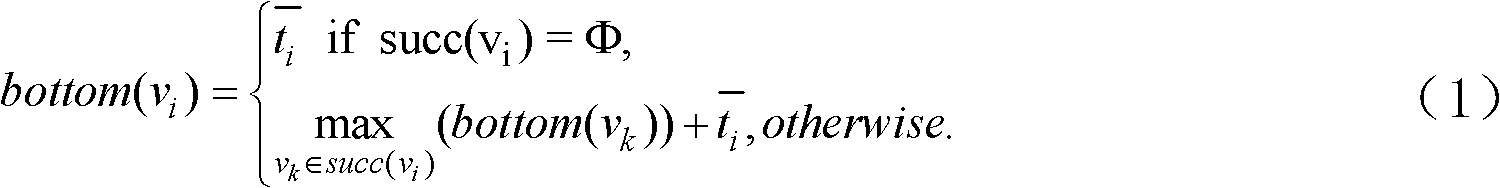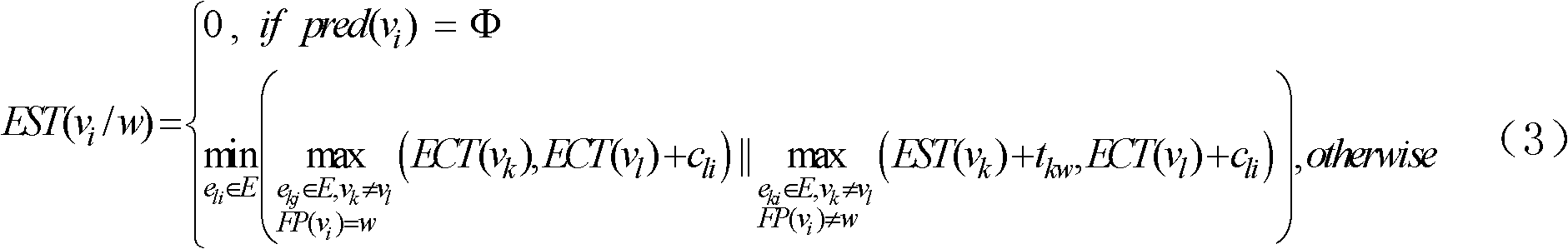Self-adaptive threshold-based energy-saving scheduling method in heterogeneous distributed system
A distributed system and self-adaptive threshold technology, applied in energy-saving computing, resource allocation, multi-programming devices, etc., can solve problems such as unstable scheduling results, inability to self-adaptive adjustment, ignoring network communication energy consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
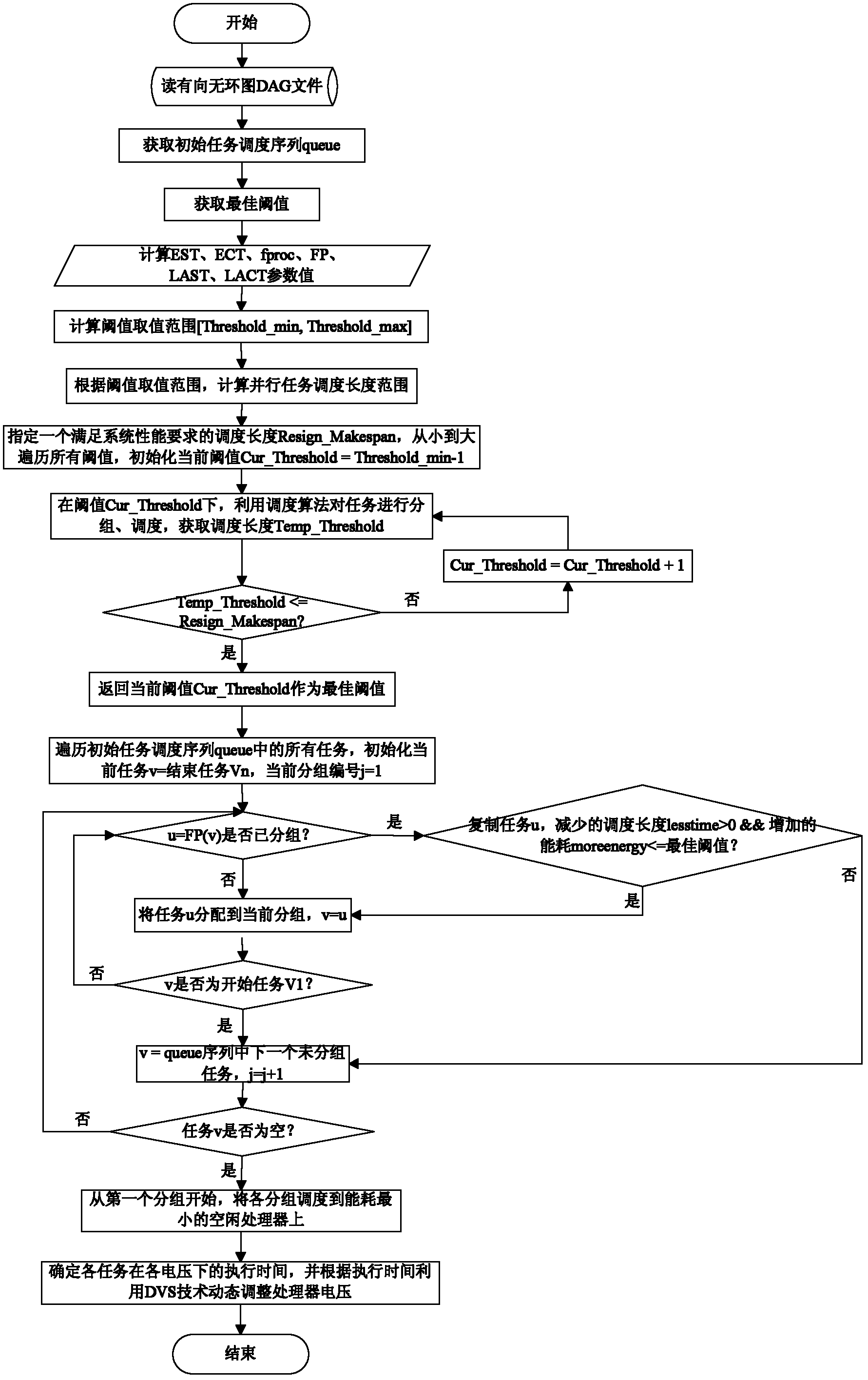
[0023] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0024] Parallel task: The task submitted by the user is represented by a directed acyclic graph DAG, which is defined as G(V, E). where V=(v 1 , v 2 ,L,v n ) represents a task set containing n tasks. For each task in V, task v i in processor p j The execution time on is t ij , where the maximum execution time is recorded as ti * Indicates the task v i Execution time on the scheduled processor. For the convenience of exposition, here respectively use {V 1 , V 2 ,K,V h} and {f 1 , f 2 , K, f h} represents the voltage and frequency set of the processor where each task is located. In particular, when task v i When there is idle time, dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) technology can be used to adjust the execution voltage of the processor where the task is located. The task is at the voltage V k The execution time under is denoted as τ ik . Additi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com