Antimony-rich Si-Sb-Te sulfur group compound phase-change material for phase change memory
A phase change memory, chalcogenide technology, applied in metal material coating process, ion implantation plating, coating and other directions, can solve the problem of low transition temperature, high current, and influence on the adhesion of phase change films to electrodes and other films. Additional problems, to achieve the effect of reducing write operation current, improving thermal stability, improving reliability and cycle times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
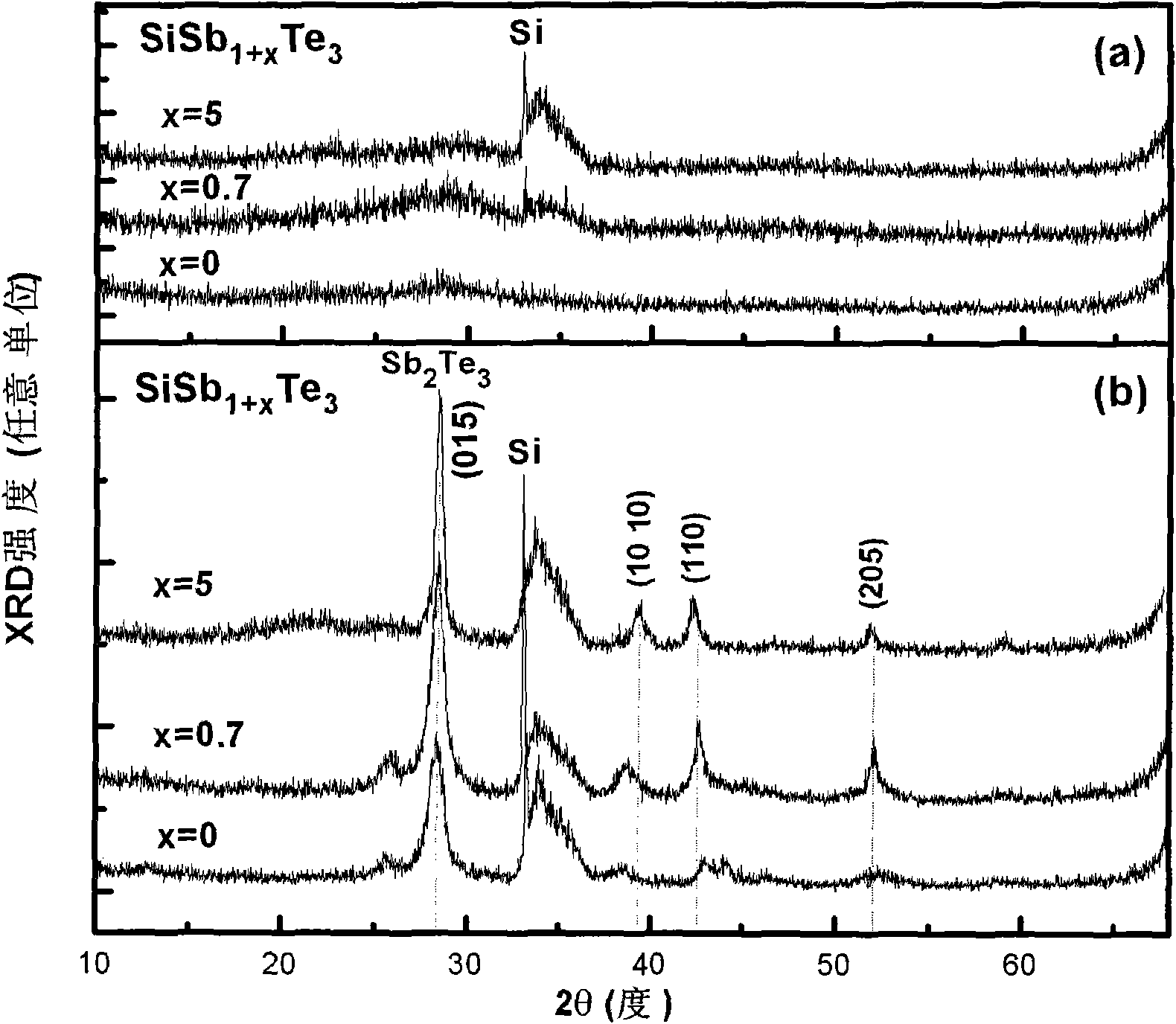
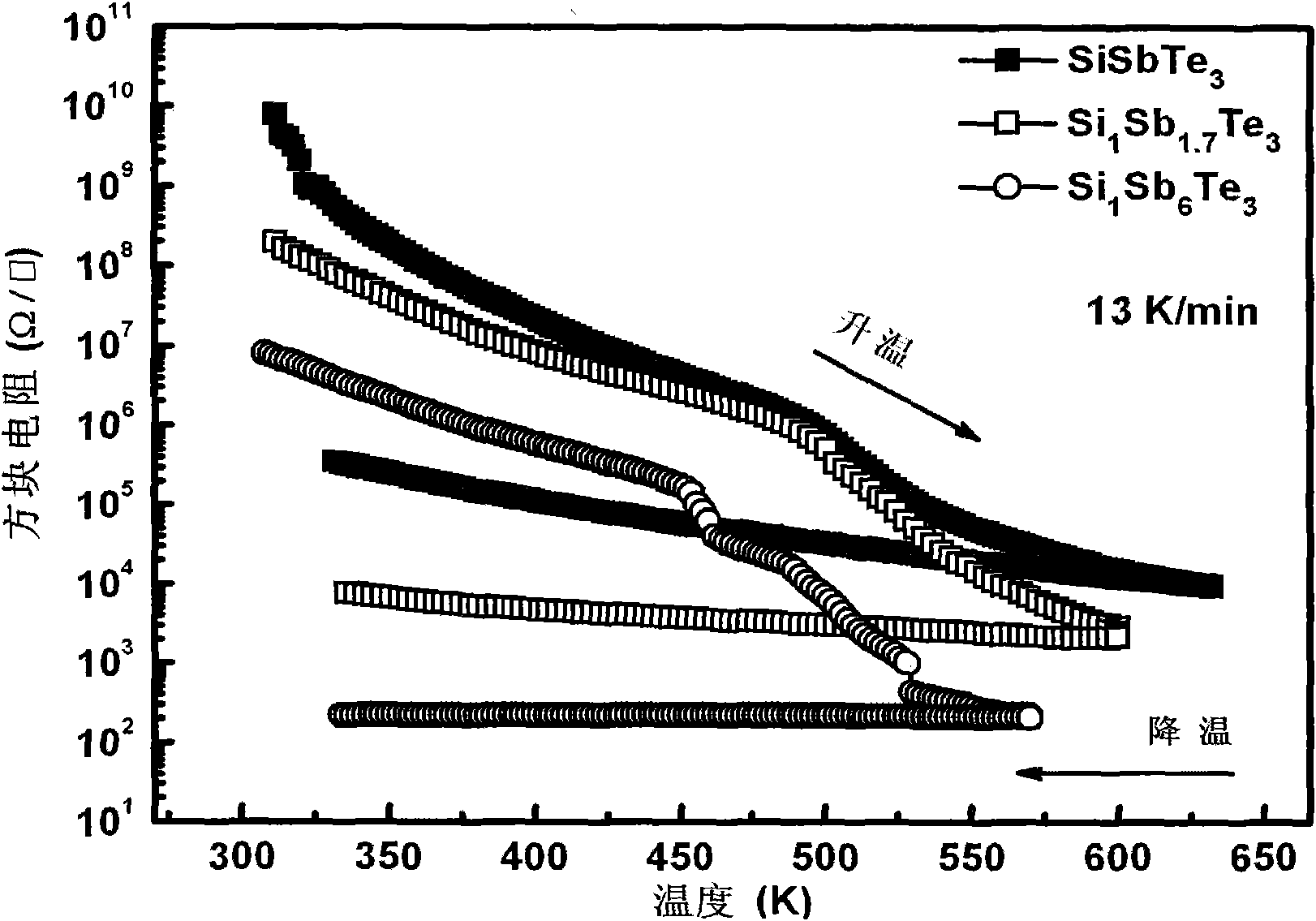
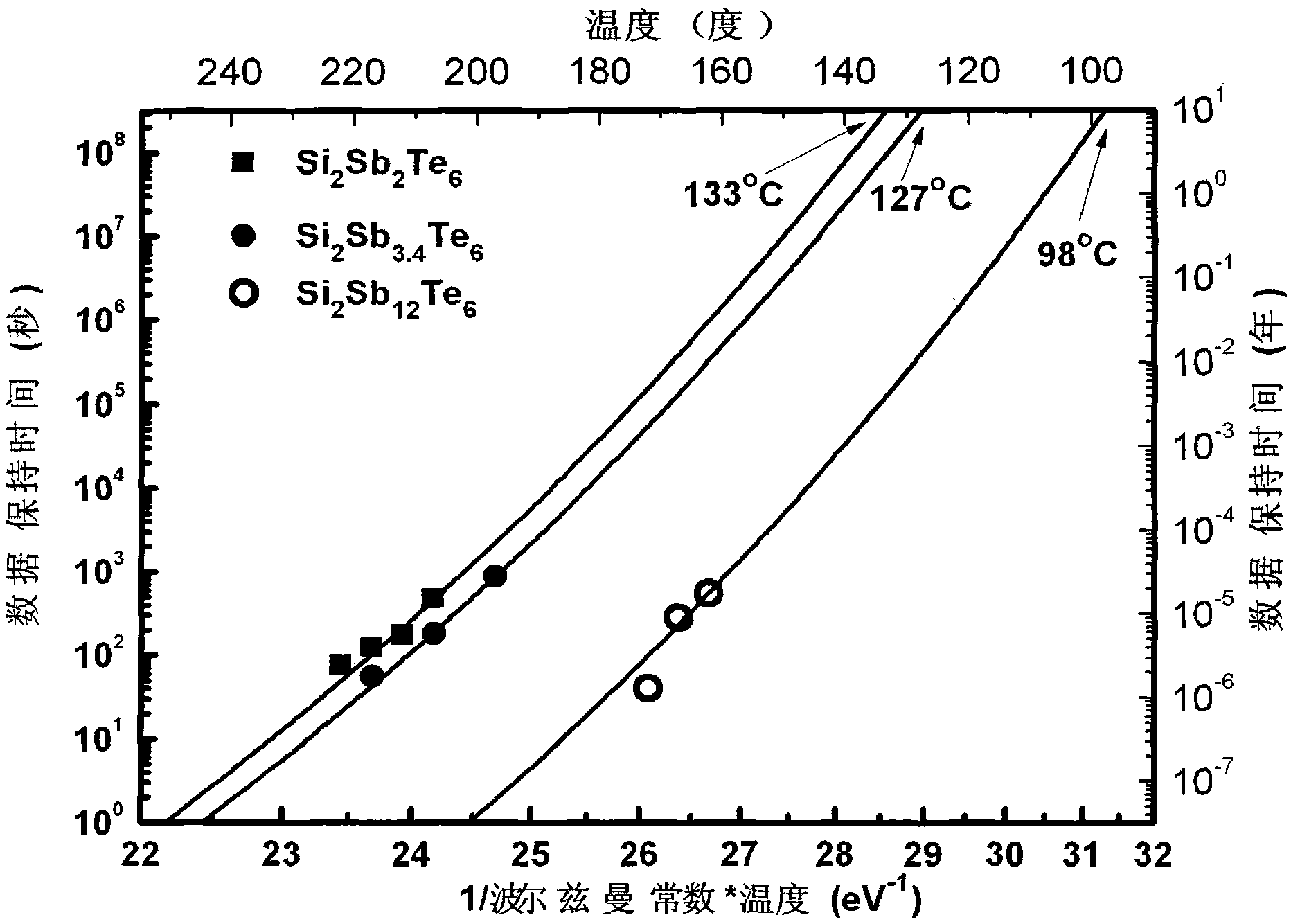
[0016] The antimony-rich Si-Sb-Te chalcogenide phase-change material for phase-change memory of the present invention has a component general formula of Si a Sb- (100-4a) Te 3a , where 10≤a≤20, which can be formed by various methods, for example, sputtering, electron beam evaporation, vapor deposition, atomic layer deposition, and the like. When sputtering is used, the various elements in the material (i.e. Si, Sb, and Te) can correspond to different targets, and the composition of the material can be controlled by applying different powers to each target, and the thickness of the material can be controlled. It can be controlled by adjusting the sputtering time; it is also possible to prepare a chalcogenide alloy target of the corresponding composition first, and then obtain a thin film of the corresponding composition by sputtering the alloy target, that is, to form a Si-Sb alloy target and a Te elemental target by co-sputtering , or formed by co-sputtering of Si-Te alloy t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com