Method for conveying nucleic acid to vivo tissue cells by flexible electrode chip
A flexible electrode and living tissue technology, which is applied in the field of electroporation of cells in living tissue to transport nucleic acids in a large-area uniform electric field, can solve the problems of uneven electric field, insufficient electric field strength, and impractical application of nucleic acid transport, etc. achieve good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
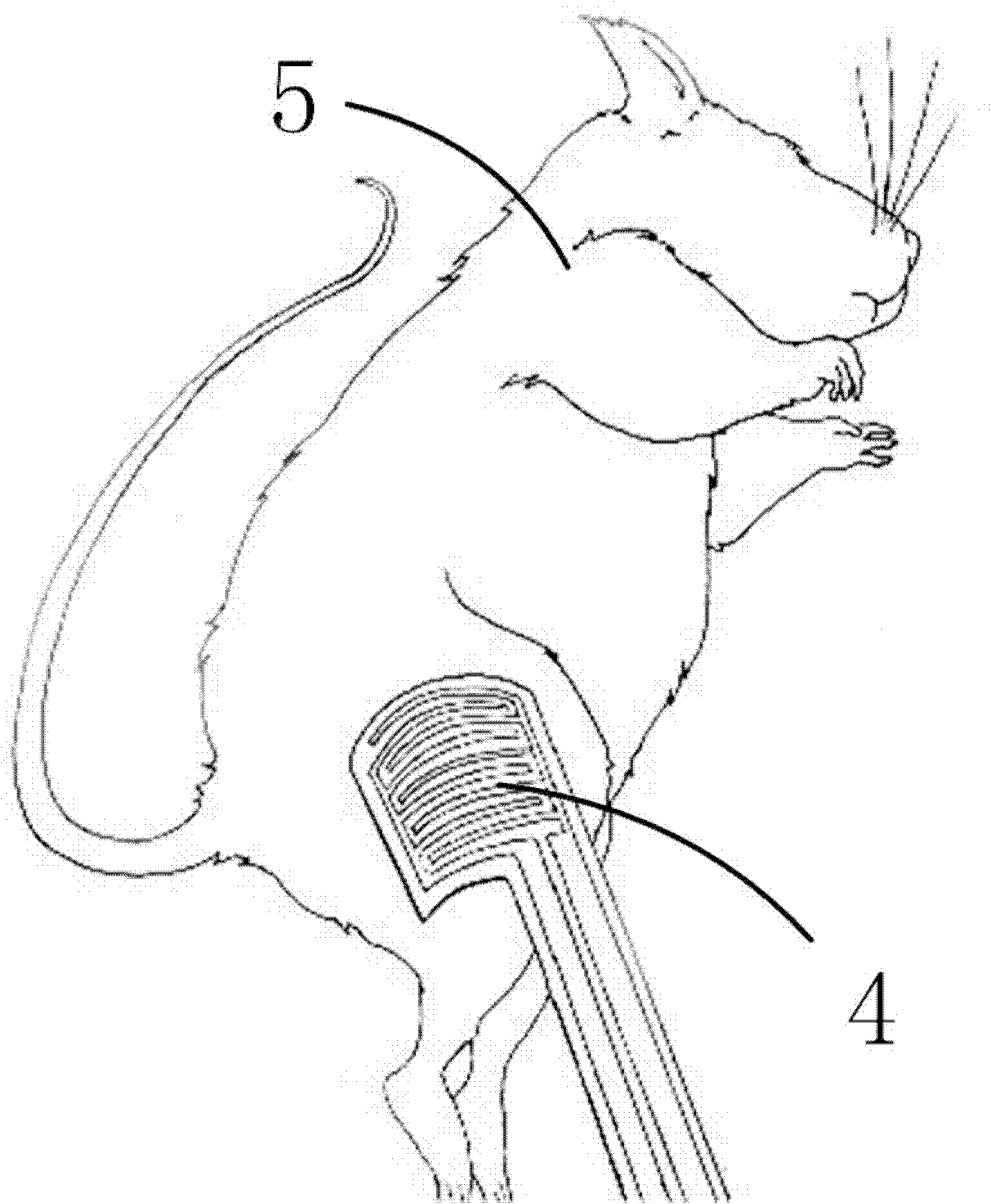
[0037] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
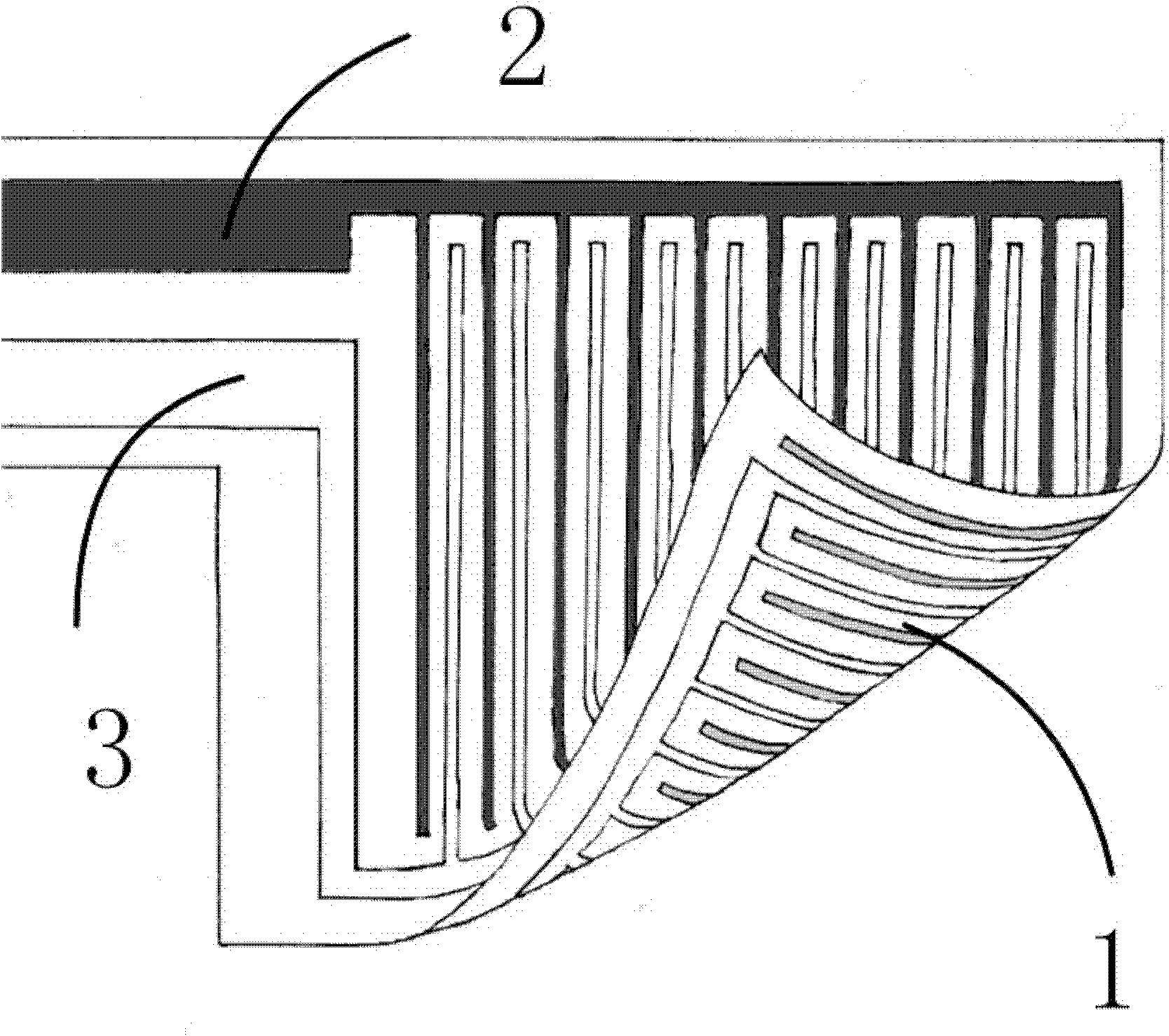
[0038] 1 flexible substrate:
[0039] Because the flexible substrate plays the role of supporting the electrodes and achieving electrical insulation between the electrodes, the flexible substrate needs to be made of insulating materials, or made of non-insulating materials covered with insulating layers. At the same time, because the micro-electrodes need to be fabricated on the flexible substrate, the flexible substrate needs to be compatible with existing micro-electrode processing methods (such as semiconductor etching). In addition, since one of the beneficial effects of the present invention is that it can be used for implantable operation of organs in a living body, the flexible substrate needs to have good biocompatibility. The flexible substrate in the present invention can be made of any material suitable for the above conditions.
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com