Method for purifying carbon nanotube polluted water body
A carbon nanotube and water technology, which is applied in the fields of nanotechnology and environmental protection, and achieves the effects of easy elution and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
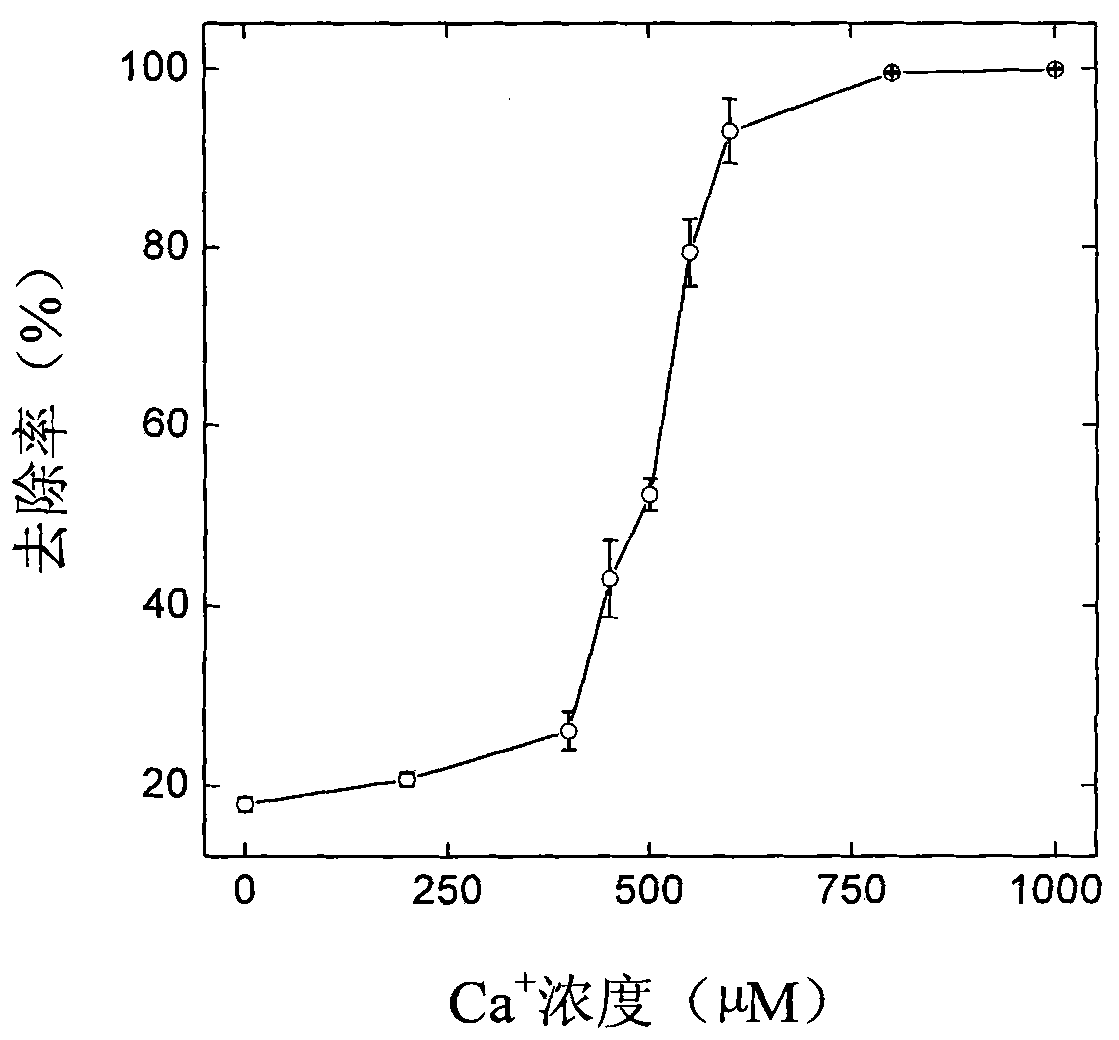
[0019] Removal of carbon nanotubes in water: 1.0mL-3.0mL of CaCl with a concentration of 2mg / mL and a pH value of 6.0 2 The aqueous solution is added to 1.0mL-3.0mL carbon nanotube aqueous solution with a concentration of 1.0mg / mL and a pH value of 6.0. After settling at room temperature for 1 hour, filter with filter paper. The removal rate of carbon nanotubes can be obtained by measuring the absorbance of the filtrate at 600 nm with a microplate reader. The filtrate is colorless, clear and transparent, indicating that the removal rate is very high ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
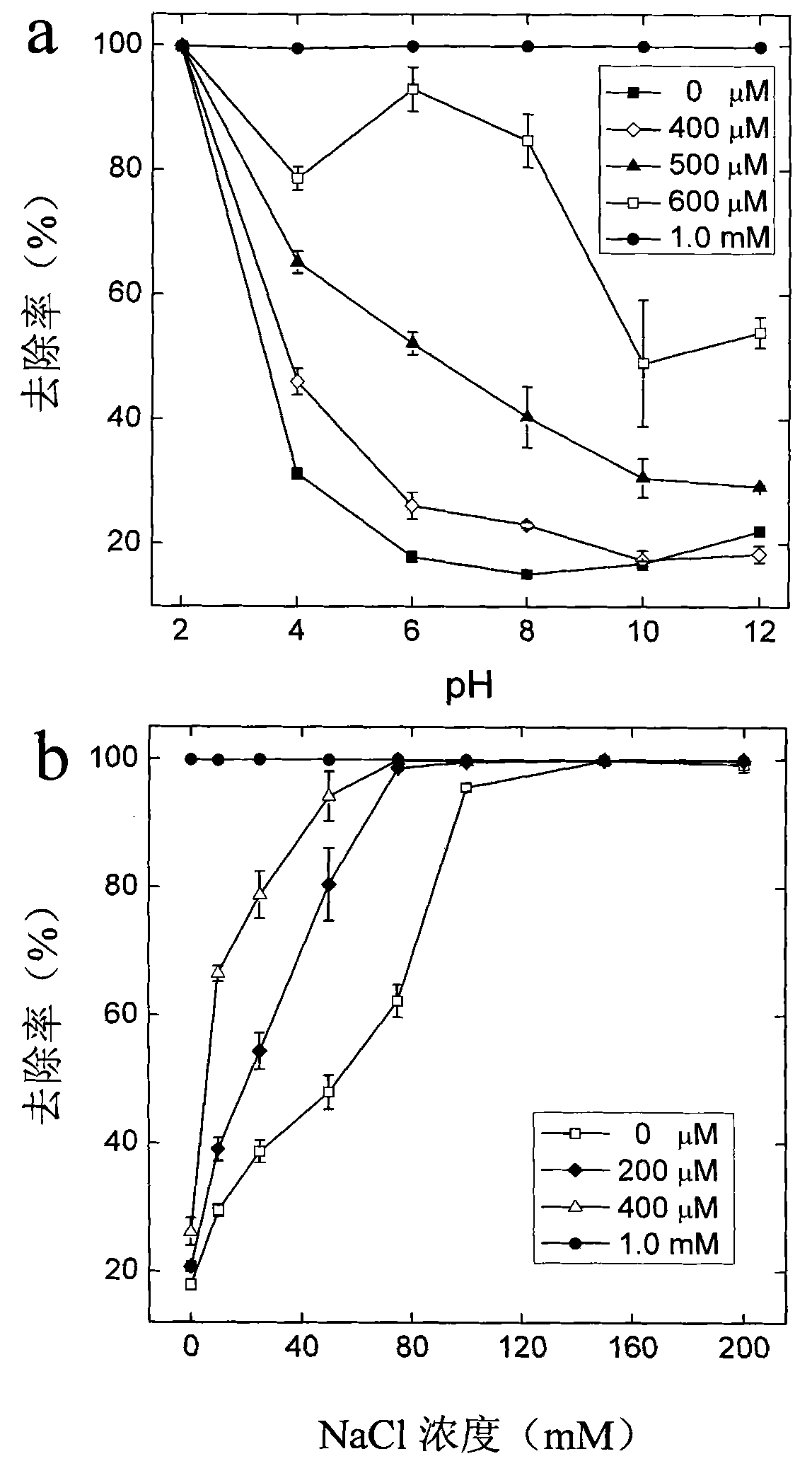
[0021] Removal of carbon nanotubes at different pH and ionic strength: 1.0 mL of CaCl with a concentration of 2 mg / mL and a pH value of 6.0 2 The aqueous solution was added to 1.0 mL of carbon nanotube aqueous solutions with a concentration of 1.0 mg / mL and different pH values. After settling at room temperature for 1 hour, filter with filter paper. The absorbance value of the filtrate at 600 nm was measured by a microplate reader, which was used to calculate the removal rate. The filtrate is colorless, clear and transparent.
[0022] 1.0 mL of CaCl with a concentration of 2 mg / mL and a pH of 6.0 2 The aqueous solution was added to 1.0 mL of carbon nanotube aqueous solutions with a concentration of 1.0 mg / mL, a pH value of 6.0, and different ionic strengths. After settling at room temperature for 1 hour, filter with filter paper. The absorbance value of the filtrate at 600 nm was measured by a microplate reader, which was used to calculate the removal rate. The filtrate w...
Embodiment 3
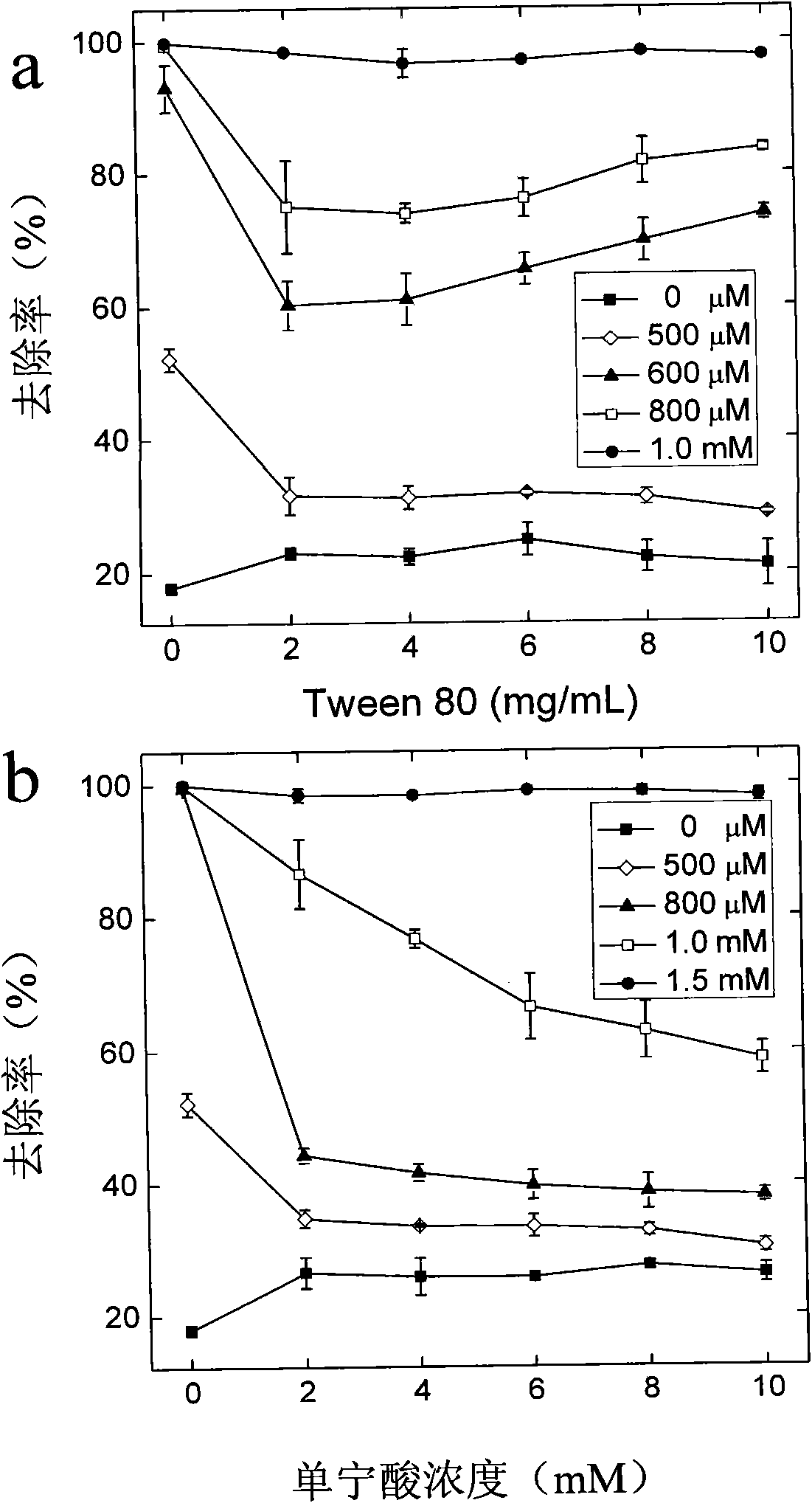
[0025] Removal of carbon nanotubes in the presence of surfactants and natural organic matter: 1.0 mL of CaCl with a concentration of 2 mg / mL and a pH value of 6.0 2 The aqueous solution was added to 1.0 mL of carbon nanotube aqueous solutions with a concentration of 1.0 mg / mL, a pH value of 6.0, and different concentrations of surfactants (or natural organic matter). After settling at room temperature for 1 hour, filter with filter paper. The absorbance value of the filtrate at 600 nm was measured by a microplate reader, which was used to calculate the removal rate. The filtrate is colorless, clear and transparent. Present embodiment illustrates that there is surfactant and natural organic matter in the polluted system and basically influences the effect of this method ( image 3 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com