Method for removing residual disinfectant left after disinfection by capturing with magnetic beads
A technology of disinfectant and magnetic beads, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms, can solve problems such as difficulty and complicated screening of neutralizers, and achieve the effect of simple method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
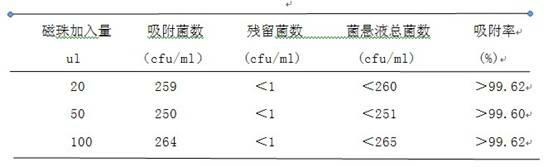
[0012] Example 1: This example compares the effects of different amounts of bare magnetic beads 1111# on the adsorption rate of Escherichia coli.
[0013] 1.1 Materials and reagents: including bare magnetic beads 1111#, indicator bacteria and magnetic frame.
[0014] Among them, the bare magnetic beads 1111# are provided by Hangzhou Bioer Technology Co., Ltd. The indicator bacteria was Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), provided by China Industrial Culture Collection Center. The magnetic frame is produced by British MATRIX company.
[0015] 1.2 Method
[0016] 1.2.1 Bacterial suspension preparation: Escherichia coli was isolated and cultivated, and a single typical colony was taken to inoculate the slant of nutrient agar medium. After cultivation, fresh slant culture cultured for 24 hours was taken, eluted with tryptone saline, and diluted into Bacteria content is 3×10 3 ~3×10 4 cfu / ml bacterial suspension.
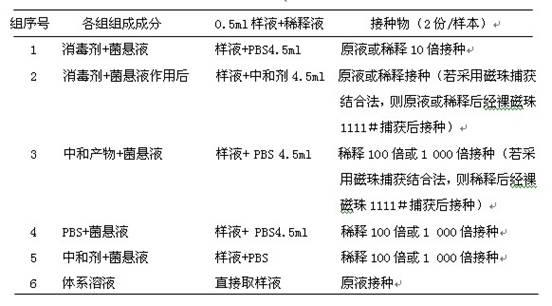
[0017] 1.2.2 Determination of the number of bacteria captured by ...
Embodiment 2
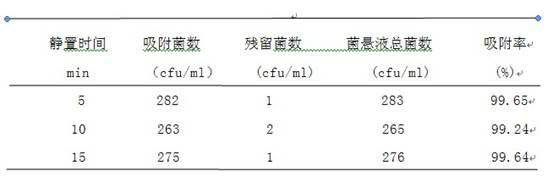
[0023] Embodiment 2: In this embodiment, the effects of the resting time before being put into the magnetic frame on the adsorption rate of Escherichia coli are compared.
[0024] 2.1 Materials and reagents
[0025] Bare magnetic beads 1111#: Provided by Hangzhou Bioer Technology Co., Ltd.
[0026] Indicator bacteria: Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), provided by China Industrial Culture Collection Center.
[0027] Magnetic frame: produced by British MATRIX company.
[0028] 2.2 Method
[0029] Determination of the number of bacteria captured by magnetic beads: Add 20 ul bare magnetic beads 1111# and 0.5 ml of the bacterial suspension prepared in 1.2.1 to a 2 ml sterile test tube, shake gently, let stand for 5 min, 10 min, 15 min, Shake gently while taking out intermittently. Take out the test tube and put it on the magnetic stand, let it stand for adsorption for 10 min, blot the liquid and place it on the blank plate A, and count it as the number of residual bacteria. Immed...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: In this embodiment, the influence of different resting times on the magnetic frame on the adsorption rate of Escherichia coli is compared.
[0036] 3.1 Materials and reagents
[0037] Bare magnetic beads 1111#: Provided by Hangzhou Bioer Technology Co., Ltd.
[0038] Indicator bacteria: Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), provided by China Industrial Culture Collection Center.
[0039] Magnetic frame: produced by British MATRIX company.
[0040] 3.2 Method
[0041] Determination of the number of bacteria captured by magnetic beads: add 20 ul bare magnetic beads 1111# to a 2 ml sterile test tube, and 0.5 ml of the bacterial suspension prepared in 1.2.1, shake gently, let stand for 10 minutes, and take out gently during the period shake. Take out the test tube and put it on the magnetic stand, let it stand for adsorption for 5min, 10min, and 15min, blot the liquid and place it on the blank plate A, and count as the number of residual bacteria. Immediately ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com