Green synthesis of nanometals using plant extracts and use thereof
A plant extract, metal technology, applied in the fields of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve problems such as expensive, high energy consumption, toxic chemical solvents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Example 1: Green synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI) or manganese (NZVMn)
[0102] The method according to the invention uses plant extracts containing reducing agents capable of forming nanoparticles in the presence of dissolved iron species. The reaction is almost instantaneous when the reducing agent-containing plant extract is mixed with dissolved iron or manganese species. Phytoreductants are mainly composed of phenolic compounds and flavonoids. An example of dissolved iron is ferric chloride (FeCl 3 ), ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ) and ferric nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 ). An example of a dissolved manganese species is manganese chloride (MnCl 2 ) and manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 ).
[0103] This green synthetic route using phytoreductants could replace milling or solution-based preparation of these materials with green synthetic methods. This approach eliminates toxic materials used in the traditional preparation of zero-valent metal nanoparticles (ie, nZ...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Example 2: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plant-based surfactants and / or co-solvents
[0106] The method according to the invention involves the green synthesis of metal nanoparticles in the presence of plant-based co-solvents and surfactants. The plant-based co-solvents and surfactants can be used to stabilize metal nanoparticles and minimize their aggregation, and they can also be used as reducing agents in the formation of metal nanoparticles. These plant-based co-solvents and surfactants are of natural origin and may be biodegradable.
[0107] Examples of plant-based co-solvents and surfactants that can be used are VerTEK US FDA generally recognized as safe (GRAS) co-solvents and surfactants for enhancing the solubility of LNAPL and DNAPL during oxidation and reduction reactions. Examples of plant-based co-solvents and surfactants that can be used include VeruSOL TM , Citrus Burst 1 (CB-1), Citrus Burst 2 (CB-2), Citrus Burst 3 (CB-3) and EZ-Mulse, produ...
Embodiment 3
[0115] Example 3: Coating of NZVI, NZVMn, and bimetallic NZVI, NZVMn
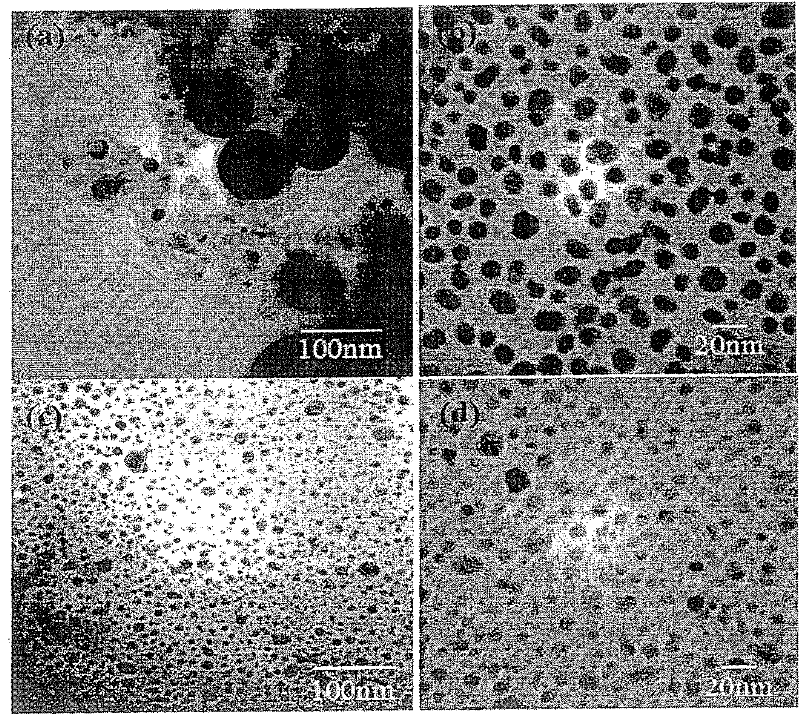
[0116] The use of nanoparticulate zerovalent iron (nZVI) and nanoparticulate zerovalent manganese (nZVMn) can be limited in environmental applications because they can show a tendency to agglomerate into micron-sized particles, thereby losing their surface area versus mass some of the benefits. Additionally, nZVI and nZVMn particles can be highly reactive and their surfaces can be rapidly passivated and oxidized. In many applications, including those used in remediation, it is required that these particles be present and remain reactive for many months or even years. Coating nZVI and nZVMn particles can reduce the rapid aggregation, oxidation and passivation of nanoscale particles.
[0117] In the green approach according to some embodiments of the present invention, biodegradable polymers such as carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) can be used at room temperature by reacting each metal salt with the sodium sa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com