Casting moulding process for preparing large ship propeller from synthetic resin
A technology of marine propeller and synthetic resin, applied in the field of casting molding process, can solve the problems of difficult temperature and solidification height management, long production time, poor workability, etc., to shorten the production cycle, facilitate cooling, and avoid dimensional deviations Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
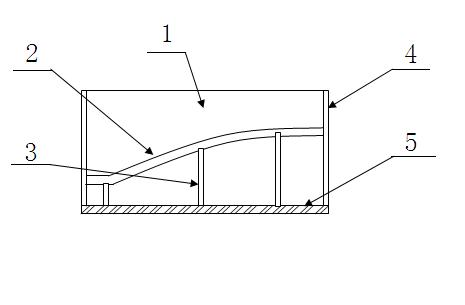
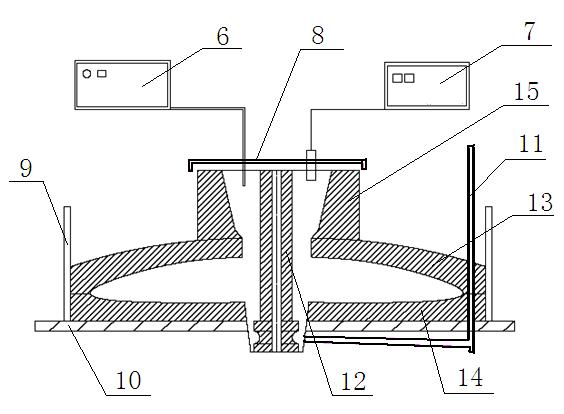
[0019] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention utilizes synthetic resin to make the casting molding process of large-scale marine propeller, comprises the following steps: A, make blade wooden cross-section by wood mold processing machine, then insert wooden mold into the shape of lattice, avoid force deformation, in The grid-shaped support is filled with resin sand, scraped evenly and waits for hardening. After making the shape of each blade in a core box 4, take the centerline on the matching platform 10 and the reference line of the blade shape 1 as Refer to to ensure accurate fit; B. Dry the shape. First, dry the unshaped paddle shape 1 naturally. The natural drying time is more than 24 hours. The drying temperature is between 100°C and 200°C, and the internal constant temperature is maintained until the interior is fully dry. The internal constant temperature is about 100°C, and the solution is poured at a high temperature to prevent defects caused...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com