A Cache Memory Replacement Method with Failed Disk Priority
A high-speed buffer and memory technology, applied in the direction of input/output to record carrier, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the number of I/O times, achieve the effect of reducing the number of times of orientation, improving system performance, and improving reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
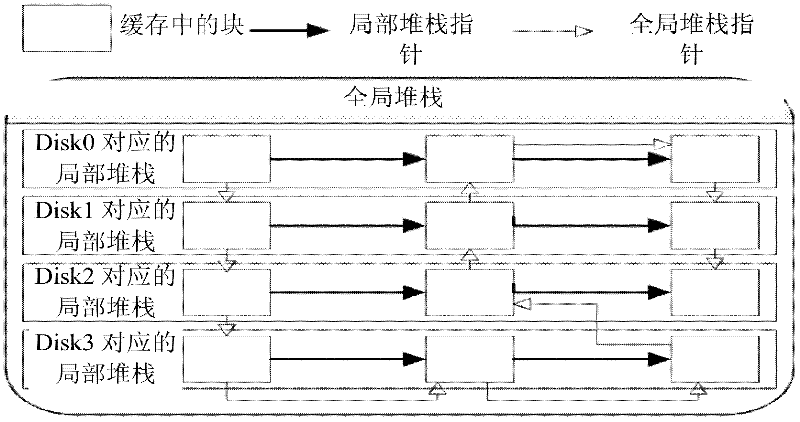
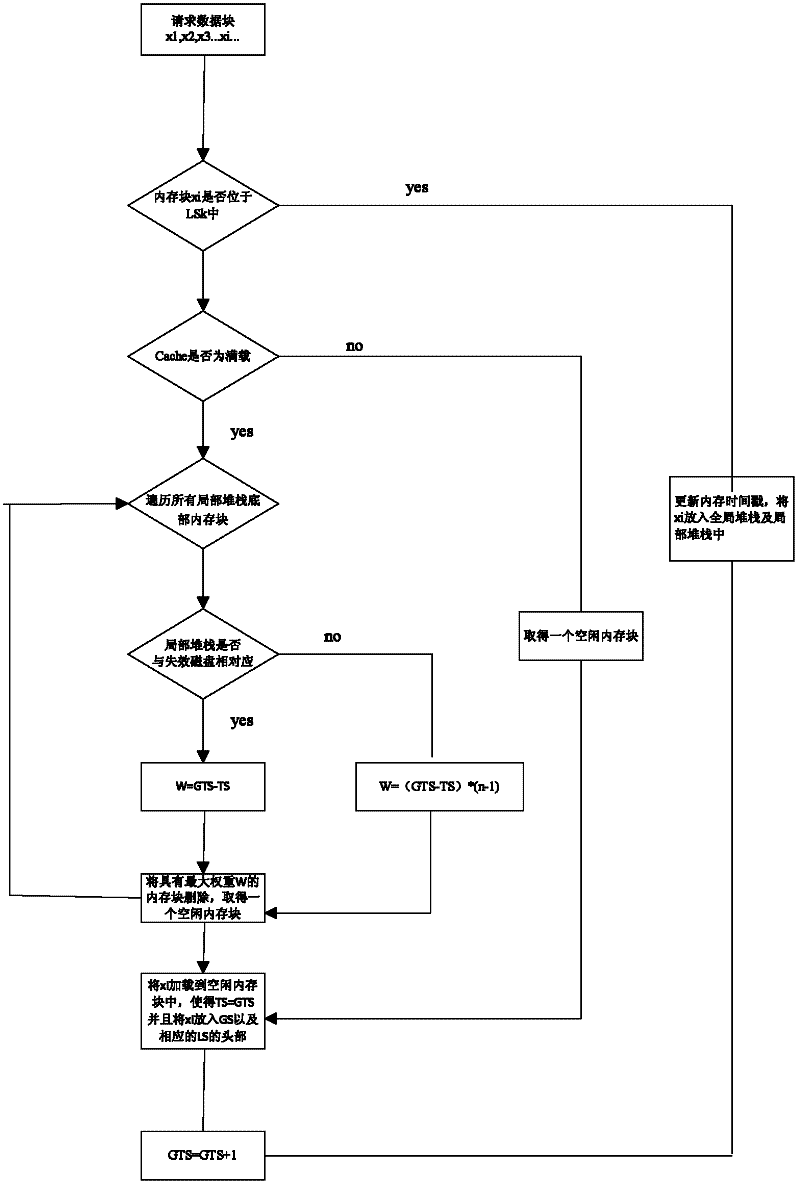
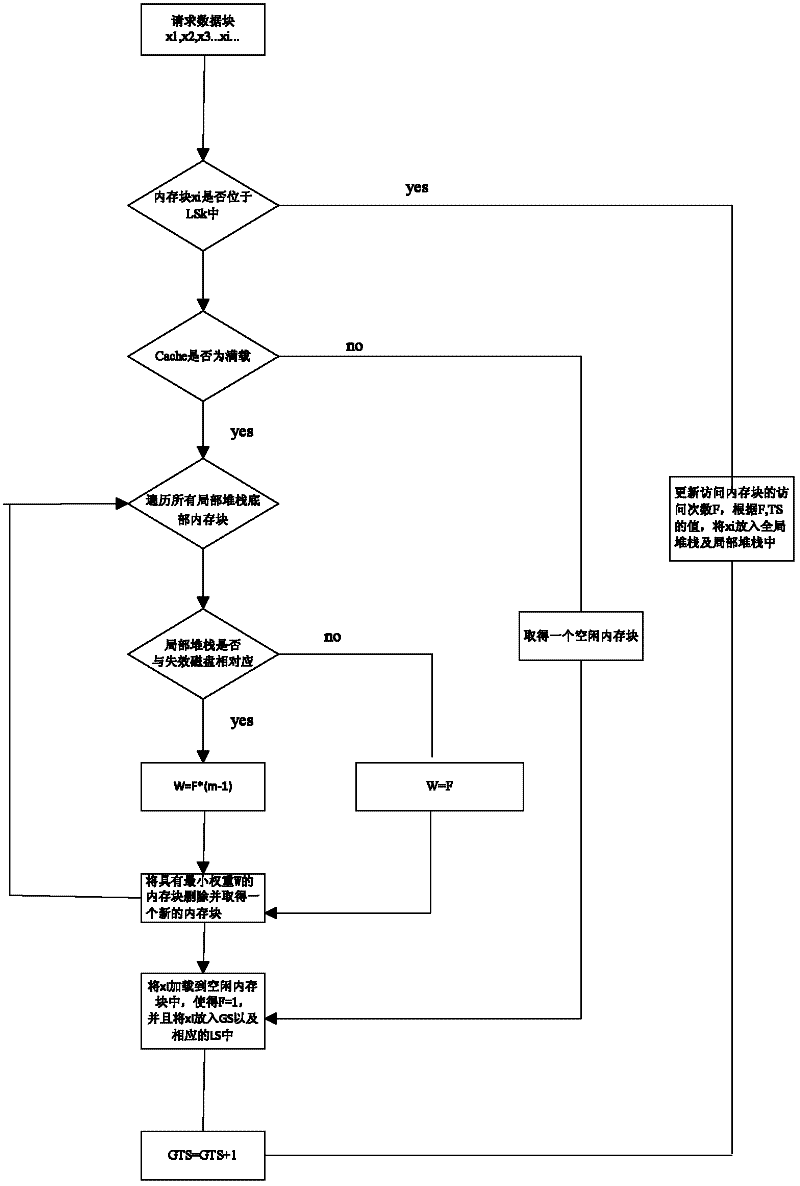
[0024] The present invention provides a Victim Disk First (VDF) Cache replacement method. The method preferentially retains the memory blocks in the invalid disk by calculating the weight of the memory block, thereby reducing the number of visits to the invalid disk, thereby reducing the number of I / O requests.
[0025] The following takes the failure of one of n disks in a RAID-5 system as an example (n is greater than or equal to 2), and compares the VDF method with the least recently used page replacement algorithm (Least Recently Used, LFU) and the least frequently used page replacement algorithm (least frequently used page replacement algorithm). used, LRU) algorithm is combined to describe the specific measures of the present invention.
[0026] In the LRU type algorithm, the weight of the memory block is determined by the storage time interval, which represents the last stored timestamp (timestamp), that is, the access sequence number. The access probability of a memor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com