Stripping transfer method of substrate of thin film solar cell
A solar cell, stripping transfer technology, applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problems of limited use range, heavy weight of thin-film batteries, and unsatisfactory, and achieve a wide range of applications, light specific gravity, and high The effect of flatness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
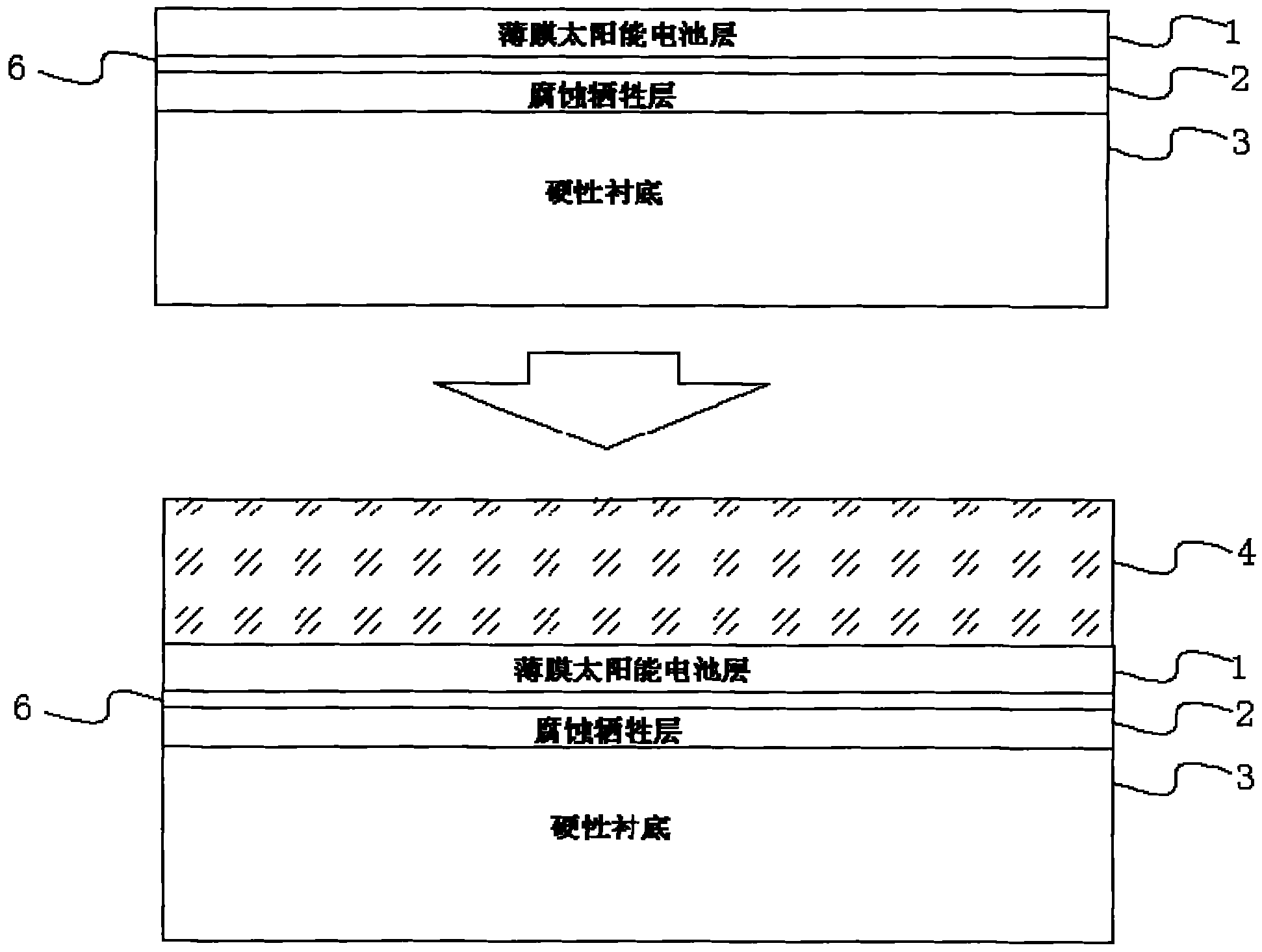
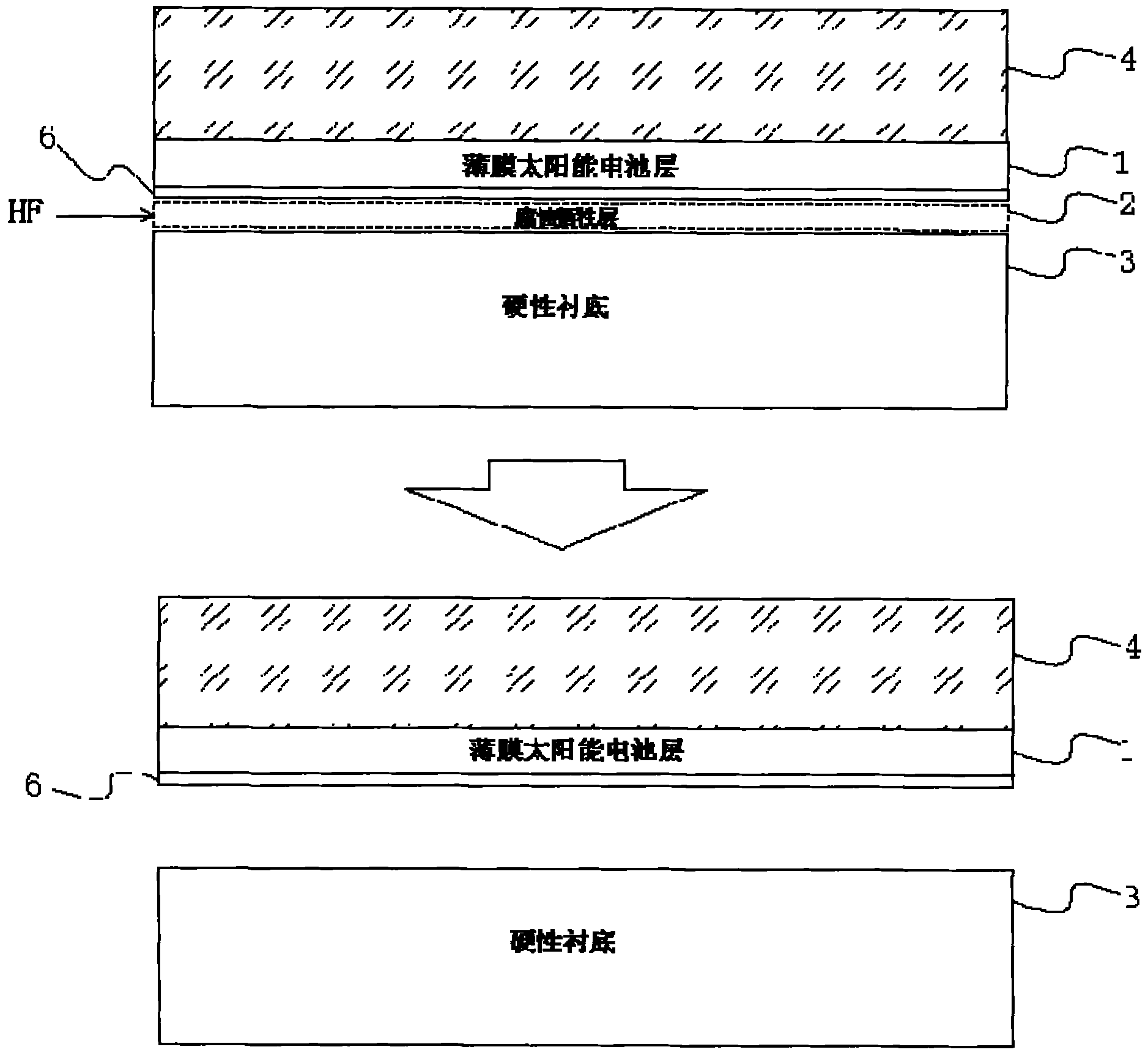
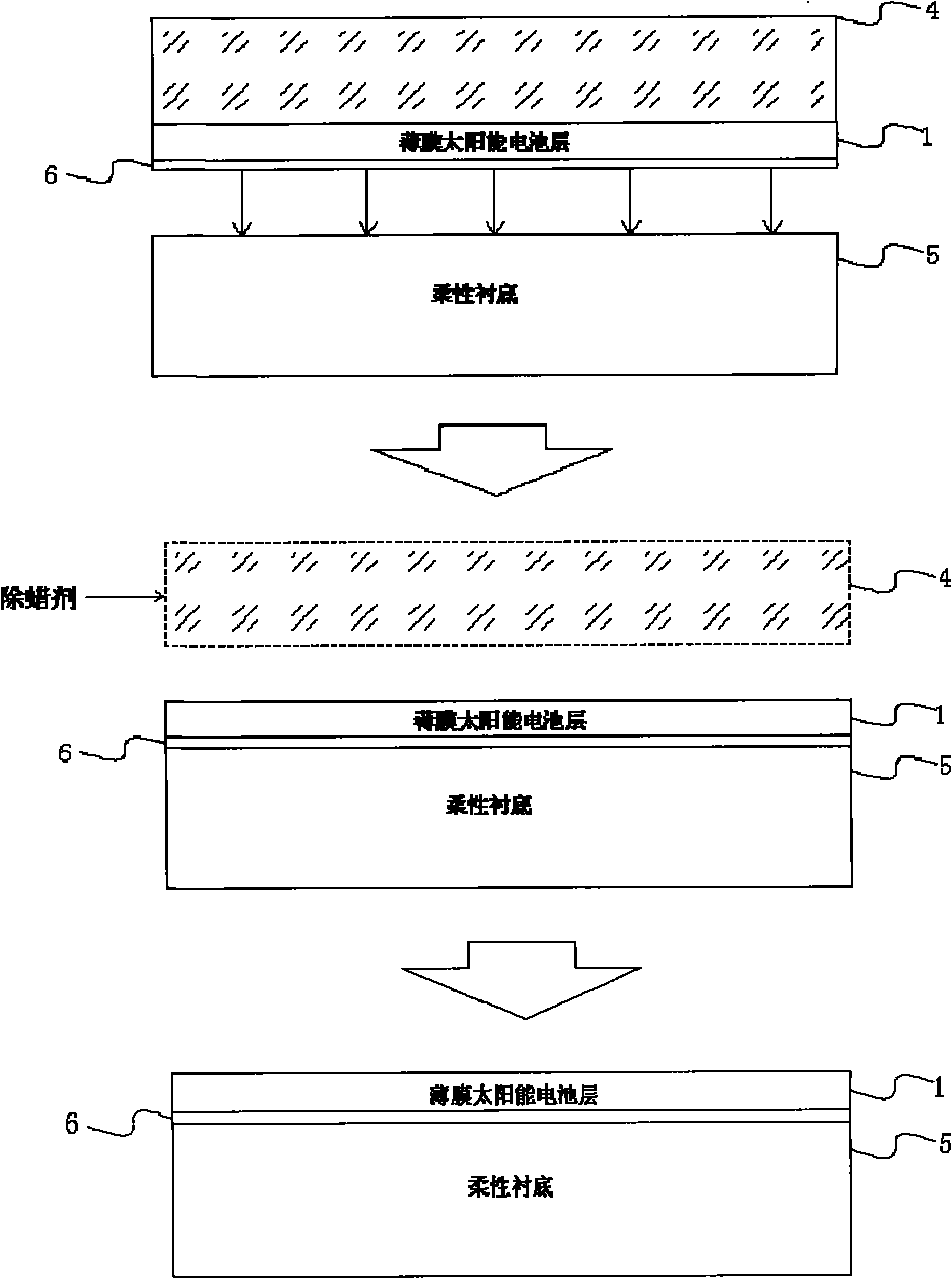
[0024] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 Shown, a kind of stripping transfer method of thin-film solar cell substrate, its concrete steps are as follows:
[0025] 1. Select a hard substrate 1. The commonly used hard substrate 1 is a GaAs substrate with a thickness between 300-500 μm. Its smoothness and hardness can ensure the high flatness and precision of the material layer deposited and grown on it.
[0026] The material aluminum arsenide (AlAs) is deposited and grown on the hard substrate 1 by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) or metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) to form a corrosion sacrificial layer 2 with a thickness of 0.5 μm. The corrosion sacrificial layer 2 is not a structure contained in the finished battery, but a material layer inserted for the realization of the subsequent lift-off transfer technology.
[0027] 2. Fabricat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com