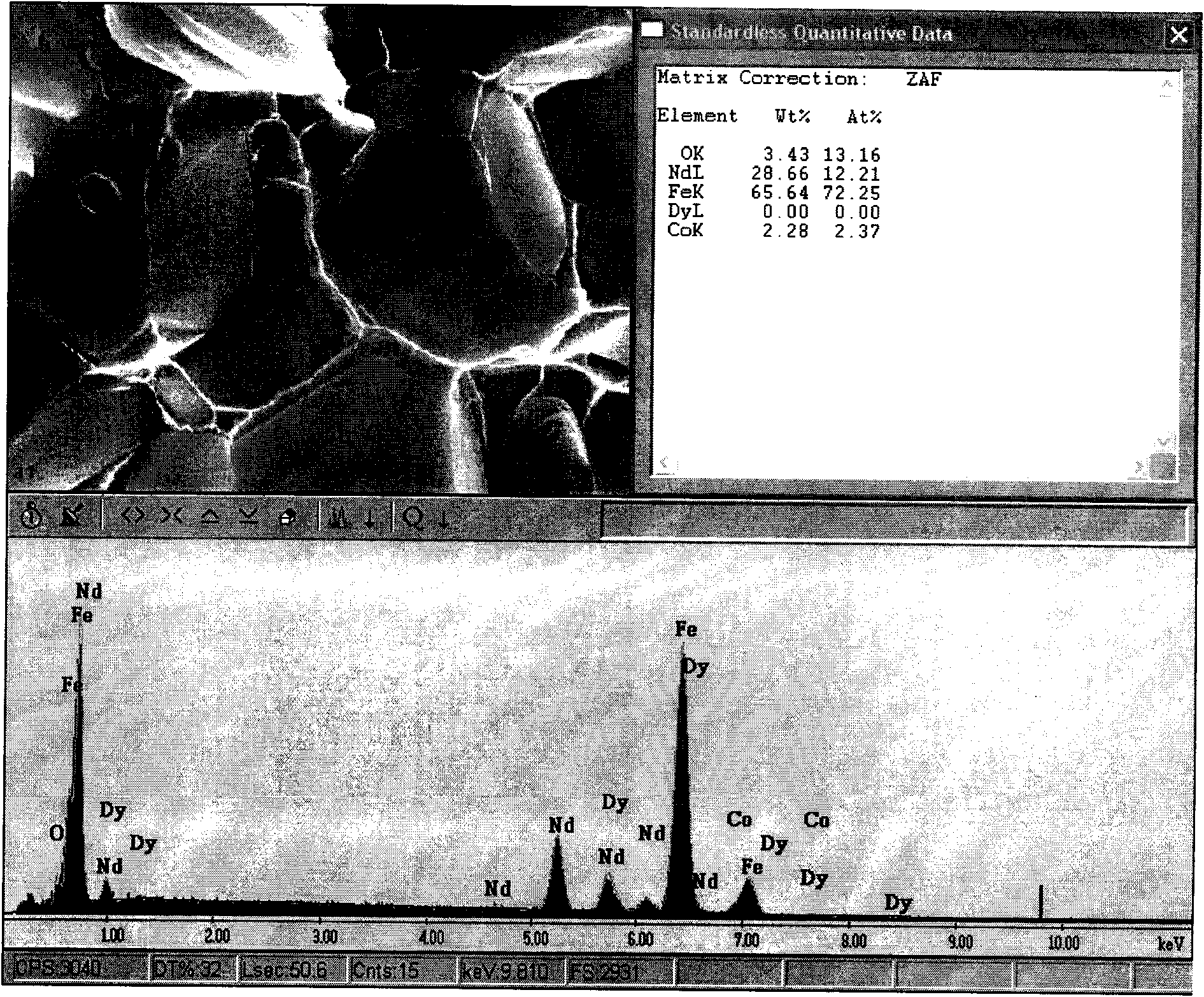
Method for improving coercive force of sintered neodymium ferrum boron (NdFeB)
A technology of NdFeB and coercive force, which is applied in the field of improving the coercive force of sintered NdFeB, can solve the problems of falling, not easy to break, and consume rare earth, so as to reduce the coercive force, promote sintering behavior, and improve sintering behavior Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The design composition is Nd 31 co 1.2 Cu 0.04 Fe bal B 0.96 The quick-setting sheet is the main phase alloy, and after hydrogen crushing, it is put into the jet mill for grinding, and the main phase alloy magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3.38 μm is obtained;
[0025] Put the rare earth Tb with a purity of 99.9 into the hydrogen furnace, absorb hydrogen and saturate it at 200°C under a hydrogen pressure of 300kpa, then take it out and send it to the jet mill for jet milling to obtain TbHx powder with an average particle size of 1.84 μm;
[0026] Put the two powders into the powder mixing machine for powder mixing, in which the TbHx powder accounts for 1.2% of the total mass of the mixed powder. After mixing evenly, press it under the protection of an inert gas, sinter at 1050 ° C for 2 hours, and then proceed to Secondary tempering heat treatment at 900°C and 500°C for 2 hours each;
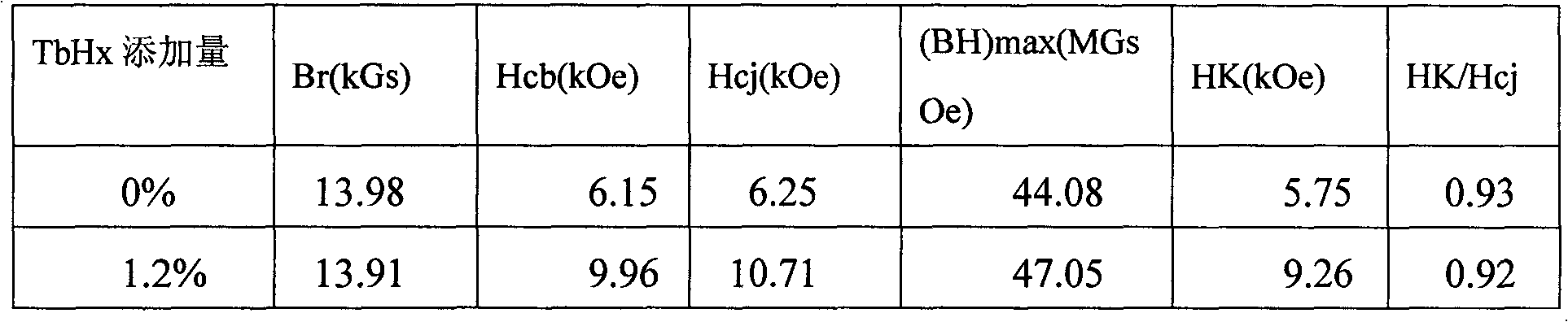
[0027] Table 1 shows the performance comparison between the sampl...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The design composition is Nd 31co 1.2 Cu 0.04 Fe bal B 0.96 The quick-setting sheet is the main phase alloy, and after hydrogen crushing, it is put into the jet mill for grinding, and the main phase alloy magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3.38 μm is obtained;
[0032] Put the rare earth Dy with a purity of 99.9 into the hydrogen furnace, absorb hydrogen and saturate it at 200°C under a hydrogen pressure of 300kpa, then take it out and send it to the jet mill for jet milling to obtain DyHx powder with an average particle size of 1.75 μm;
[0033] Put the two powders into the powder mixing machine for powder mixing, in which the DyHx powder accounts for 2% of the total mass of the mixed powder. After mixing evenly, press it under the protection of an inert gas, and sinter at 1050°C for 2 hours, and then proceed Secondary tempering heat treatment at 900°C and 500°C for 2 hours each;
[0034] The performance comparison of the sample processed into Φ10×10...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The design composition is Nd 31 co 1.2 Cu 0.04 Fe bal B 0.96 The quick-setting sheet is the main phase alloy, and after hydrogen crushing, it is put into the jet mill for grinding, and the main phase alloy magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3.38 μm is obtained;
[0040] Mix the rare earths Dy and Tb with a purity of 99.9 in a ratio of 2:3 and put them into a hydrogen furnace. After absorbing hydrogen and saturating them at 200°C and a hydrogen pressure of 300kpa, they are taken out and then sent to a jet mill for jet milling to obtain an average Mixed rare earth hydride powder with a particle size of 1.8 μm;
[0041] Put the two powders into a powder mixing machine for powder mixing, wherein the mixed rare earth hydride powder accounts for 1% of the total mass of the mixed powder, after mixing evenly, press it under the protection of an inert gas, and sinter at 1050 ° C for 2 hours. Then carry out secondary tempering heat treatment at 900°C and 500°C ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com