Method for identifying common warehousing liposcelis quickly based on multiple PCR technology
A technology for storing booklice and booklice, which is applied in the fields of plant protection and biology, and can solve problems such as cumbersome steps, undiscussed identification of individual booklice, and insufficient efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
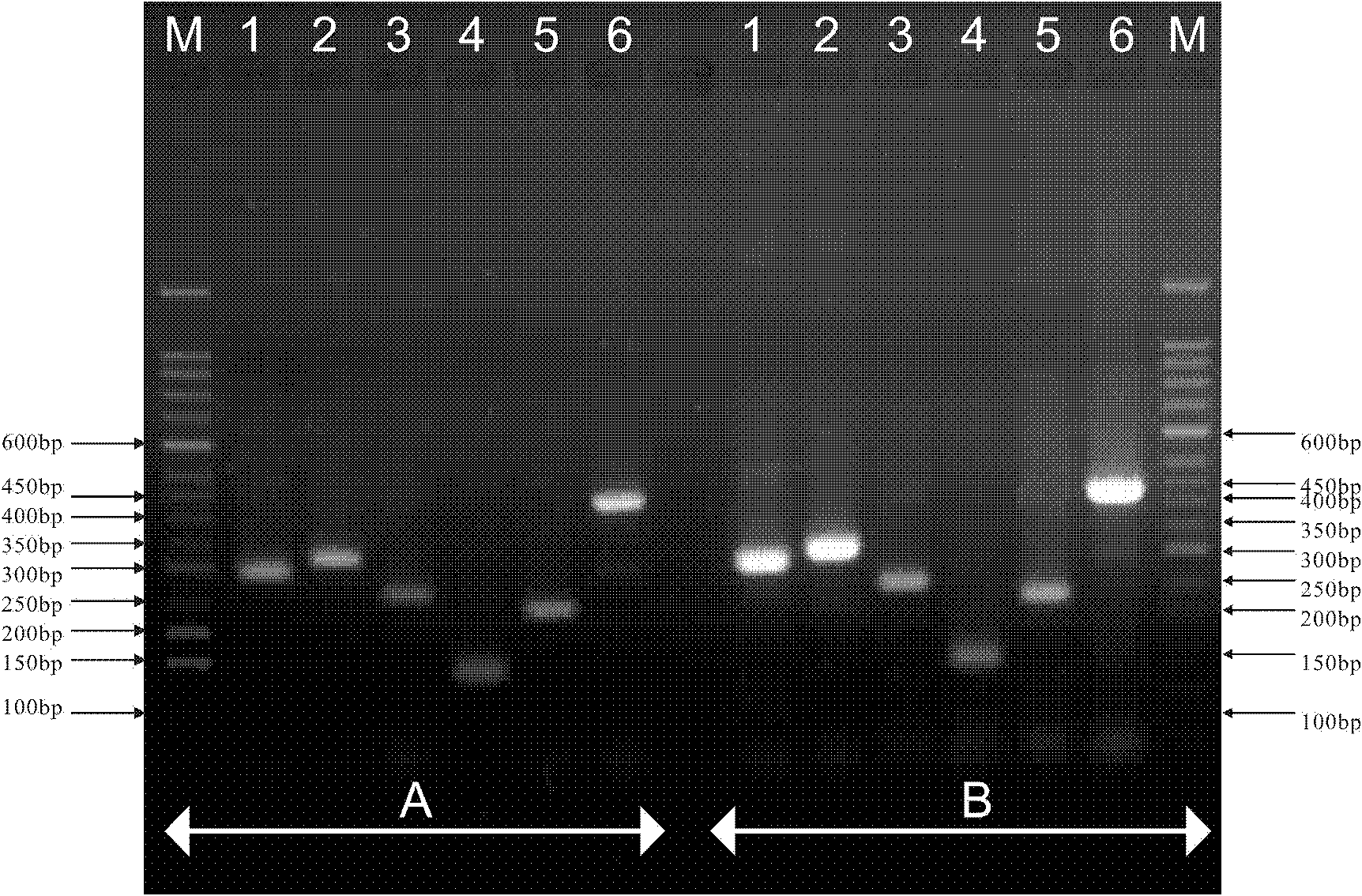
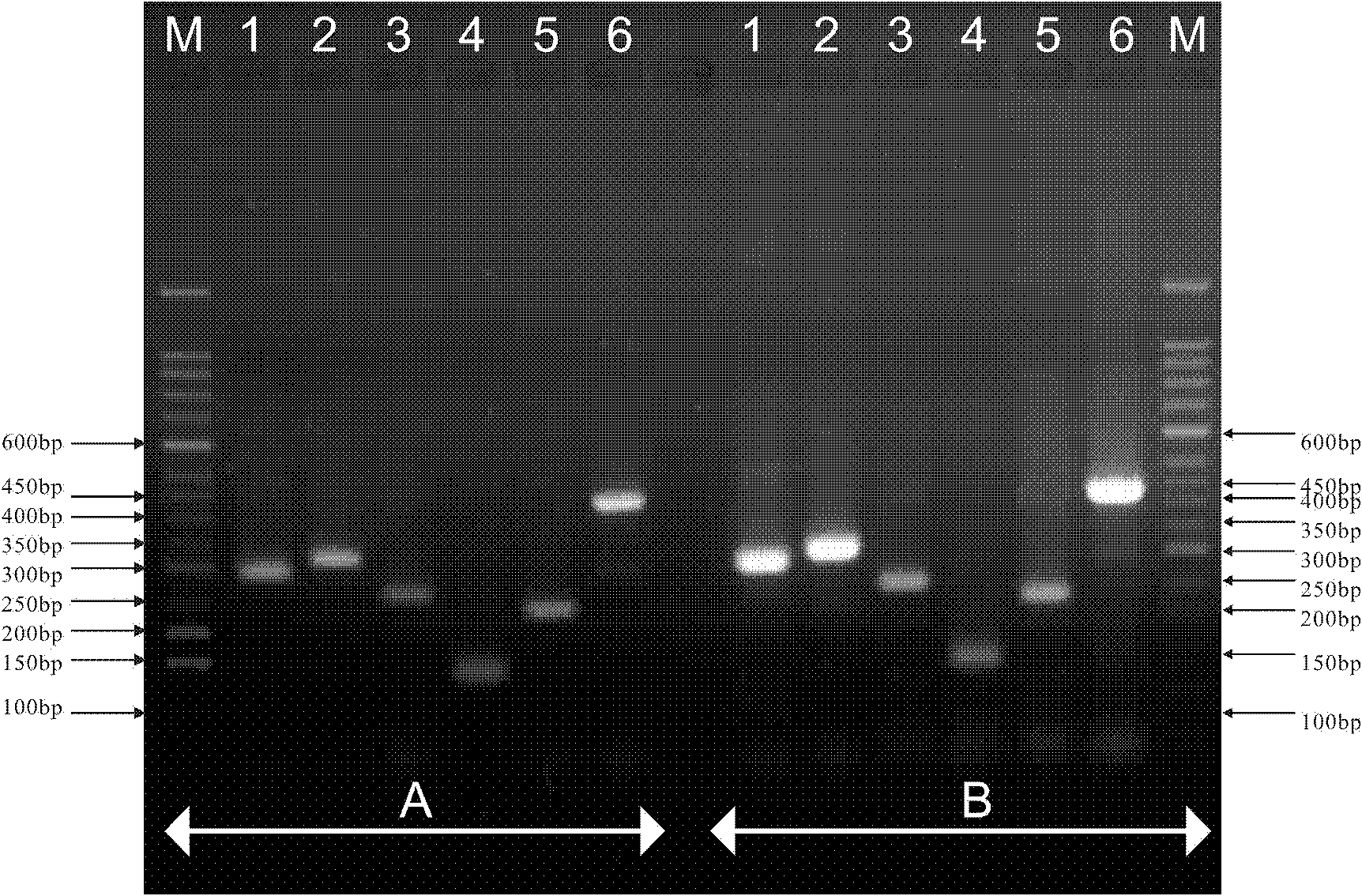
[0025] Example 1: Using the STE method to extract the monomeric and population genomic DNA of 6 kinds of booklice
[0026] A. Monomer DNA extraction of 6 species of booklice: Use 25 μL of STE lysate (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) to fully grind the monomers of 6 known species of booklice, and Add 0.3 μL of proteinase K (20 mg / mL) and incubate at 37°C for 40 min. Immediately after the incubation, place each mixture at 95°C for 5 min to denature proteinase K. After denaturation, the mixture was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 1 min, and the supernatant was the DNA template of the book lice, which could be stored at -20°C for a long time. The control of the above temperature can be operated in the PCR instrument.
[0027] B. Genomic DNA extraction of 6 kinds of booklice populations: Take about 10 mg of each known species of booklice and grind them thoroughly in liquid nitrogen; add 450 μL of STE extraction solution (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM EDTA, pH 8....
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: PCR system and procedure: Two sets of PCR amplification were carried out, one of which used the DNA of 6 individual booklices as a template, and the other set used the population DNA of 6 kinds of booklice as a template. One kind of booklice corresponds to one PCR reaction, and the volume of the reaction system is 25 μL. The specific order and dosage of the samples are shown in Table 1:
[0029] 10×PCR buffer
2.5 μL
10×PCR buffer
2.5 μL
Mg 2+ (25mmol / μL)
2 μL
Mg 2+ (25mmol / μL)
2 μL
dNTPs (10mmol / μL)
2 μL
dNTPs (10mmol / μL)
2 μL
A single booklice DNA
1 μL
DNA of a certain booklice population
1 μL
7 primers (10 pmol / μL)
1μL each
7 primers (10 pmol / μL)
1μL each
wxya 2 o
10.2 μL
wxya 2 o
10.2 μL
Taq (5U / μL, TaKaRa)
0.3 μL
Taq (5U / μL, TaKaRa)
0.3 μL
Total
25μL
Total
25...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: PCR products were detected by electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel, using 50 bp DNA Marker (TaKaRa) as a reference. The criteria for judging the species of booklice are: 300 bp for Booklice volata, 329 bp for Booklice entomophagia, 262 bp for Booklice microphthalmia, 145 bp for Booklice tricolor, 234 bp for Booklice Yunnan, and 450 bp for Booklice achromophora.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com