Martensite stainless steel and preparation method for flat strip of martensite stainless steel
A martensitic stainless steel and flat strip technology, applied in the field of stainless steel materials, can solve the problems of large diameter-to-thickness ratio, strict size requirements, high strength and hardness requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
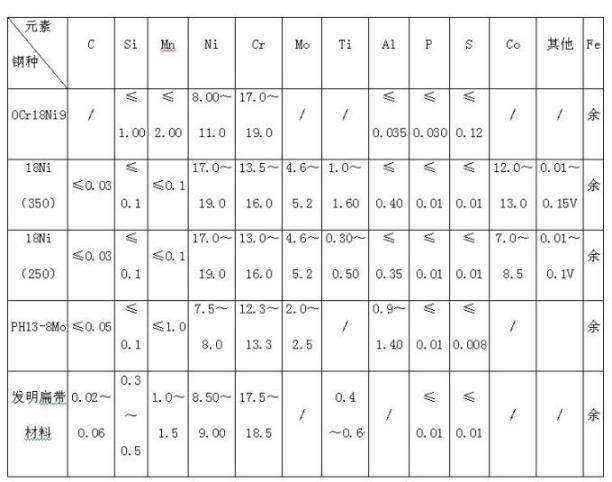
[0078] A martensitic stainless steel, the chemical composition of which is calculated by weight percentage: C: 0.049%; Si: 0.35%; Mn: 1.11%; Ni: 8.59%; Cr: 18.09%; Ti: 0.60%; P≤0.009% ; S≤0.009%; the balance is Fe.
[0079] The method for preparing a flat strip with the above-mentioned martensitic stainless steel comprises the following steps:
[0080] a) Weigh each chemical component by weight percentage;
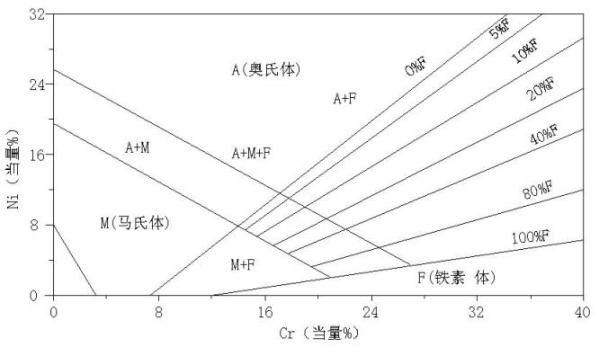
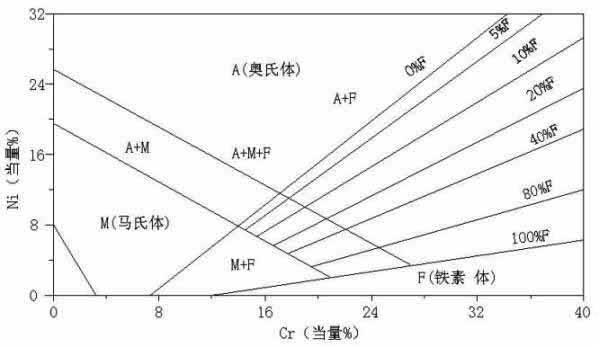
[0081] According to the nickel-chromium equivalent law, through the design and analysis of each chemical element composition, the ingredients are prepared according to the weight percentage of each chemical composition;
[0082] b), vacuum induction melting;
[0083] Vacuum induction melting adopts secondary refining process;
[0084] The first refining is at a temperature of 1530±5°C, the vacuum degree is controlled at 1Pa, and refining is performed for 20 minutes;
[0085] The second refining is at a temperature of 1530±5°C, the vacuum degree is controlled at 0.1Pa, ...
Embodiment 2
[0101] A martensitic stainless steel whose chemical composition is calculated by weight percentage: C: 0.02; Si: 0.3; Mn: 1.0; Ni: 8.5; Cr: 17.5%; Ti: 0.4; P≤0.009%; S≤0.009% ; The balance is Fe.
[0102] The method for preparing a flat strip with the above-mentioned martensitic stainless steel comprises the following steps:
[0103] a) Weigh each chemical component by weight percentage;
[0104] According to the nickel-chromium equivalent law, through the design and analysis of each chemical element composition, the ingredients are prepared according to the weight percentage of each chemical composition;
[0105] b), vacuum induction melting;
[0106] Vacuum induction melting adopts secondary refining process;
[0107] The first refining is at a temperature of 1560±5°C, the vacuum degree is controlled at 6Pa, and refining is performed for 10 minutes;
[0108] The second refining is at a temperature of 1560±5°C, the vacuum degree is controlled at 0.02Pa, and the refining i...
Embodiment 3
[0124] A martensitic stainless steel, the chemical composition of which is calculated by weight percentage: C: 0.06%; Si: 0.5%; Mn: 1.5%; Ni: 9.0%; Cr: 18.5%; Ti: 0.6%; P≤0.009% ; S≤0.009%; the balance is Fe.
[0125] The method for preparing a flat strip with the above-mentioned martensitic stainless steel comprises the following steps:
[0126] a) Weigh each chemical component by weight percentage;
[0127] According to the nickel-chromium equivalent law, through the design and analysis of each chemical element composition, the ingredients are prepared according to the weight percentage of each chemical composition;
[0128] b), vacuum induction melting;
[0129] Vacuum induction melting adopts secondary refining process;
[0130] The first refining is at a temperature of 1540±5°C, the vacuum degree is controlled at 3Pa, and refining is performed for 15 minutes;
[0131] The second refining is at a temperature of 1540±5°C, the vacuum degree is controlled at 0.06Pa, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com