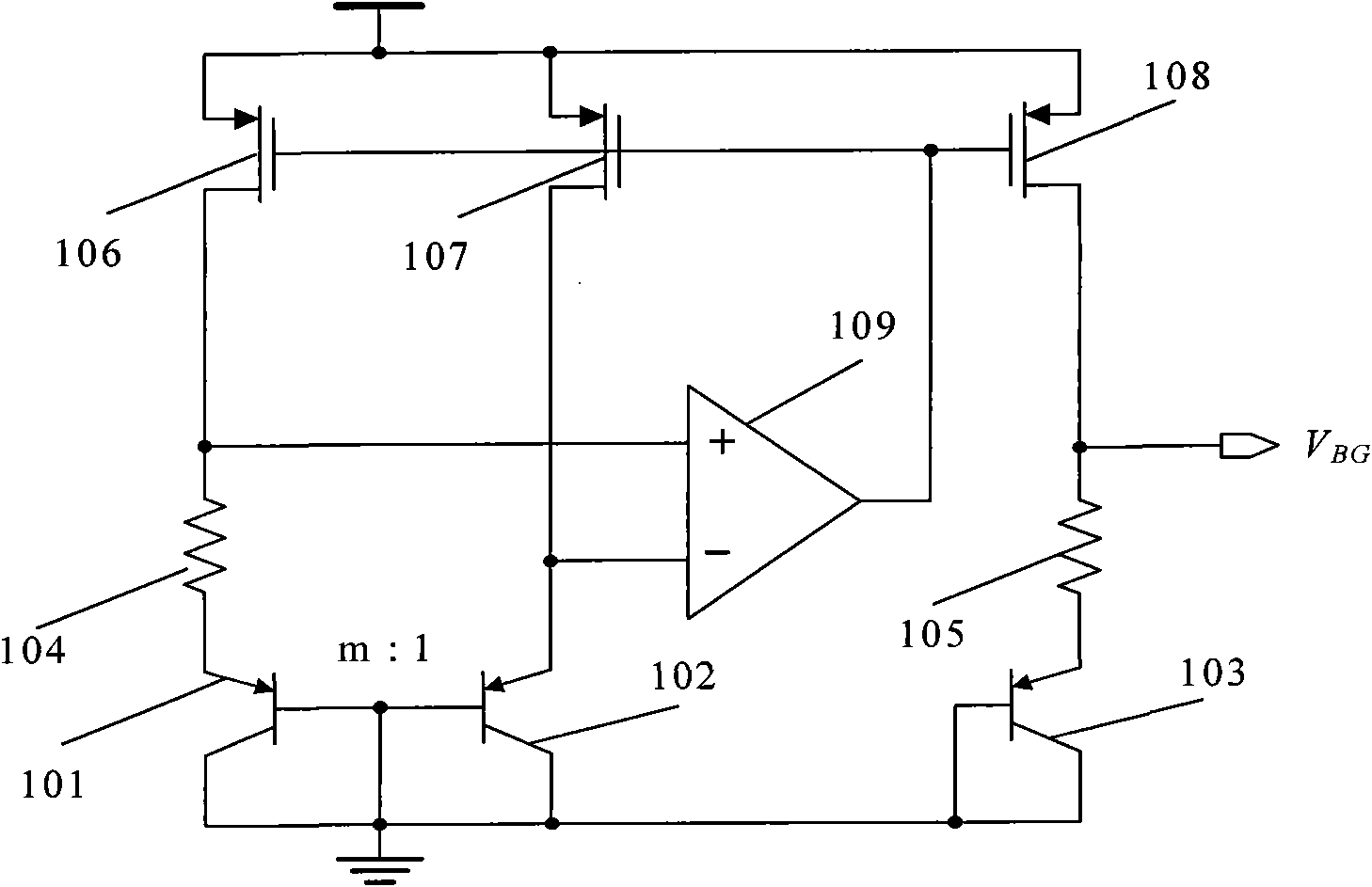
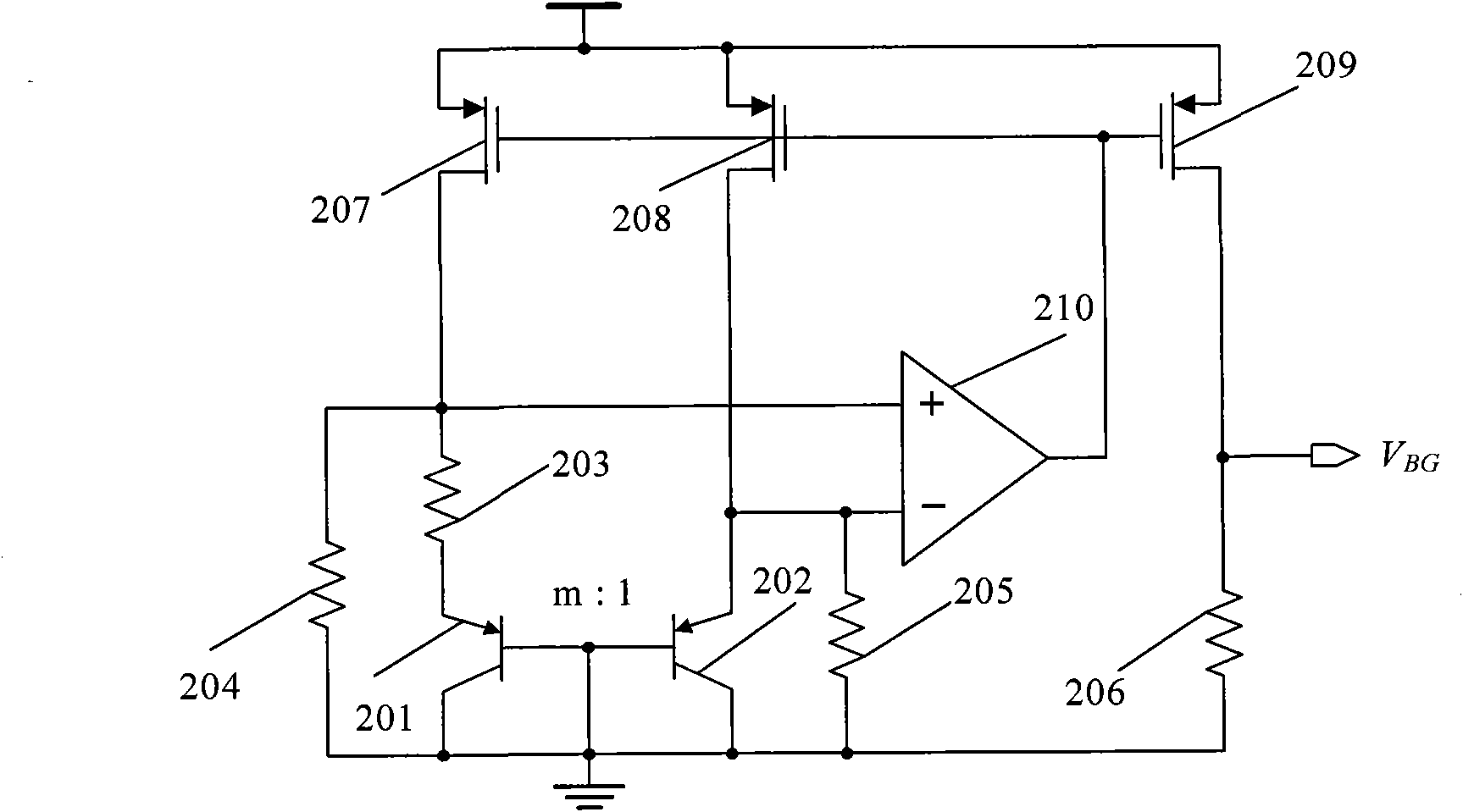
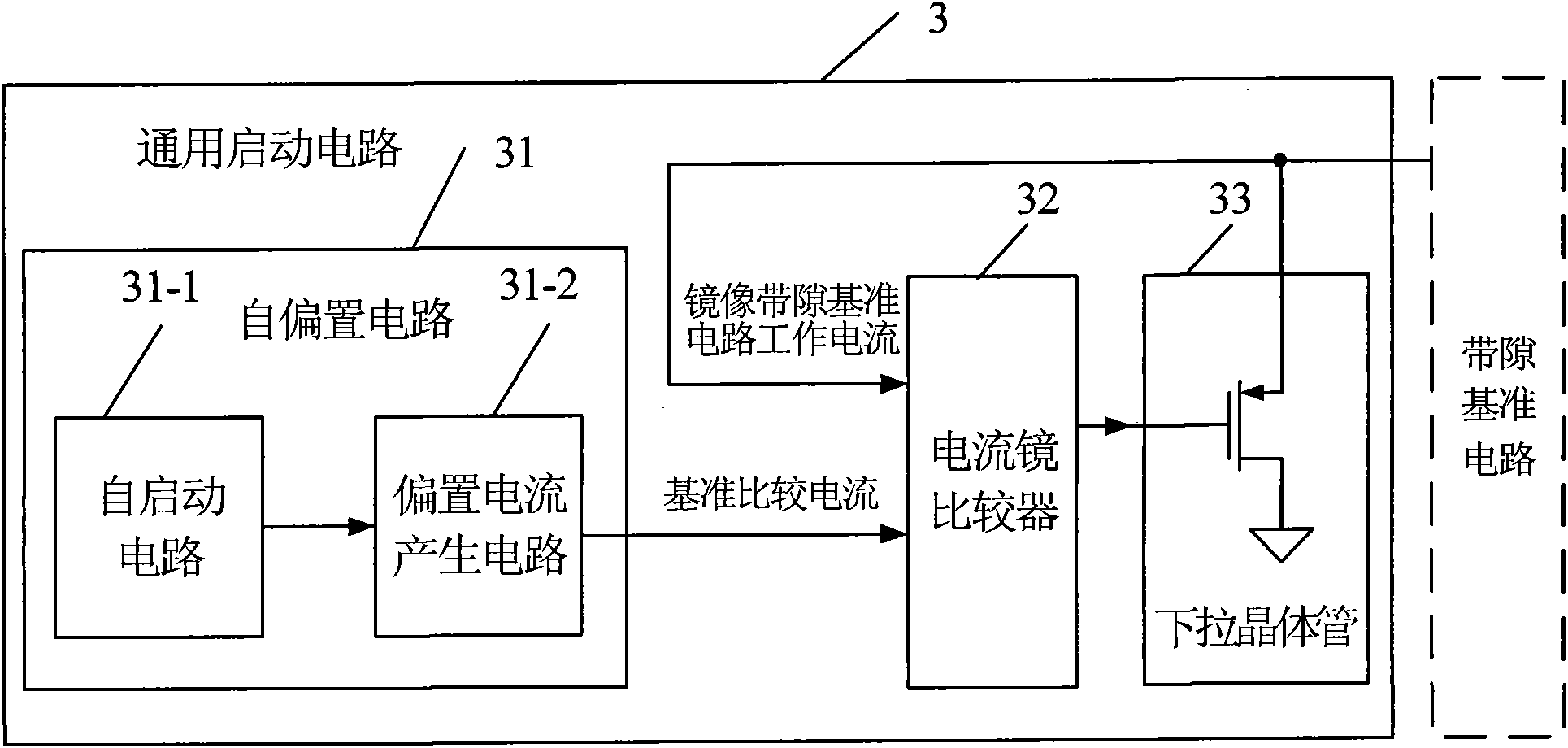
[0054] Figure 4 An electrical schematic diagram of the general bandgap reference starting circuit structure of the first embodiment of the present invention is given. The start-up circuit 4 is composed of a self-bias circuit 41, a current mirror comparator 42 and its pull-down transistor 43 connected in sequence. The self-bias circuit 41 includes a self-start circuit 41-1 and a bias current generating circuit 41-2.
[0055] The self-starting circuit 41 - 1 of the self-bias circuit is composed of NMOS transistors 401 and 402 and a PMOS transistor 406 . The PMOS tube 406 of the self-starting circuit is a PMOS capacitor tube. The drain and source of the PMOS capacitor tube 406 are the upper plate connected to the power supply, and the gate is the lower plate connected to the drain of the NMOS transistor 401 and the gate of the self-bias circuit 402 . The source of the NMOS transistor 401 and the gate of the NMOS transistor 402 of the self-starting circuit are connected to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com