Peer-to-peer communication in wireless sensor network through delay response between packets
A wireless sensor and network technology, applied in the wireless sensor network field of virtual communication, can solve the problems of energy loss, insufficient error control technology, VCDR packet loss, etc., and achieve the effect of saving power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention is shown as a peer-to-peer data communication technique for nodes in a wireless sensor network based on Virtual Communication via Delayed Response (VCDR). Two key advantages of VCDR are energy saving and data security.
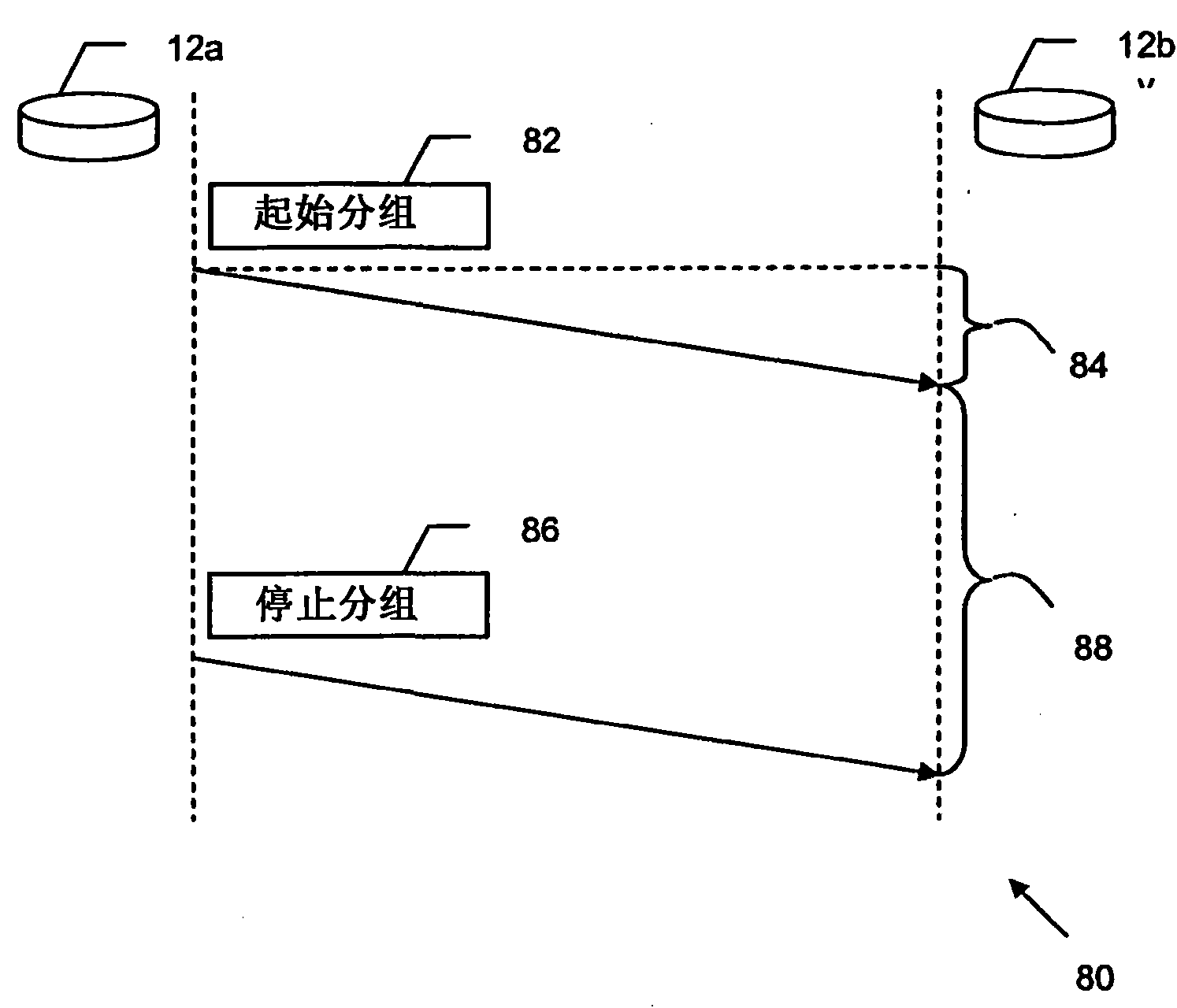
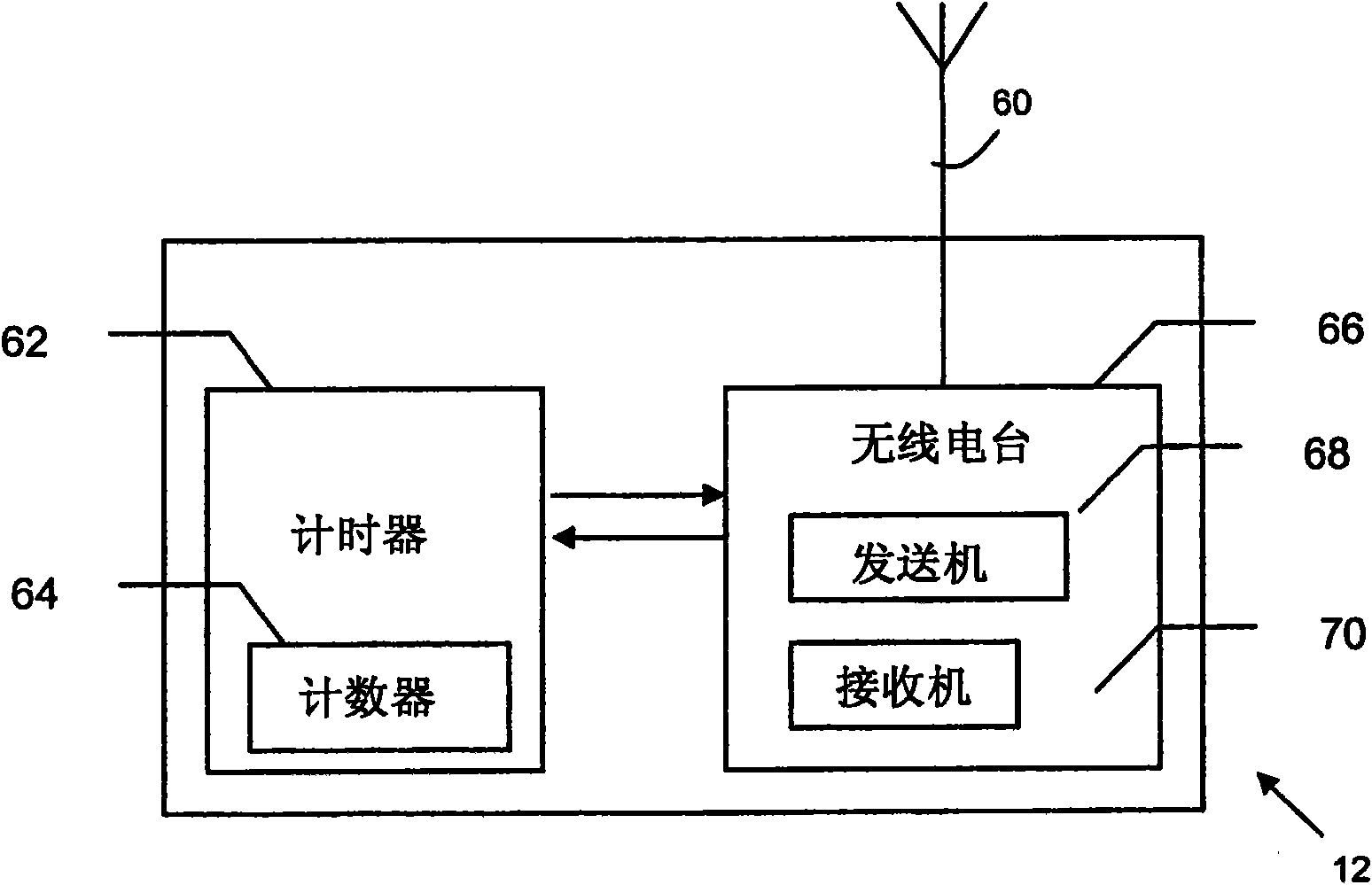
[0039] VCDR reduces energy consumption and improves data security by counting time at nodes instead of sending actual data. For a particular value n to be sent, the sender node initiates the data sending process by sending a start packet to the receiver node. Once the start packet is received, the receiver node activates the counter and starts counting the elapsed time. The counter fires every fixed period of time and each fired event represents a count. Therefore, the receiver node continuously counts from 1 to a finite number according to the elapsed time. The sender node operates its own counter in a similar way. Once the sender node has counted to the value n, the sender node sends a stop packet to the receiver node. Likew...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com