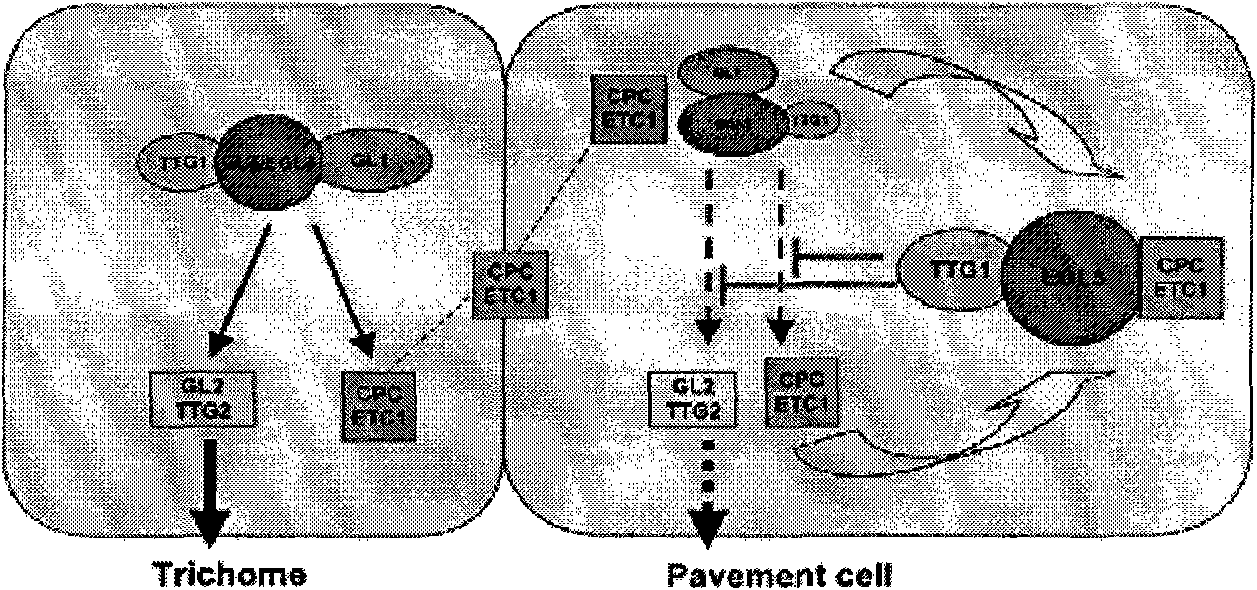
Cloning and application of key gene Wo for controlling tomato hair generation
A gene, tomato technology, applied in the field of cloning of the key gene Wo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
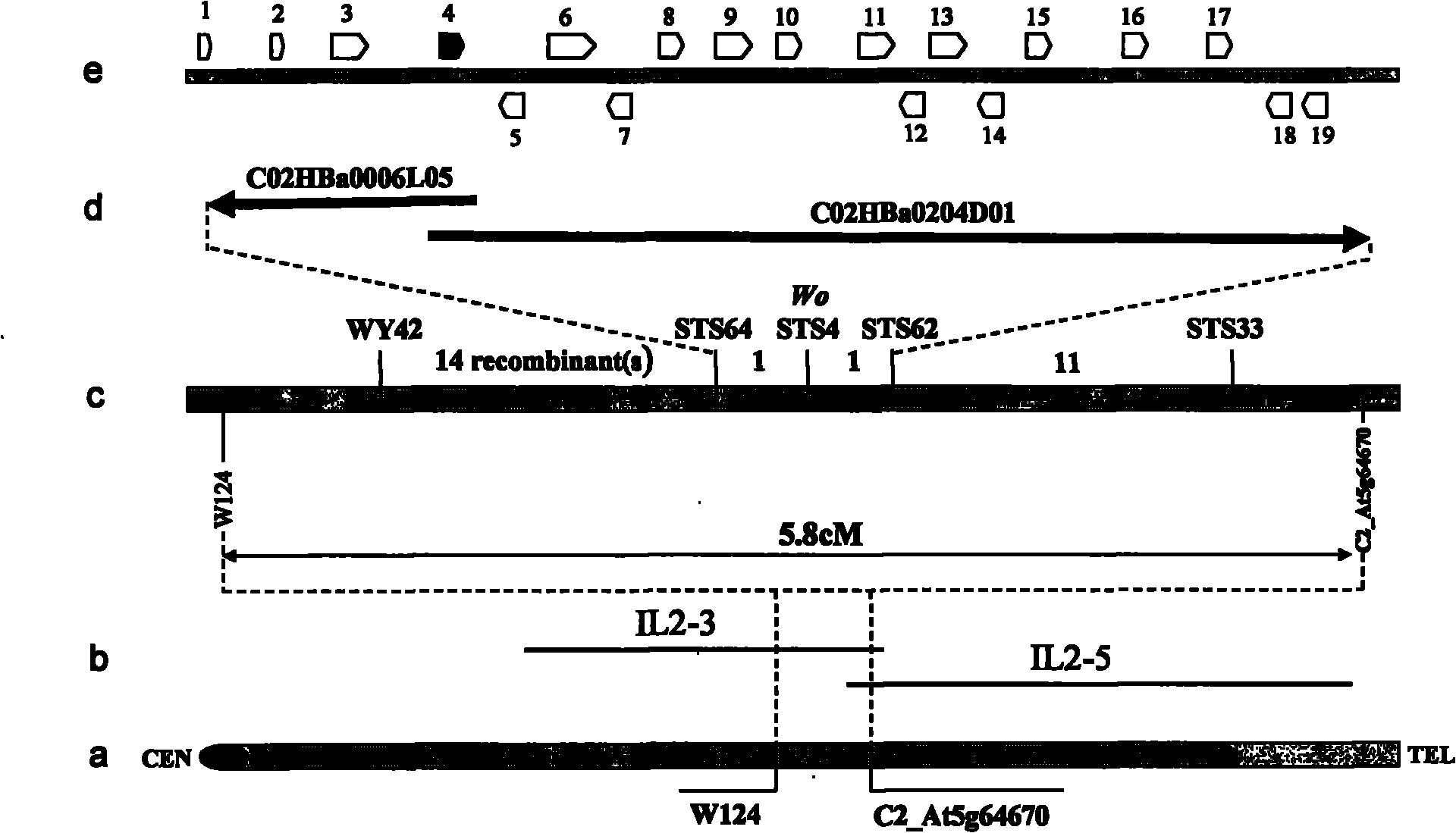
[0037] Embodiment 1: the precise location of Wo gene of the present invention
[0038] Through the analysis of the existing classic tomato genetic map Tomato-EXPEN 2000, Tomato-ILs and integrated map (see: Tanksley, 1992, http: / / sgn.cornell.edu / ), it is known that the tomato fuzz regulation gene (Woolly, Wo, the gene not cloned) in the interval where the introgressed fragments of IL2-3 and IL2-5 (cited from the Tomato Genetic Resource Center (TGRC), http: / / tgrc.ucdavis.edu / ) were located. In the present invention, the applicant first uses IL2-5 as the female parent and the hairy mutant LA3186 (quoted from the Tomato Genetic Resource Center of the United States, http: / / tgrc.ucdavis.edu / ) as the male parent for hybridization, and pulls out the F 1 Medium to less hairy plants, selfed more hairy plants and harvested F 2 Generation seeds, followed by sowing F 2 106 of the less-haired plants were randomly selected as the mapping population, using the reported molecular markers U23...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: Cloning and sequence analysis of Wo gene
[0049] According to the information of the candidate Wo gene, PCR primers capable of amplifying the full length of the gene were designed: forward primer: 5'-TTCAAGATGTTTAATAACCACCAGC-3', reverse primer: 5'-ACCTTTCATGCATTTGCGGAAGTTAC-3'. Genomic RNA was extracted from tomato leaves, and the RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using reverse transcriptase (purchased from TOYOBO Company) (refer to J. Society, 2002 version), the full-length gene product of Wo was obtained by PCR amplification, detected by 0.8% agarose gel, and the target fragment was recovered with a recovery kit (purchased from Axgen Company), and the pMD18-T vector (purchased from Baobio Engineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd.) cloning, take 5 μ L of the ligation product and carry out heat shock treatment, the specific method refers to J. Sambrook et al., translated by Huang Peitang et al., Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition), Science Press,...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Determination of the stage of embryo abortion in hairy mutant plants
[0053] The fuzzy mutant LA3186 has the characteristic of homozygous embryonic lethality, and the applicant used LA3186 as a material to observe its embryonic lethality period microscopically. The seeds in the tomato fruit from the 4th day to the 40th day after pollination were collected (tomato plants grow uniformly, and the third sedge was adopted) and were fixed, stained, dehydrated and other steps were taken to make paraffin sections (refer to Wang Zaoan, 1992 ), observed and counted the development of tomato embryos in each period after flower pollination, and found that the development of the embryos on the 7th day after pollination was not much different. , the embryonic stalk began to degrade, and the embryos showed obvious differentiation, and then gradually matured through globular embryos, torpedo-shaped embryos, and cotyledon-shaped embryos. However, the aborted embryos stagnat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com