Lithium bromide absorption-compression type series boosting refrigeration/heating pump system
A lithium bromide absorption and heat pump system technology, applied in the field of absorption-compression series boosting refrigeration system, can solve problems such as large compression, and achieve the effects of reducing superheat loss, reducing compression ratio requirements, and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
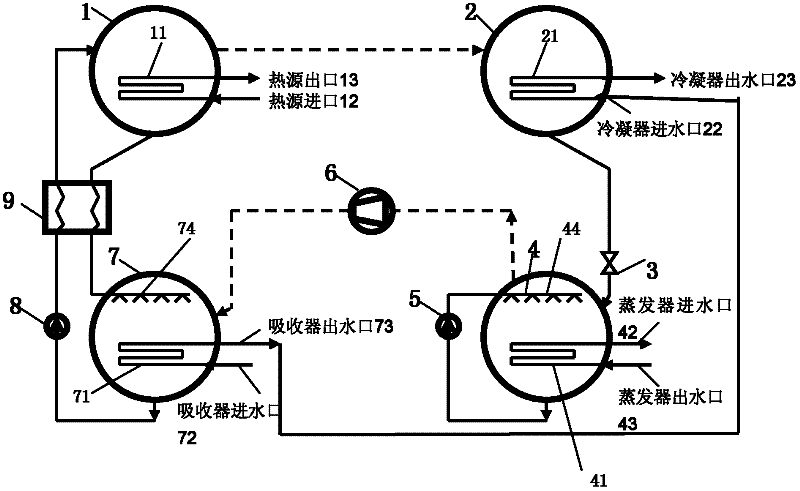
[0035] Embodiment 1, figure 1 A lithium bromide absorption-compression series step-up refrigeration system is given. The system consists of a generator 1, a condenser 2, a throttling element 3, an evaporator 4, a compressor 6, an absorber 7, a solution regenerator 9, and a refrigeration unit. Composed of a solvent circulation pump 5 and a solution circulation pump 8, a sprayer I 44 is provided on the top of the evaporator 4, and a sprayer II 74 is provided on the top of the absorber 7. The compressor 6 is placed before the absorber 7 and after the evaporator 4 . The liquid refrigerant outlet of the evaporator 4 is located at the bottom of the evaporator 4 , and the refrigerant vapor outlet of the evaporator 4 is located at the top of the evaporator 4 .
[0036] A heat source coil 11 is arranged inside the generator 1 , and a heat source inlet 12 and a heat source outlet 13 are respectively arranged at both ends of the heat source coil 11 . The condenser 2 is provided with a ...
Embodiment 2
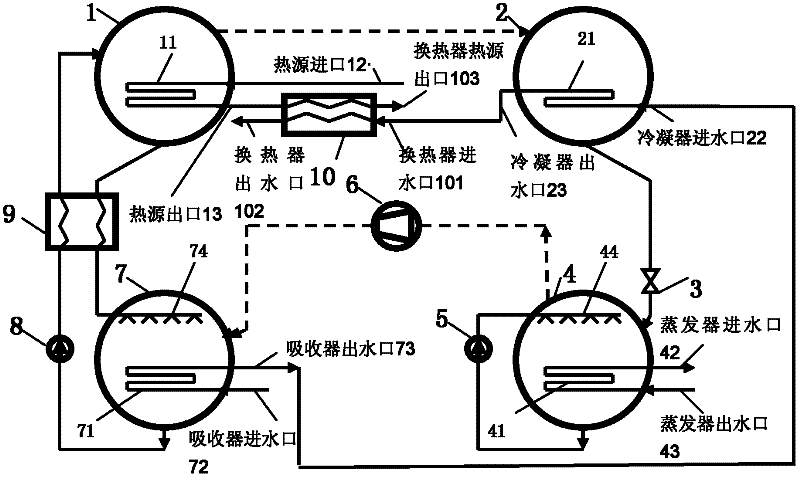
[0054] Embodiment 2, figure 2 A lithium bromide absorption-compression series step-up refrigeration system is provided; the difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0055] The water inlet and outlet of the absorber 7 and the condenser 2 are arranged in series, specifically: the water outlet 73 of the absorber communicates with the water inlet 22 of the condenser. Therefore, the cooling water supply of the external cooling water system is only connected to the absorber water inlet 72 , and the cooling water return water of the external cooling water system is only connected to the condenser water outlet 23 .
[0056] The difference between specific work content and embodiment 1 is as follows:
[0057] The cooling water at normal temperature passes through the absorber water inlet 72, the absorber heat exchange coil 71, the absorber water outlet 73, the condenser water inlet 22 and the condenser heat exchange coil 21, and is finally discharged from the condenser water outlet 23 into...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, figure 2 A lithium bromide absorption-compression series booster heat pump system is given; its structure is exactly the same as that in Example 2. But when actually used:
[0060] The hot water return water (such as 50° C.) of the external hot water system flows in from the water inlet 73 of the absorber, and the water discharged from the condenser water outlet 23 is used as hot water supply (such as 60° C.) of the external hot water system.
[0061] The heat source inlet 12 is connected with the heat source (for example, 100° C.); the heat source outlet 13 is connected with the external heating system;
[0062] The evaporator water inlet 42 and the evaporator water outlet 43 communicate with the water supply and return water pipelines of the external waste heat system respectively.
[0063] The specific work content is as follows:
[0064] 1. The low-temperature and low-pressure liquid refrigerant (referring to the water evaporated from the lithium b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com