Method for treating biomass process residues
A treatment method and biomass technology, applied in the direction of solid waste removal, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as shortage, complicated post-treatment process, environmental pollution, etc., to avoid pollution, cumbersome post-treatment process, high social value effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
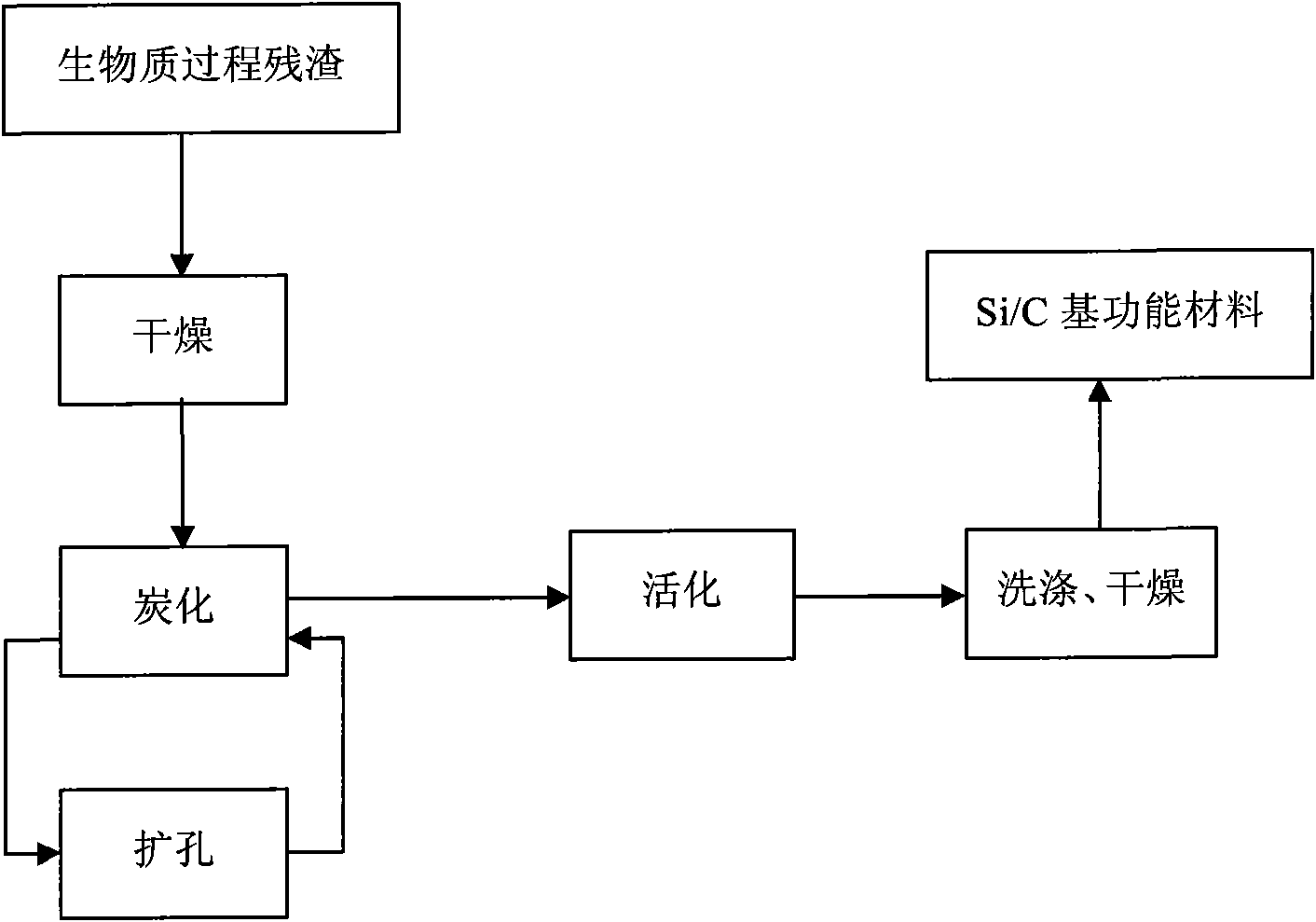
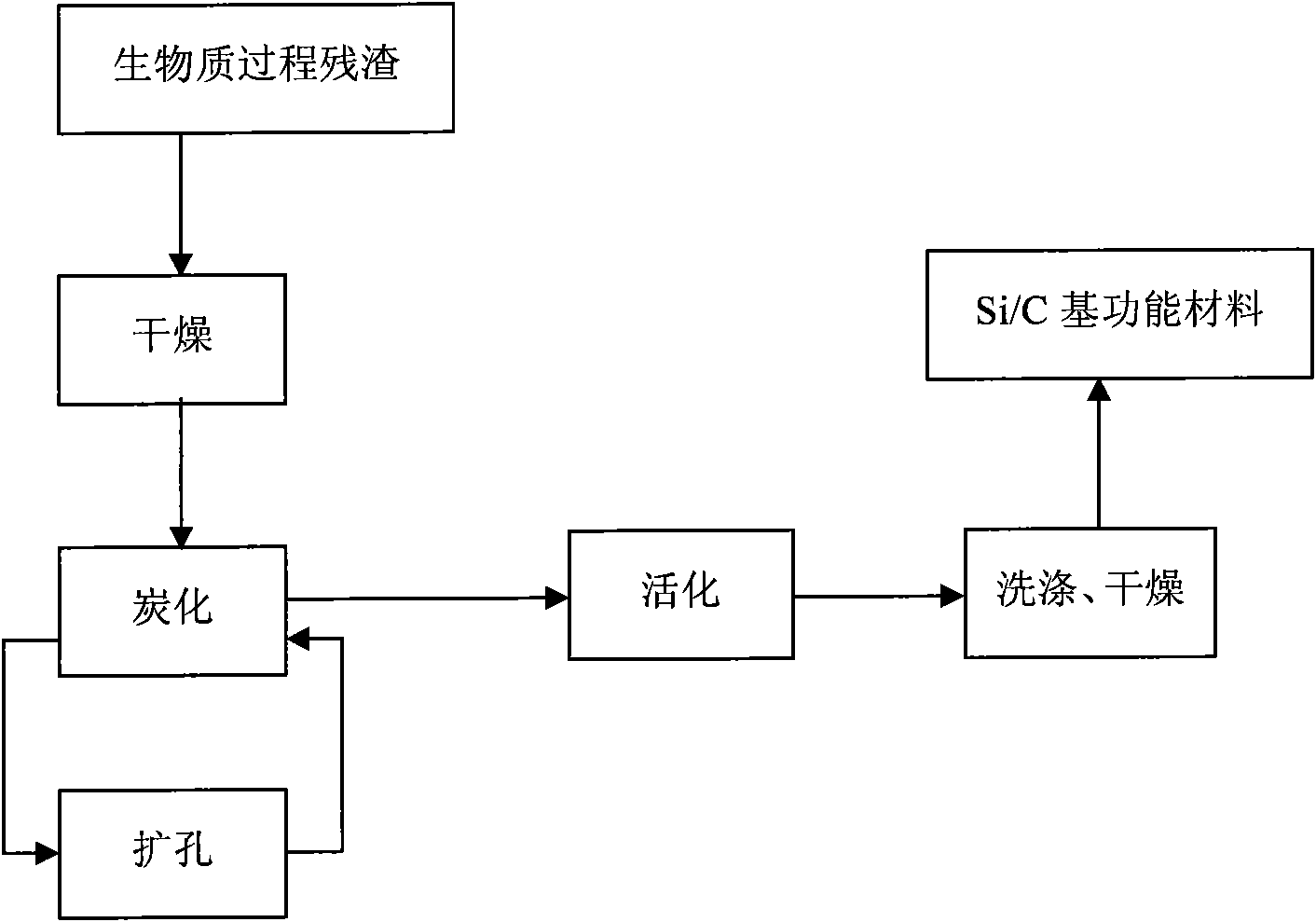
[0052] The dried vinegar grains 100g is placed in a fixed-bed carbonization furnace, and the gas velocity is 500ml / min of N 2 Under the atmosphere, the temperature was programmed to rise to 800°C within 1 hour, and kept for 1 hour to complete carbonization, then the temperature was raised to 875°C, and the reaction gas was switched to CO 2 , with a gas velocity of 500ml / min, activated for 3 hours, washed with deionized water, dried in a drying oven at 110°C, and prepared Si / C-based functional materials for about 2 hours, using nitrogen adsorption method, Autosorb-3B to compare the area The specific surface area measured by the tester is 460m 2 / g, the pore size is 0.8nm.
Embodiment 2
[0054] In this example, except that the activation time is 1 hour, other process conditions are the same as Example 1, and the specific surface area of the prepared Si / C-based functional material is 480m 2 / g, the pore size is 0.6nm.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Place 100 g of dried distiller's grains in a fixed-bed carbonization furnace under N 2 Under the atmosphere, the gas velocity was 500ml / min, the temperature was programmed to rise to 650°C within 1 hour, kept for 1 hour, and then cooled to room temperature. 5g of carbonized material is placed in the fluidized bed activation furnace, and the gas velocity is 0.15g / min H 2 Activated under O atmosphere for 1 hour, the Si / C-based functional material was prepared with a specific surface area of 349m 2 / g, the pore diameter is 3.97nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com