Functional additive applied to non-aqueou electrolyte of lithium ion battery
A technology of functional additives and non-aqueous electrolytes, applied in the field of electrolytes, can solve problems affecting battery cycle performance and battery system performance degradation, and achieve the effects of improving cycle performance, low cost, and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
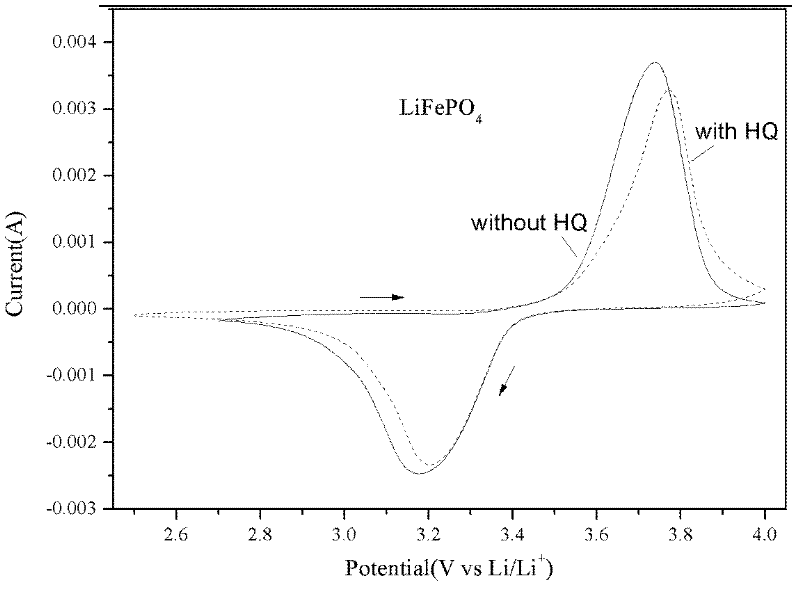
[0017] Prepare 1M LiPF 6 The basic electrolyte of EC / EMC / DEC (1:1:1w), adding 1.0wt% additive HQ to the basic electrolyte to make a new electrolyte, tested the electrolyte and LiFePO with a three-electrode system on a CHI660D electrochemical workstation 4 Positive compatibility. The working electrode was prepared by uniformly mixing the lithium iron phosphate sample, conductive carbon black and polytetrafluoroethylene at a mass ratio of 82:10:8, and the reference electrode and the counter electrode were metal lithium sheets. figure 1 for LiFePO 4 From the cyclic voltammograms in the two electrolytes, it can be seen that the additive HQ does not affect the normal deintercalation of lithium ions in the electrode material.
Embodiment 2
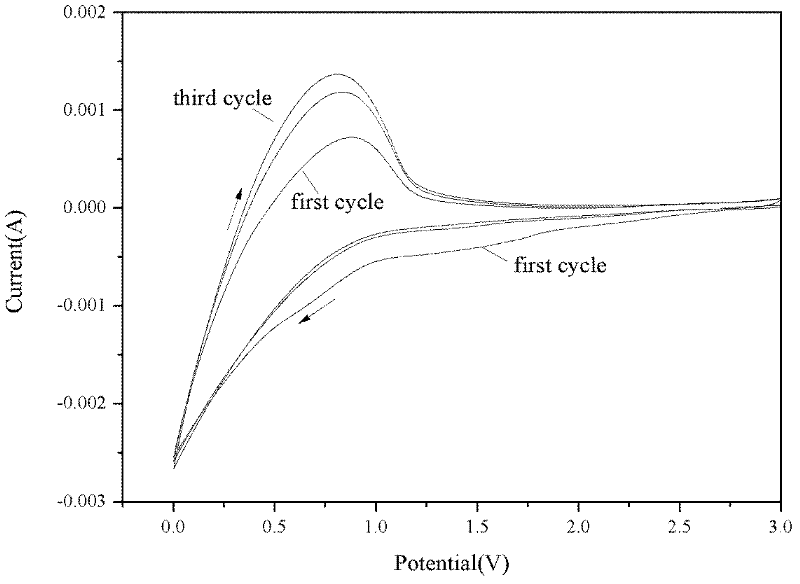
[0019] Mix graphite, binder and conductive agent in a ratio of 90:2:8 to make negative electrode slurry, evenly coat it on copper foil, and dry it at 80°C for 60 minutes to make lithium ion battery negative electrode sheet. Test of 1M LiPF with additive HQ using three-electrode system on CHI660D electrochemical workstation 6 Compatibility of EC / EMC / DEC (1:1:1w) basic electrolyte with graphite anode. figure 2 The cyclic voltammogram of graphite anode in the basic electrolyte containing 1wt% additive HQ is given, which shows that the additive HQ has good compatibility with graphite anode.
Embodiment 3
[0021] At 1M LiPF 6 Add 0.5wt% additive HQ to the EC / EMC / DEC (1:1:1w) basic electrolyte, then seal the electrolyte and place it in a vacuum drying oven in a vacuum glove box with a moisture content of less than 5ppm, at 45°C It was stored under high temperature for 2 days, and the changes of moisture and HF content in the electrolyte before and after high temperature storage treatment were investigated. The moisture content was measured by Karl Fischer potentiometric titrator, and the HF content was analyzed by acid-base neutralization titration. Table 1 shows the change values of moisture and HF content in the electrolyte before and after treatment at 45 °C. It can be seen that the additive HQ can effectively inhibit the generation of HF in the electrolyte and improve the stability of the electrolyte.
[0022] Table 1
[0023]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com