Conductive member and method for producing the same
A technology of conductive parts and manufacturing methods, applied in contact parts, thin material handling, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of easy peeling, peeling, poor adhesion, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
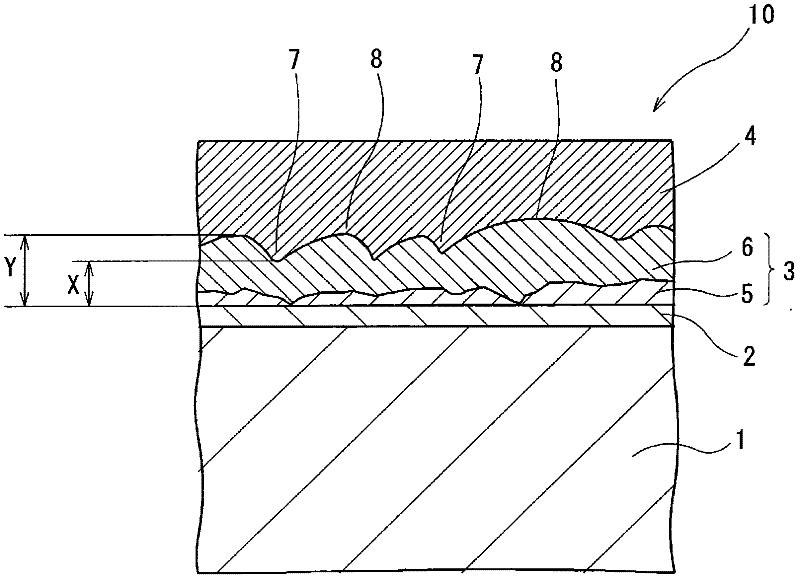
[0048] First, the first embodiment will be described. The conductive member 10 of the first embodiment is, for example, a conductive member used in a terminal of an automotive connector, such as figure 1 As shown, the Cu-Sn intermetallic compound layer 3 and the Sn-based surface layer 4 are sequentially formed on the surface of the Cu-based substrate 1 through the Ni-based base layer 2, and the Cu-Sn intermetallic compound layer 3 is further composed of Cu 3 Sn layer 5 and Cu 6 sn 5 Layer 6 constitutes.
[0049] The Cu-based substrate 1 is, for example, a plate-shaped substrate made of Cu or a Cu alloy. The material of the Cu alloy is not necessarily limited, but Cu-Zn-based alloys, Cu-Ni-Si-based (Colson-based) alloys, Cu-Cr-Zr-based alloys, Cu-Mg-P-based alloys, As Cu—Fe—P alloys and Cu—Sn—P alloys, for example, MSP1, MZC1, MAX251C, MAX375, and MAX126 manufactured by Mitsubishi Shindoh Co., Ltd. are suitably used.
[0050] The Ni-based base layer 2 is formed by electrop...
Embodiment 1
[0083] Next, examples of the first embodiment will be described.
[0084] A MAX251C material manufactured by Mitsubishi Shindoh Co., Ltd. with a thickness of 0.25 mm was used as a Cu alloy plate (Cu-based base material), and plating treatments of Ni, Cu, and Sn were sequentially performed on this material. At this time, as shown in Table 4, a plurality of samples were prepared by changing the current density of each plating treatment. The target thickness of each plating layer was 0.3 μm for the Ni plating layer, 0.3 μm for the Cu plating layer, and 1.5 μm for the Sn plating layer. In addition, a water washing step for rinsing the plating solution from the surface of the material to be treated is added between the three plating steps.
[0085] In the plating treatment in this example, a plating solution was sprayed at a high speed on a Cu alloy plate, and an insoluble anode of an iridium oxide-coated Ti plate was used.
[0086] After performing the above three plating treatmen...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0107] Next, according to Figure 7 A second embodiment will be described. in the Figure 7 In the description, the same parts as those in the first embodiment are given the same symbols to simplify the description.
[0108] Such as Figure 7 As shown, in the conductive member 30 of the second embodiment, a Ni-based base layer 2, a Cu-Sn intermetallic compound layer 3, and a Sn-based surface layer 4 are sequentially formed on the surface of a Cu-based base material 1 via an Fe-based base layer 31, and The Cu-Sn intermetallic compound layer 3 is further composed of Cu 3 Sn layer 5 and Cu 6 sn 5 Layer 6 constitutes.
[0109] The Cu-based substrate 1 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0110] Fe-based base layer 31 is formed by electroplating Fe or Fe alloy, and is formed on the surface of Cu-based base material 1 with a thickness of 0.1 to 1.0 μm. If the Fe-based underlayer 31 is less than 0.1 μm, the Cu-diffusion preventing function of the Cu-based substrate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com