New energy-saving production process of ethyl acetate
A technology of ethyl acetate and a new process, which is applied in the field of new energy-saving production process of ethyl acetate, which can solve the problems of high energy consumption, limited production capacity, large reflux ratio of esterification tower and light removal tower, etc., and achieve the reduction of moisture content , Improve production capacity, reduce the effect of reflux ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
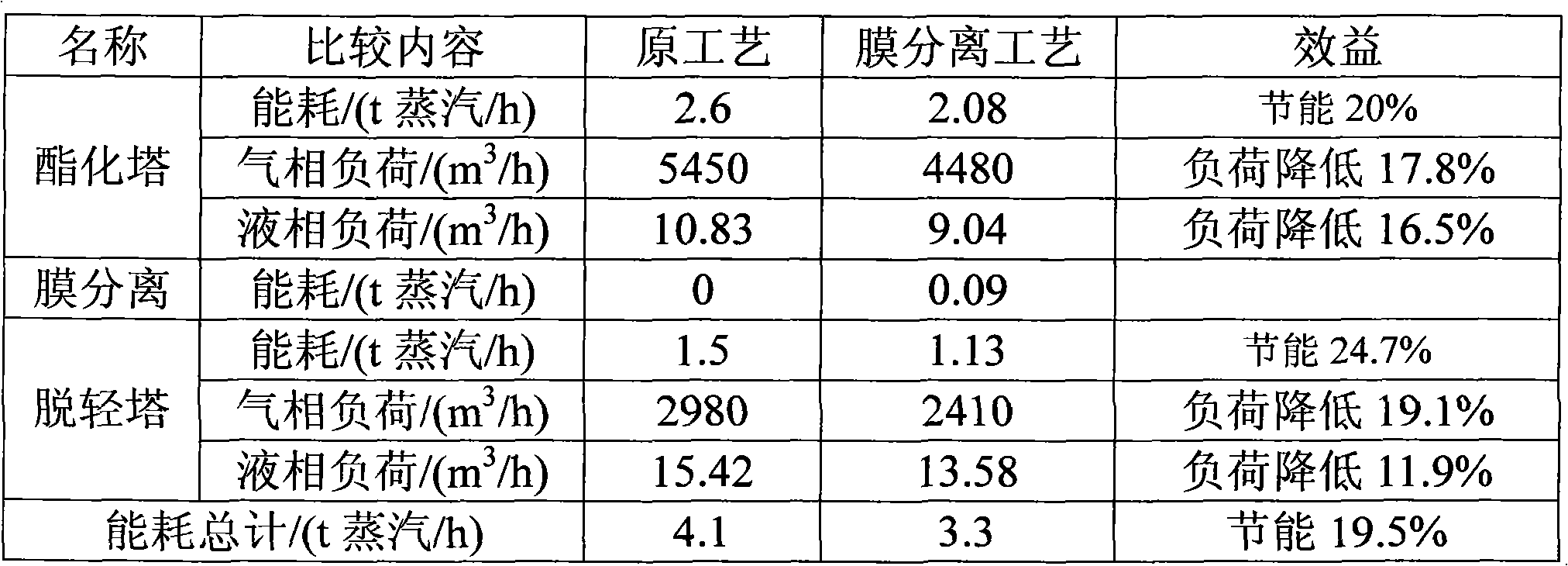
[0017] Taking a set of 15,000 t / a ethyl acetate plant as an example, PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) / PAN (polyacrylonitrile) composite membrane is used, and the temperature of the 2-esterified top organic phase entering the 5-vacuum hood is 45°C , the vacuum pressure is absolute pressure 200pa, the water content of crude ester is reduced from 5% to 0.95% after membrane separation and dehydration, compare the energy consumption and load of the esterification tower and light removal tower after the original process and this process, the results are shown in Table 1 (where the steam grade is pressure 0.8MPa, temperature 200°C).
[0018]
[0019] Table 1: Comparison of energy consumption and load between the membrane separation process and the original process
Embodiment 2
[0021] Taking a set of 15,000 t / a ethyl acetate plant as an example, using CS (chitosan) / PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone) composite membrane, the temperature at which the 2-esterification tower top organic phase enters the 5-vacuum hood is 41°C , the vacuum pressure is an absolute pressure of 300pa, and the water content of the crude ester is reduced from 5% to 1.03% after membrane separation and dehydration. The energy consumption and load of the esterification tower and the light removal tower are compared between the original process and this process, and the results are shown in Table 2 (where the steam grade is pressure 0.8MPa, temperature 200°C).
[0022]
[0023] Table 2: Comparison of energy consumption and load between the membrane separation process and the original process
Embodiment 3
[0025] Taking a set of 15,000 t / a ethyl acetate plant as an example, PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) / PAN (polyacrylonitrile) composite membrane is used, and the temperature of the 2-esterified top organic phase entering the 5-vacuum hood is 45°C , the vacuum pressure is 200pa absolute pressure, the moisture content of the crude ester after membrane separation and dehydration is reduced from 5% to 0.95%, increasing the production load of the esterification tower and light removal tower, comparing the original process with the esterification tower after adopting this process And the production capacity of the light removal tower and the unit consumption of steam, the results are shown in Table 3 (where the steam grade is 0.8MPa at pressure and 200°C at temperature).
[0026]
[0027] Table 3: Comparison of the production capacity and steam unit consumption of the membrane separation process and the original process.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com