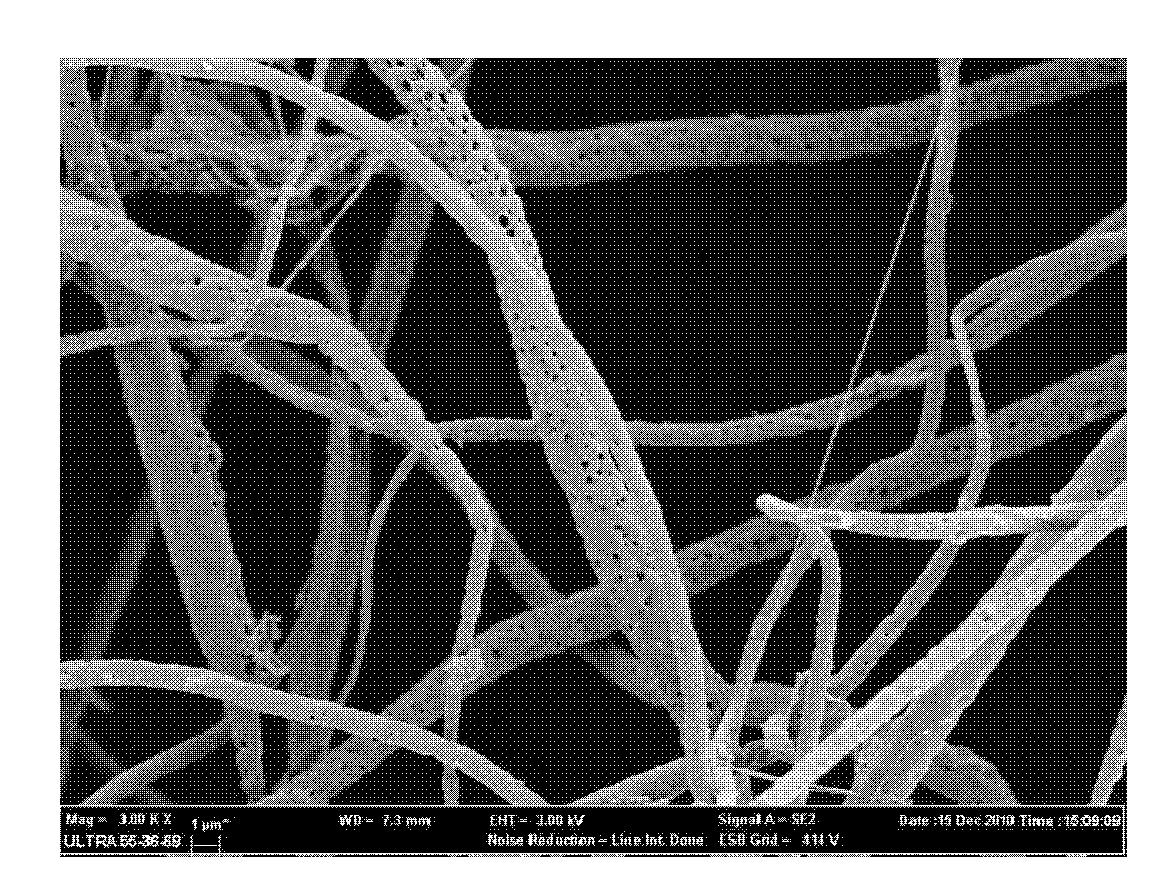
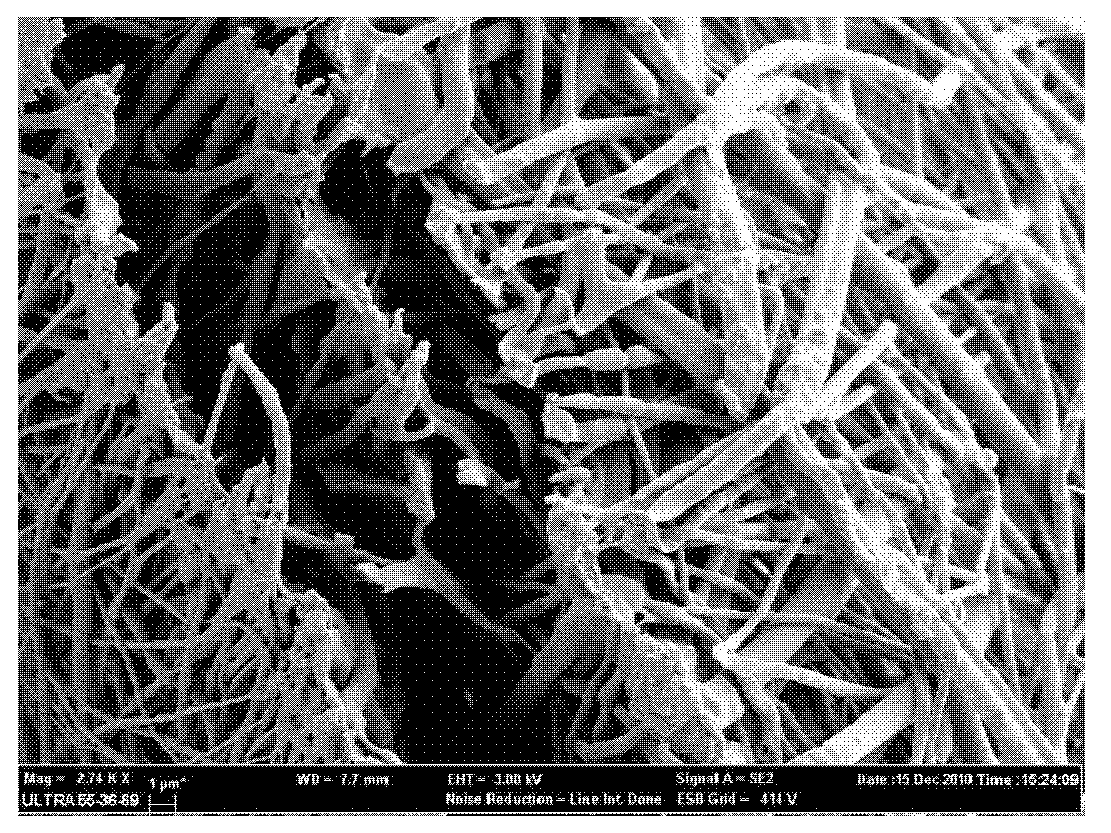
Method for preparing protein-loaded tissue engineering fiber support
A fiber scaffold and tissue engineering technology, applied in fiber processing, non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of not mentioning protein conformational protection results, not achieving sustained release effect, etc., to improve the release curve and reduce aggregation. phenomenon, the effect of good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Fabrication and in vitro release of protein-loaded tissue engineering fibrous scaffolds by ordinary electrospinning
[0034] a) Dissolving BSA (0.5%, w / w) in 0.5 ml of an aqueous polymer polysaccharide (0.5%, w / w) solution as the inner water phase;
[0035] b) Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer (99%, w / w) was dissolved in 2.5 ml of an equal volume mixed organic solvent of N,N-dimethylformamide and chloroform as the external oil phase;
[0036] c) The inner water phase is added dropwise to the outer oil phase, and magnetically stirred at 200 rpm for 30 minutes to form a W / O emulsion.
[0037] d) Add the above-mentioned W / O emulsion into a syringe, apply high-voltage static electricity, use a micro-injection pump and a receiver, and electrostatically spin a fiber film at room temperature;
[0038] e) The fiber film is left to dry at room temperature to obtain tissue engineering fibers by emulsion electrospinning. The fiber has strong plasticity and can be molded in...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Fabrication of protein-loaded tissue engineering fibrous scaffolds by ordinary electrospinning and its release in vitro
[0043] a) Dissolving BSA (0.5%, w / w) in 0.5 ml of an aqueous polymer polysaccharide (0.5%, w / w) solution as the inner water phase;
[0044] b) Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer (99%, w / w) was dissolved in 10 ml of N,N-dimethylformamide and chloroform equal volume mixed organic solvent as the external oil phase;
[0045] c) The inner water phase is added dropwise to the outer oil phase, and magnetically stirred at 2500 rpm for 15 minutes to form a W / O emulsion.
[0046]d) Add the above-mentioned W / O emulsion into a syringe, apply high-voltage static electricity, use a micro-injection pump and a receiver, and electrostatically spin a fiber film at room temperature;
[0047] e) The fiber film is left to dry at room temperature to obtain tissue engineering fibers by emulsion electrospinning. The fiber has strong plasticity and can be molded into ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Fabrication of protein-loaded tissue engineering fibrous scaffolds by ordinary electrospinning and its release in vitro
[0050] a) Dissolving BSA (5%, w / w) in 0.5 ml of an aqueous polymer polysaccharide (0.5%, w / w) solution as the inner water phase;
[0051] b) Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer (99%, w / w) was dissolved in 2.5 ml of an equal volume mixed organic solvent of N,N-dimethylformamide and chloroform as the external oil phase;
[0052] c) The inner water phase is added dropwise to the outer oil phase, and magnetically stirred at 2500 rpm for 15 minutes to form a W / O emulsion.
[0053] d) Add the above-mentioned W / O emulsion into a syringe, apply high-voltage static electricity, use a micro-injection pump and a receiver, and electrostatically spin a fiber film at room temperature;
[0054] e) The fiber film is left to dry at room temperature to obtain tissue engineering fibers by emulsion electrospinning. The fiber has strong plasticity and can be molded...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com