Distributed optical fiber vibration sensor
A technology of vibration sensor and distributed optical fiber, which is applied in the field of sensors, can solve the problems of not meeting the practical application of real-time detection, increasing the cost of signal detection circuit, and not being able to reproduce the action function, so as to achieve long-distance detection, compensation of polarization fading phenomenon, The effect of cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
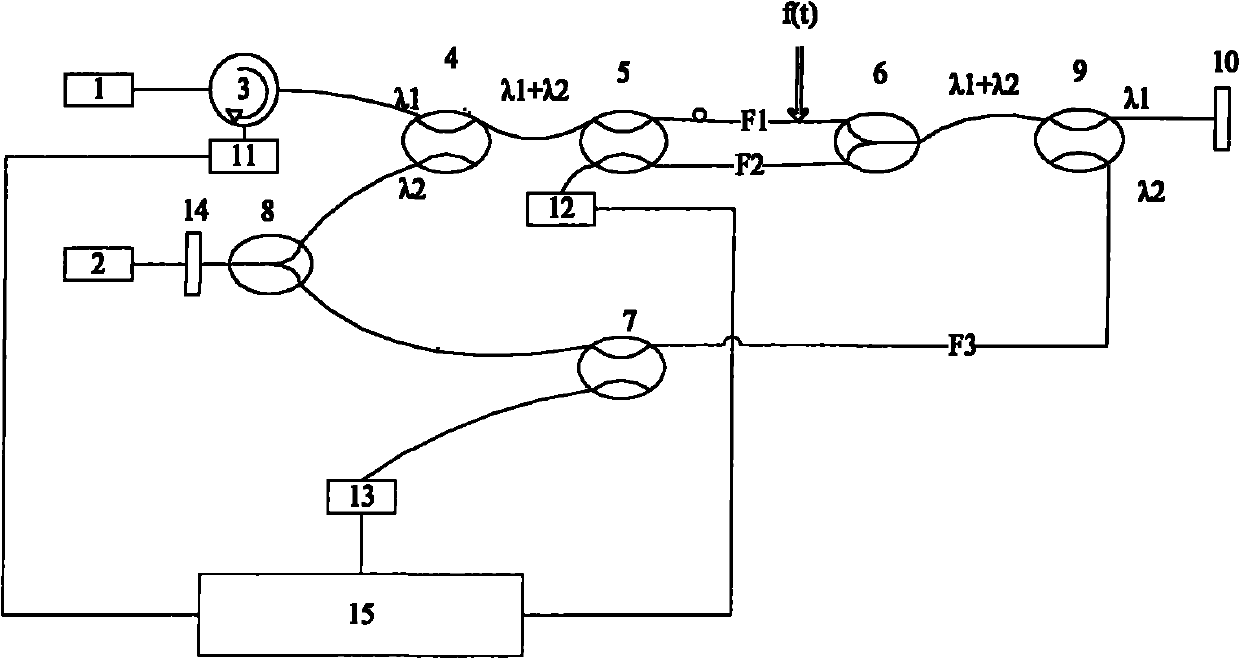
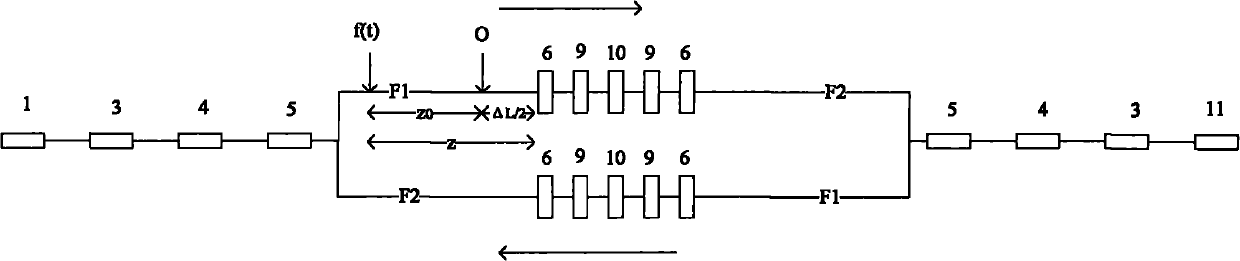
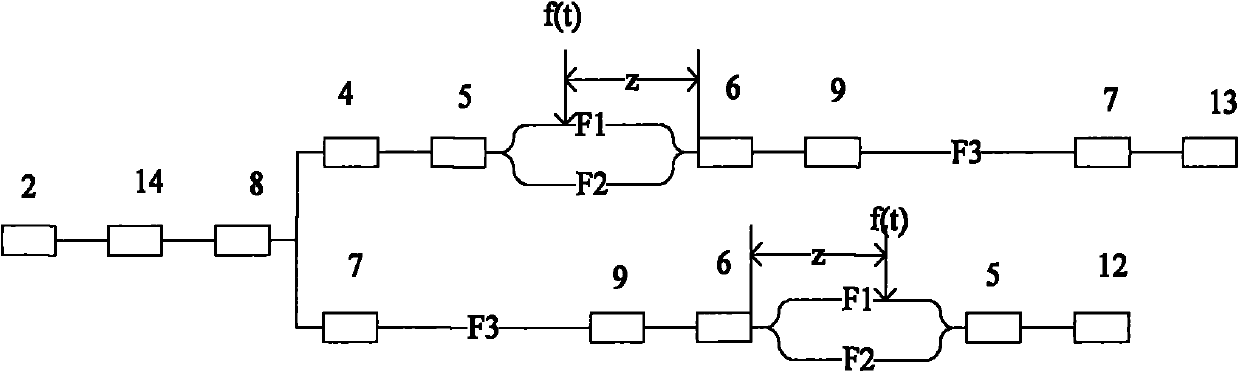
[0027] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the distributed optical fiber vibration sensor of the present invention. It can be seen from the figure that the distributed optical fiber vibration sensor of the present invention comprises a signal processing device 15, a first sensing optical fiber F1, a second sensing optical fiber F2, a third sensing optical fiber F3, a broadband light source 1, a narrowband light source 2, and an optical ring 3, the first optical wavelength division multiplexer 4, the second optical wavelength division multiplexer 9, the first coupler 5, the second coupler 6, the third coupler 7, the fourth coupler 8, the Faraday rotating mirror 10, The first photodetector 11, the second photodetector 12, the third photodetector 13 and the optical isolator 14; the connection relationship of the above-mentioned comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com