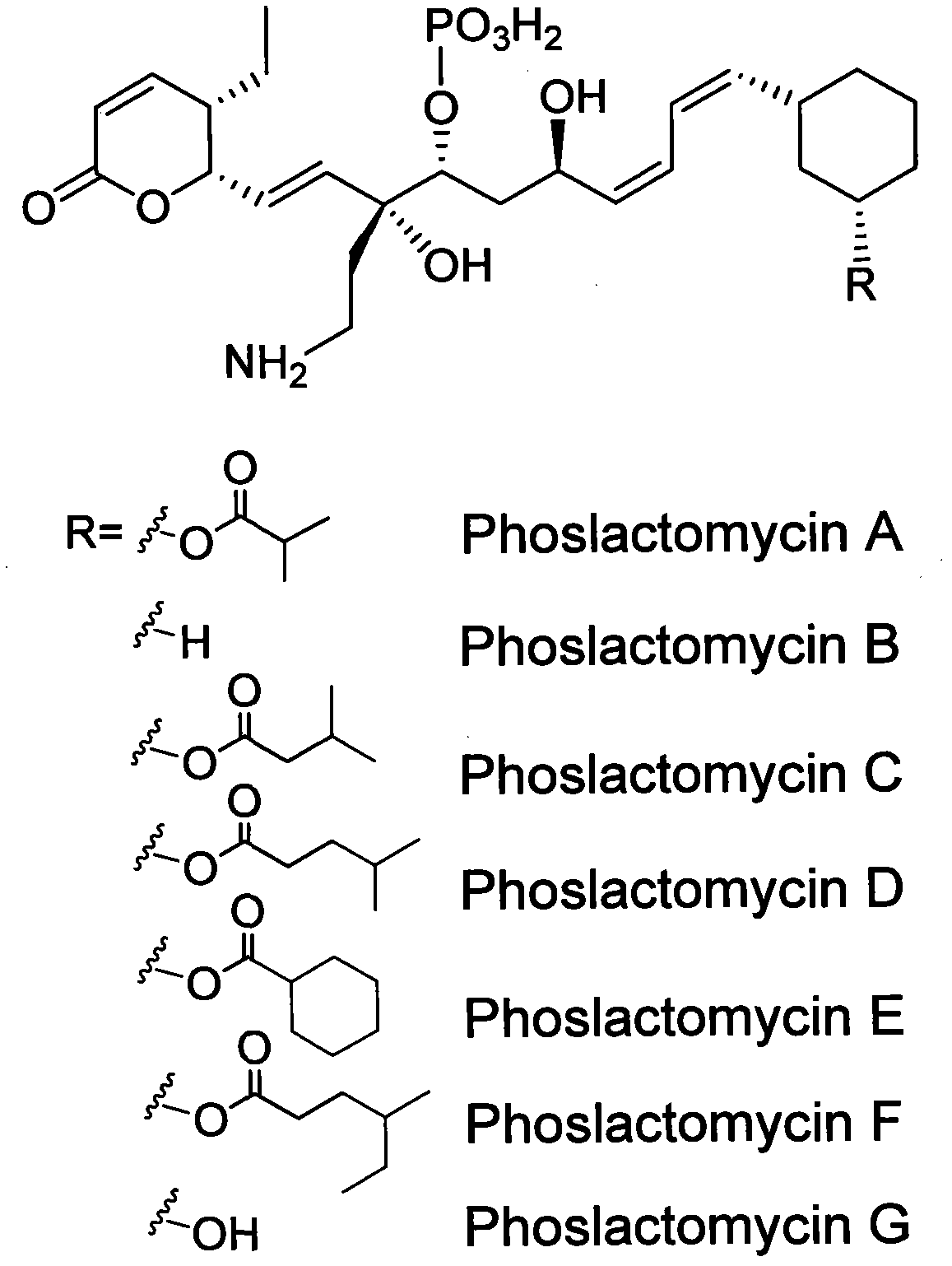
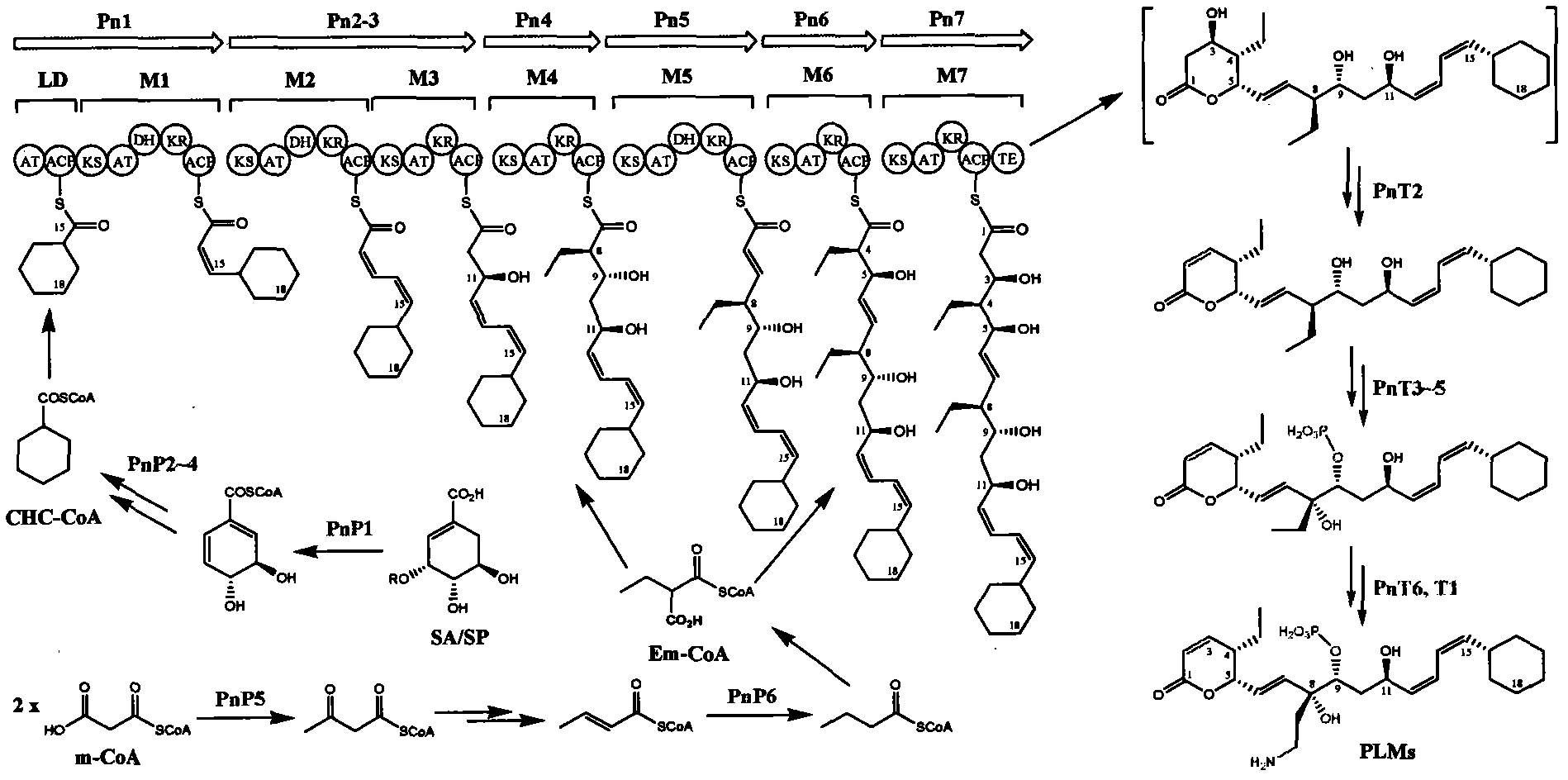
Biosynthetic gene cluster of phoslactomycins
A phosphazomycin biosynthesis technology, applied in the field of microbial genetic resources and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of complex synthetic routes, yield less than 3%, and low yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098]Extraction of the total DNA of the phosphazomycin-producing bacteria Streptomyces platensis SAM-0654:
[0099] Dispense 100 μL 1x10 8 Streptomyces platensis SAM-0654 spore suspension was inoculated into 3mL ISP-2 (yeast extract 0.4%, malt extract 1.0%, glucose 0.4%, pH 7.2) liquid medium, 30°C, 230rpm cultured for about 24hrs to reach logarithm In the late growth period, take 2 mL and inoculate it into 50 mL ISP-2 (containing 25 mM magnesium chloride), culture at 30°C, 250 rpm for about 23 hours, and then reach the early stage of the stable growth phase. Silk, washed with lysate, and collected 0.5 mL of light milky yellow mycelium. Add 10 mL of lysate (containing 5 mg / mL of lysozyme) to 1 mL of mycelium, a total of four tubes, vortex until uniform, and bathe in 37 ° C water for 15 min. Add 0.1mL proteinase K (10mg / mL, freshly prepared with lysate), 1mL 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate, mix well and quickly put it in a 70°C water bath for 15min, and it becomes clear. Cool o...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Establishment of the genetic transfer system of Streptomyces platensis SAM-0654, a phosphazomycin-producing bacterium:
[0102] Culture E.coli ET12567 containing appropriate plasmids to OD 600 0.4-0.6, the bacterial cells in 20mL LB culture medium were collected by centrifugation, washed twice with an equal volume of LB, resuspended in 2mL LB, and used as E. coli donor cells. Take 500 μL of 20% glycerol spore suspension of Streptomyces platensis SAM-0654 frozen at -80°C, and add an equal volume of TES (2-[(tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl)amino]-1-ethanesulfonic acid ) buffer (50 mM TES Na, pH 8.0), washed twice, resuspended in an equal volume of TES buffer, and heat-shocked at 50°C for 10 min to germinate the spores. Add an equal volume of TSB medium and incubate at 37°C for 2-5hr. Centrifuge and resuspend in 0.5-1 mL LB as Streptomyces recipient cells. Mix 100 μL of different concentrations of recipient cells with an equal volume of donor cells and spread directly on MS ...
Embodiment 3
[0104] The construction of the genomic library of Streptomyces platensis SAM-0654, a phosphazomycin-producing bacterium:
[0105] EPI300-T1 R Recovery of strains: the host strain EPI300-T1 provided in the kit R Take it out, smear or draw a line on an LB plate without any antibiotics, culture overnight at 37°C and store in a refrigerator at 4°C (preferably not more than one week). On the day before preparation for packaging, single clones were picked from the preserved plate and cultured overnight at 37°C in 50ml LB containing 10mM magnesium sulfate.
[0106] Preparation of insert fragments: The size of the insert fragments of the Fosmid DNA library is about 40kb, and its preparation can be achieved by repeatedly sucking and pushing out with a syringe or a small-hole straw (pipette). The number of times depends on the original size of the fragment. Generally, Check the effect by electrophoresis every 50 times until the fragment size meets the requirements (about 10% of the fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com