Method for identifying function and capability of cells for phagocytizing exogenous foreign bodies
A technology of cells and foreign bodies, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
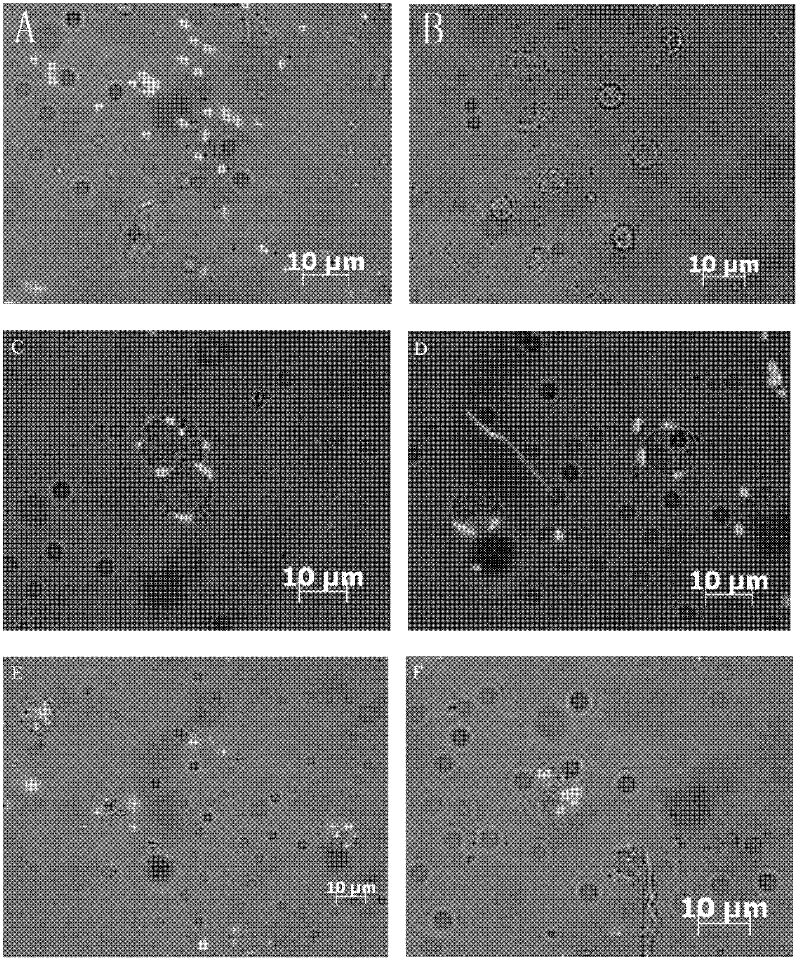
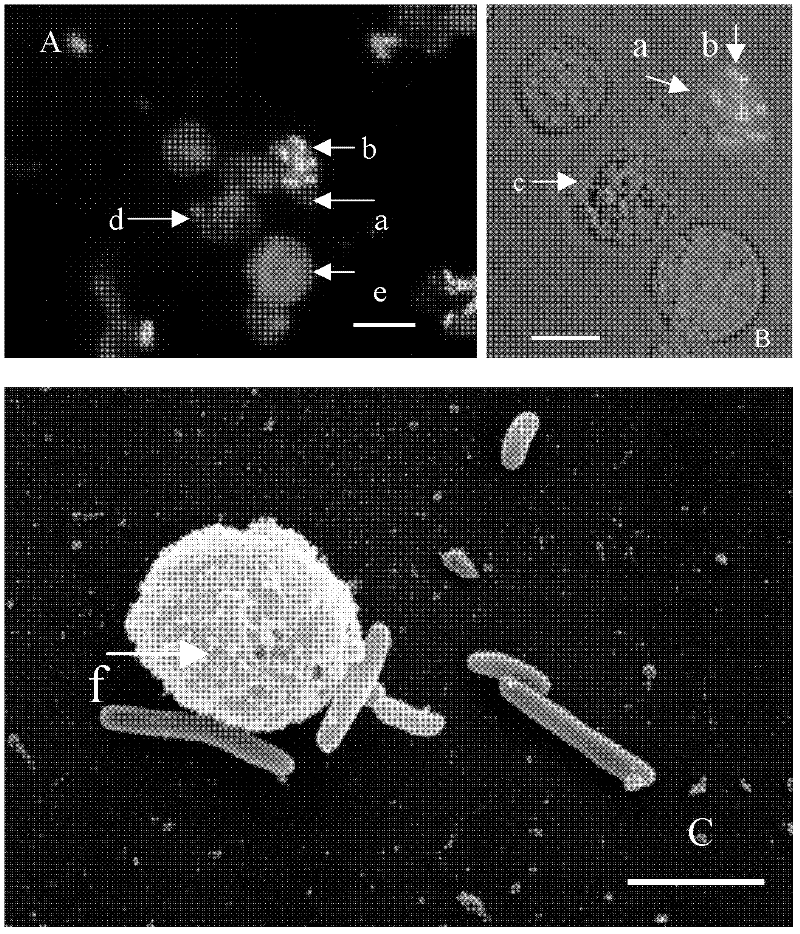
[0027] Phagocytosis of Escherichia coli expressing green fluorescent protein by Procambarus clarkii hemolymphocytes cultured in vitro.
[0028] 1. Construct Escherichia coli expressing green fluorescent protein:
[0029] a. Extract and purify pEGFP from E.coli DH5α transformed with plasmid pEGFP with B-type mini-plasmid rapid extraction kit (Broadtech), and store at -20°C;
[0030] b. Prepare competent cells (CaCl 2 Law).
[0031] c. Add 200 μl competent cells to 1 μl EGFP plasmid, shake gently, place on ice for 30 minutes, heat shock at 42°C for 90 seconds, place on ice for 2 minutes, add 800 μl LB medium, shake at 200 rpm at 37°C for 1 hour, and centrifuge at 4000 rpm at room temperature After 5 minutes, discard most of the supernatant and resuspend the cells with the remaining 50 μl medium. Bacteria were spread on plates containing 100 µl of X-gal coated ampicillin (100 µg / ml) at a concentration of 20 mg / ml and grown overnight. →Pick positive monoclonal colonies and cul...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Escherichia coli infection in Ciona in vitro
[0037] Cultivate Ciona blood lymphocytes in vitro, (medium formulation 80% Leibovitz L-15, FBS15%, add glucose with a final concentration of 1g / l, 300U of penicillin, streptomycin, 0.1mg / l Vc, 20mMHepes, 0.75g / l KCl, 1.1g / l CaCl2, 2g / l MgCl2, NaCl20g / l, 7.5%NaCO3 adjust the pH value,), all the other are the same as embodiment 1, see specifically figure 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com