Method for dehydrating and conditioning sludge and preparing raw materials of slow-release fertilizer
A sludge dehydration and slow-release technology, which is applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, dehydration/drying/concentrated sludge treatment, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of unreached, secondary pollution of the environment, and large land occupation. Good effect, water content reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
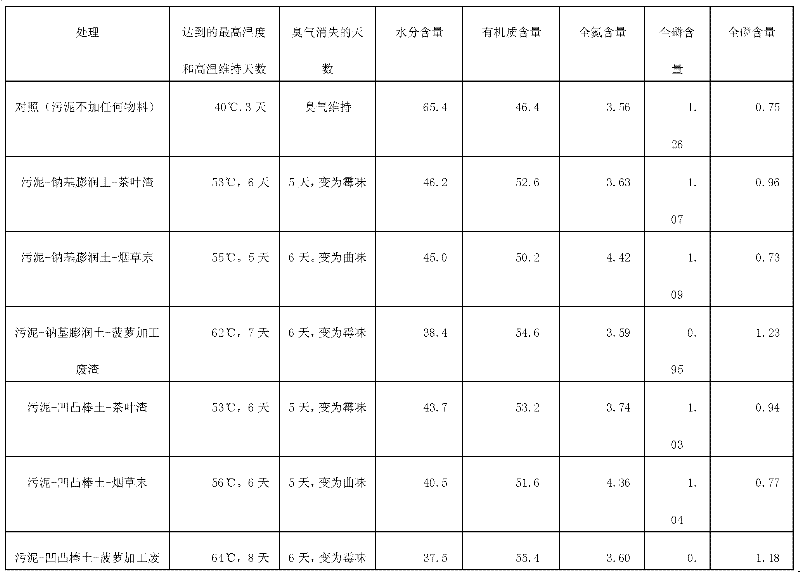
[0023] Sludge (with a water content of about 80%), water-absorbing clay minerals, and plant slag are mixed in a ratio of dry matter weight ratio of 1:0.3:1, and composted according to conventional aerobic composting methods, wherein water-absorbing clay minerals are respectively made of sodium-based bentonite and attapulgite Soil and plant dregs are respectively tea dregs, tobacco powder, and pineapple processing waste dregs. Measure the temperature of the heap during composting, and measure the moisture, organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content of the heap after 15-20 days of fermentation. The test results are shown in Table 1:
[0024] Table 1 Comparison of moisture and nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents after mixed fermentation of different materials
[0025]
[0026]
Embodiment 2
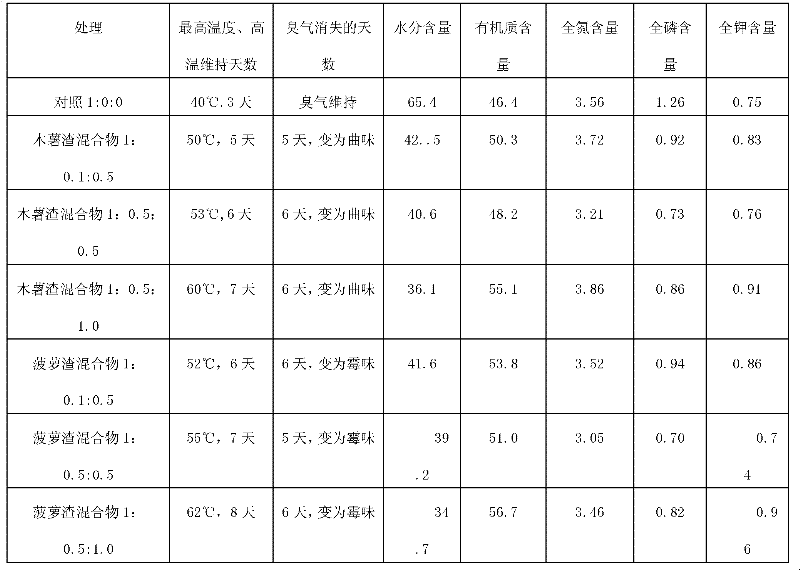
[0028] Sludge (about 80% water content), calcium-based bentonite, cassava residue or pineapple processing waste residue are mixed according to the ratio of dry matter weight ratio 1: 0.1-0.5: 0.5-1.0 (Table 2), and composted according to conventional aerobic composting methods. Measure the temperature of the heap during composting, and measure the moisture, organic matter, and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium contents of the heap after 15-20 days of fermentation. The test results show that mixing in the above proportions can achieve good results.
[0029] Table 2 Comparison of compost moisture and nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content in different mixing ratios
[0030]
Embodiment 3
[0032] Sludge (about 80% water content), water-absorbing clay minerals, and pineapple residue are mixed in a ratio of 1: 0.3: 1 by weight of dry matter. The ratio of dry matter weight to other materials) adding magnesium-containing alkaline substances, compounds or materials containing phosphate and ammonium ions, and water-absorbing polymer compounds for conditioning, after mixing, determine the content of moisture, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
[0033] Table 3 Effects of different conditioners on compost moisture and nutrients
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com