Organophosphorus degrading enzyme mutants and coding genes and application thereof
A technology for degrading enzymes and organophosphorus, applied to mutants of organophosphorus-degrading enzymes and their encoding genes, applications in degrading organophosphorus pesticides, and the field of enzyme mutants, which can solve problems such as low degradation rate of sulfur and phosphorus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
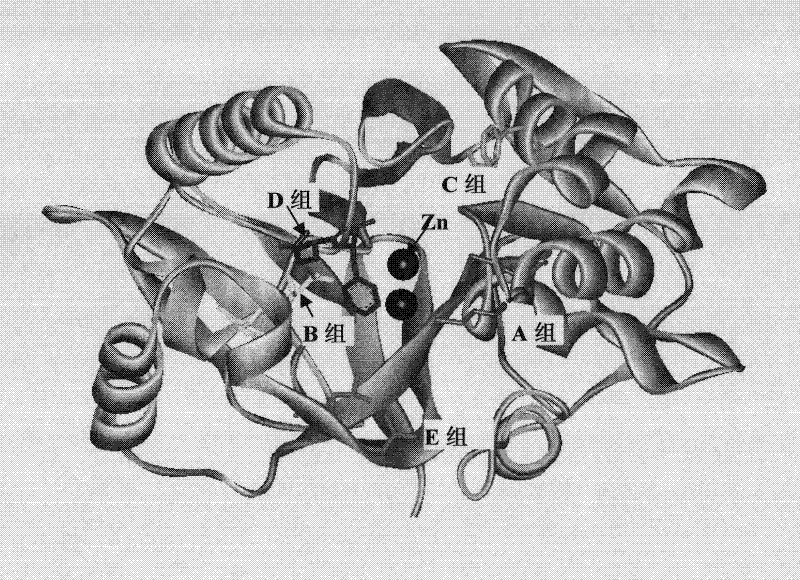
[0066] The first is to analyze the three-dimensional structure of the organophosphate degrading enzyme OPHC2 (the accession number in GenBank is AJ605330): using the published crystal structure of MPH derived from Pseudomonas sp.WBC-3 as a template, using Accelrys Discovery Studio software (Ver.2.5) The software constructs the three-dimensional structure of OPHC2 and determines the active center. The three-dimensional structure is as figure 1 . OPHC2 is a homodimer, belonging to a typical β / α (TIM) folding barrel structure, in which 8 folding structures constitute a barrel, which is the active center region of the enzyme, and contains two Zn in the middle. 2+ . According to the spatial structure characteristics of OPHC2, five mutation regions are designed in the pockets where the enzyme binds to the substrate near the active center. These mutations cannot affect the structure of the enzyme catalytic active center. To ensure that the selected amino acid pairs are close to each ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Obtaining mutant gene fragments
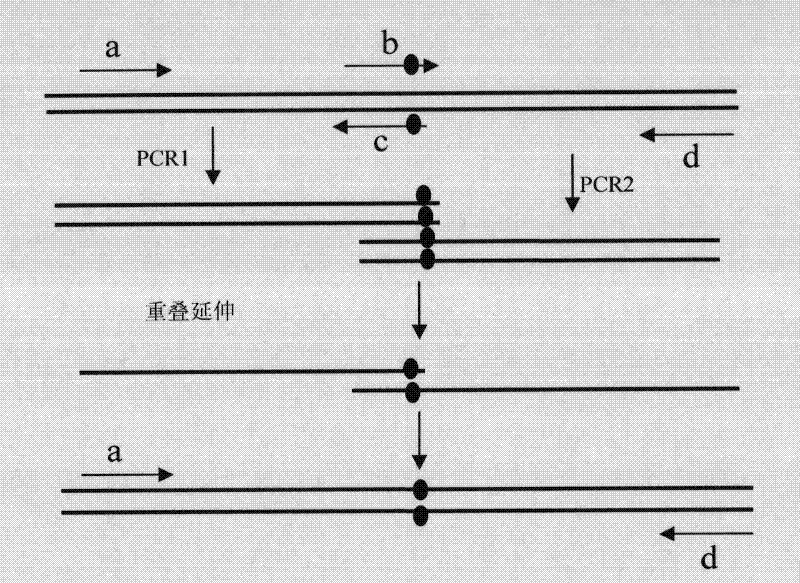
[0068] The overlap extension PCR technique is used. Design a pair of flanking primers (a and d) at both ends and five pairs of primers (b and c) containing the desired mutation sites, wherein the b primer contains the desired mutation site. The mutation site is a double-point saturation mutation. The middle primer of the amino acid pair to be mutated corresponds to 6 bases, and the base corresponding to each amino acid is replaced with nnk. The primer sequence is shown in Table 1. For each point mutation, two rounds of PCR were carried out. The first round of PCR used primers a and c to amplify the DNA fragments of the upstream sequence of the gene, while using primers b and d to amplify the DNA fragments containing the mutation site and its downstream sequence . Use an agarose gel to recover these two DNA fragments, and then mix the two PCR products. Because b and c have overlapping regions, the overlapping fragments anneal be...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 Construction of Saturation Mutant Library
[0077] Ligation: The PCR product recovered in Example 2 was directly digested with BamHI and HindIII and then ligated with the pUC19 vector treated with the same double digestion. The connection system was: pUC19 2μL, PCR product 6.5μL, T 4 Ligase 0.5μL, 10X reaction buffer 1μL, mix gently, and react at 16°C overnight. Each library does 5 connection systems.
[0078] Transformation: Freeze and thaw Top10 competent cells stored at -70°C on ice, add 50μL of competent cells to the above connection system, gently pipette to mix, and ice bath for 30 minutes. The ice-bathed system was accurately heat-shocked at 42°C for 90sec, and then immediately placed on ice for 2min, and 400μL of pre-cooled LB was added to equilibrate to room temperature, 200rpm, 37°C shaker and incubated for 1h. Add 4μL of 1mol / L IPTG and 40μL of 20mg / ml X-gal to mix, all the transformed bacteria solution is coated with LB (containing 100μg / mL, Amp) 23cm×...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com