Ligand-free Transition Metal Catalytic Activity/Controlled Radical Polymerization Method in Aqueous Phase
A technology of transition metal catalysis and polymerization method, which is applied in the field of transition metal catalyzed radical polymerization without ligands in aqueous phase, and can solve the problems of poor solubility of transition metals and deviation of water solvent from research field of view.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Synthesis of P(PEGMA) (sample 1)
[0032] In a 100mL single-necked bottle, add 2.0mL polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether (PEGMA) (Mw=300) and 20mL ultrapure water as monomers, fully dissolve, and after bubbling nitrogen for 30 minutes, add 0.04mmol copper sulfate and 0.06 Mmol ascorbic acid, 20 μL isopropane bromide, continue to pass nitrogen gas for 5 minutes, seal and react at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction was quenched with liquid nitrogen, and the product was freeze-dried. Get 20 milligrams of dry matter and dissolve in 2.0 milliliters of tetrahydrofuran, detect its molecular weight and its fraction distribution with GPC as figure 1 shown. It shows that the present invention can successfully polymerize polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomer, and obtain a polymer with narrow molecular weight distribution.
Embodiment 2
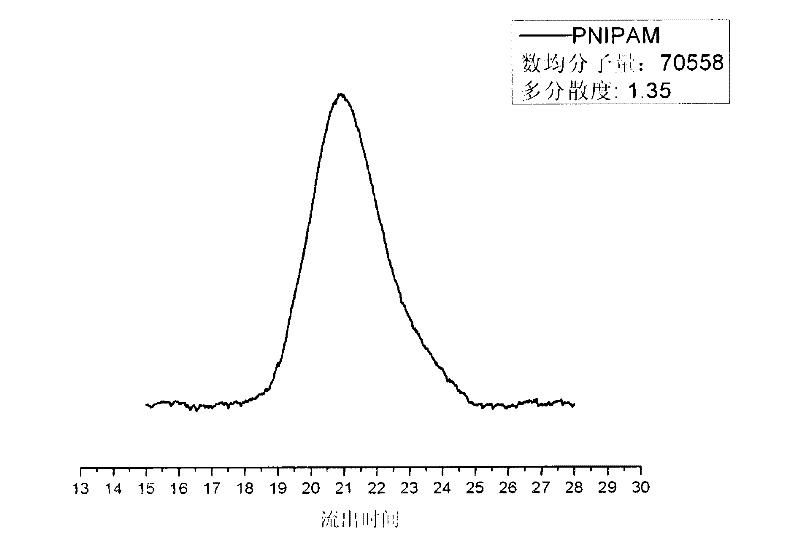
[0034] Synthesis of P(NIPAM) (sample 2)
[0035] Add 0.3192g of isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and 20mL of ultrapure water into a 100mL single-necked bottle, fully dissolve, and after bubbling nitrogen for 30 minutes, add 0.04mmol of copper sulfate and 0.06mmol of ascorbic acid in sequence, 20μL of bromoiso Propane, continue to flow nitrogen for 5 minutes, seal, and react at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction was quenched with liquid nitrogen, and the product was freeze-dried. Get 20 mg dry matter and dissolve in 2.0 milliliters of tetrahydrofuran, detect its molecular weight and its molecular weight distribution with GPC as figure 2 shown. It shows that the present invention can successfully polymerize polyisopropylacrylamide monomers and obtain polymers with narrow molecular weight distribution.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Synthesis of HPC-g-P(PEGMA) (sample 3)
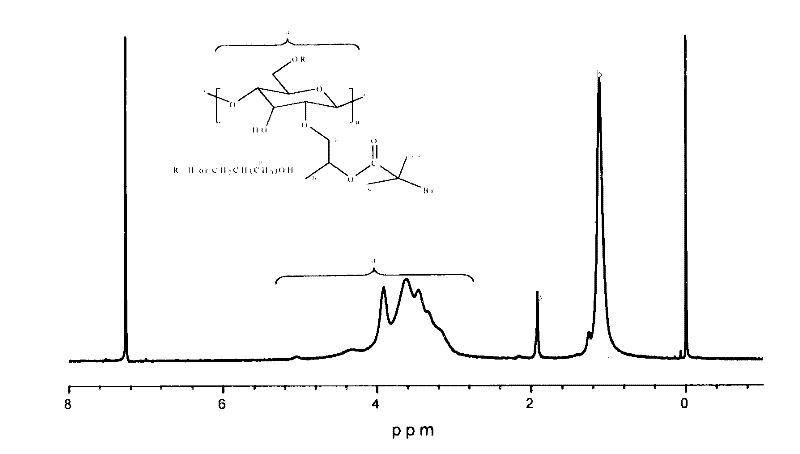
[0038] In a 1000mL single-necked bottle, add 4.0g hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), 400mL anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (THF) and 5.0mL anhydrous pyridine, stir well to dissolve. The reactor was placed in an ice-water bath, and a mixed solution of 1.0 mL of bromoisobutyryl bromide and 20 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran was slowly dropped into it. After the dropwise addition is completed, seal and place at 30 degrees Celsius for 48 hours of reaction. After standing still, the precipitate was discarded by filtration, and after the excess THF was rotary evaporated, the remaining solution was dialyzed in water for one week, and the water was changed every 8 hours. Freeze-dry the dialyzed solution to obtain hydroxypropyl cellulose macromolecular initiator (HPC-Br). image 3 It is a macromolecular initiator HPC-Br NMR characterization. The NMR characterization shows that the initiator has been successfully prepared, and its Br substitution ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com