Method for recovering nickel and magnesium elements from high-magnesium low-grade nickel sulfide ore
A nickel sulfide ore, low-grade technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of low leaching rate, environmental pollution, high energy consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
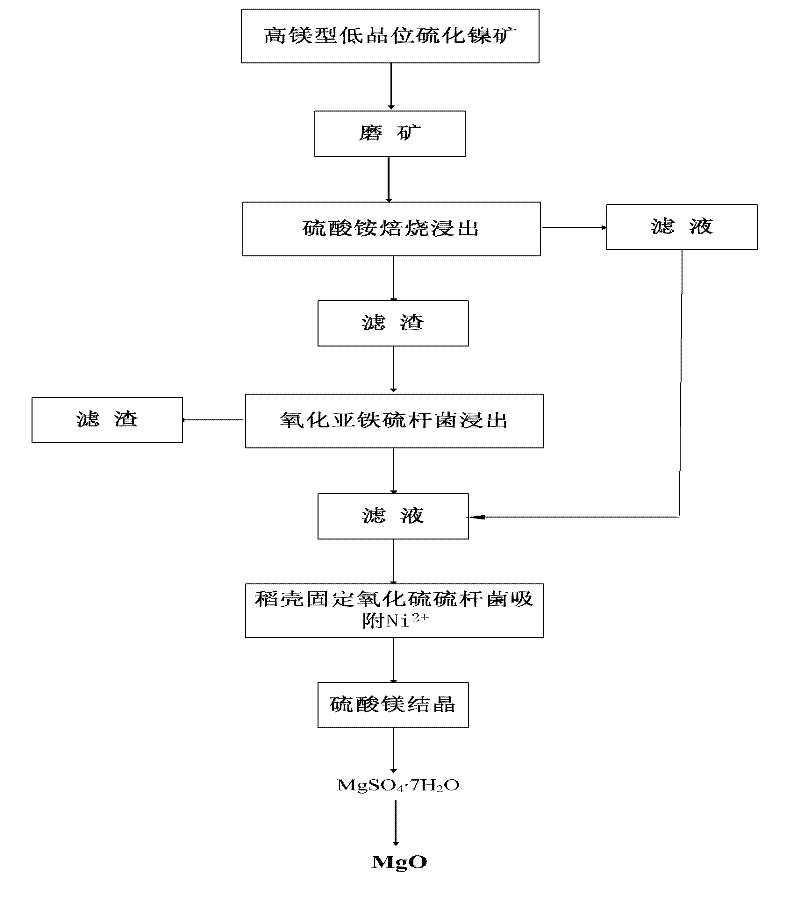
[0028] (1) Mix -200 mesh ore sample with ammonium sulfate in a ratio of 5:1, roast at 350°C for 1.5h, and then leaching with aqueous solution for 1h.
[0029] (2) Carry out solid-liquid separation of the infusion, and leaching the filter residue with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for 7 days. The leaching conditions are: solid-liquid ratio 1:10, temperature 30±2°C, inoculum size 15%, rotation speed 170rpm, pH value 2.2 . After two-stage leaching, the leaching rates of nickel and magnesium ions were 87.12% and 56.38%, respectively.
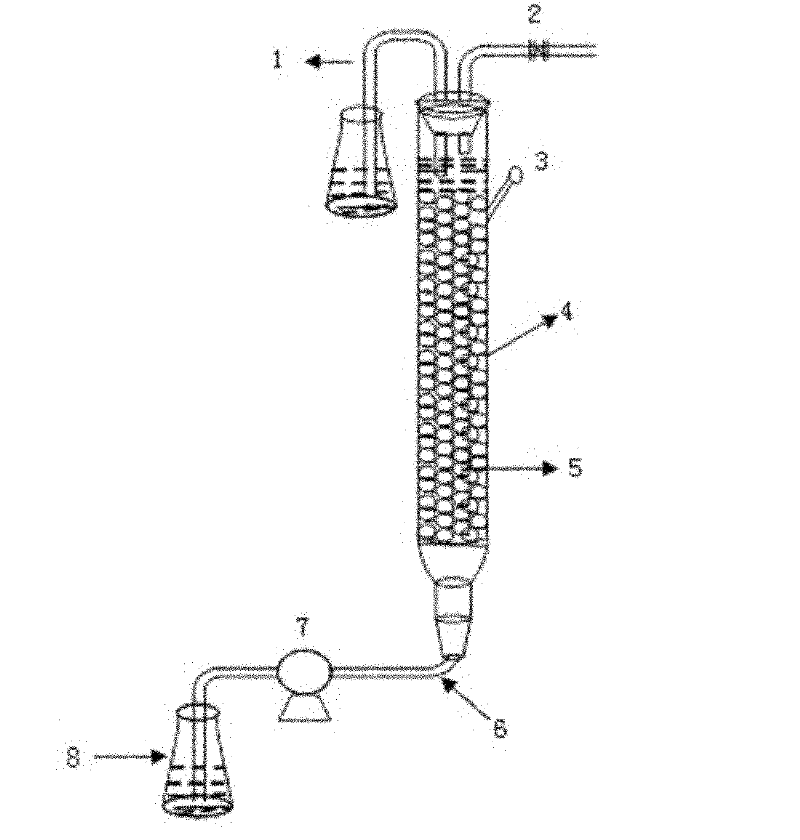
[0030] (3) Rice husks were filled into an upflow fixed-bed reactor to immobilize sulfate-reducing bacteria. The packing density is 0.05g / ml. at 6000mL·L -1 d -1 Pump the mixed leaching solution into the fixed-bed reactor at an injection rate of 2 h, and 73% of the nickel ions in the solution are adsorbed.
[0031] (4) Crystallize the solution obtained in the step (3), and control the crystallization temperature to 10°C to obtain magnesium sulfate h...
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) Mix -200 mesh ore sample with ammonium sulfate in a ratio of 5:2, roast at 400°C for 2 hours, and then leaching with aqueous solution for 2 hours.
[0035] (2) Carry out solid-liquid separation of the infusion, and leaching the filter residue with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for 10 days. The leaching conditions are: solid-liquid ratio 1:10, temperature 30±2°C, inoculum size 15%, rotation speed 170rpm, pH value 2.0 . After two-stage leaching, the leaching rates of nickel and magnesium ions were 90.37% and 60.54%, respectively.
[0036] (3) Rice husks were filled into an upflow fixed-bed reactor to immobilize sulfate-reducing bacteria. The packing density is 0.15g / ml. With 4800 mL·L -1 d -1 Pump the mixed leaching solution into the fixed-bed reactor at an injection rate of 4 h, and 87% of the nickel ions in the solution are adsorbed.
[0037] (4) Crystallize the solution obtained in the step (3), and control the crystallization temperature to 15° C. to obtain magne...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Mix the -200 mesh ore sample with ammonium sulfate in a ratio of 5:4, roast at 450°C for 3 hours, and then leaching with dilute sulfuric acid solution for 3 hours.
[0041] (2) Separation of solid and liquid from the immersion liquid, leaching the filter residue with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for 15 days, the leaching conditions are: solid-liquid ratio 1:20, temperature 30±2°C, inoculum size 15%, rotation speed 170rpm, pH value 1.8 . After two-stage leaching, the leaching rates of nickel and magnesium ions were 93.59% and 65.73%, respectively.
[0042] (3) Rice husks were filled into an upflow fixed-bed reactor to immobilize sulfate-reducing bacteria. The packing density is 0.1g / ml. at 3600mL·L -1 d -1 Pump the mixed leaching solution into the fixed-bed reactor at an injection rate of 8 hours, and 99% of the nickel ions in the solution are adsorbed.
[0043] (4) Crystallize the solution obtained in the step (3), and control the crystallization temperature to 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com