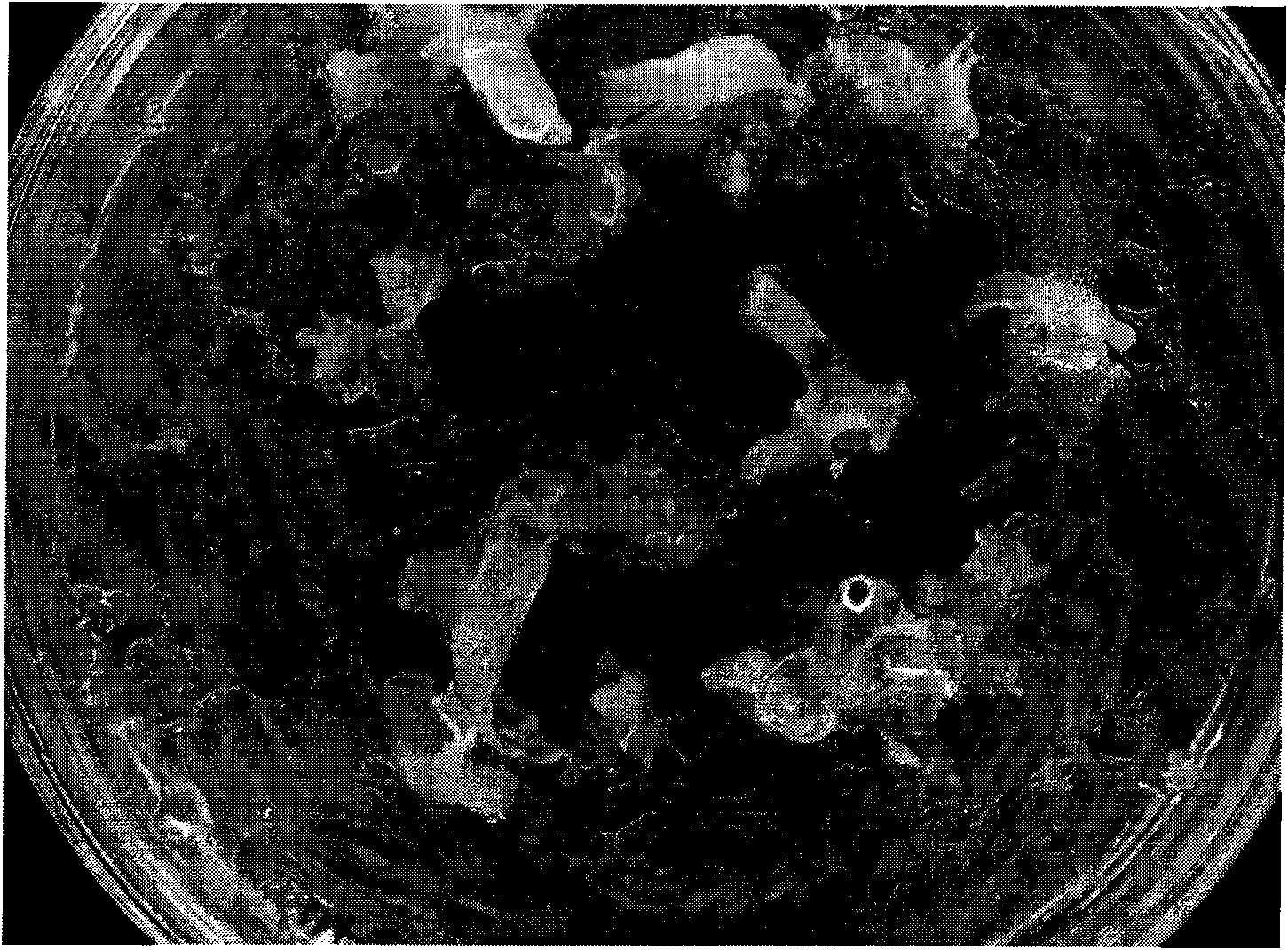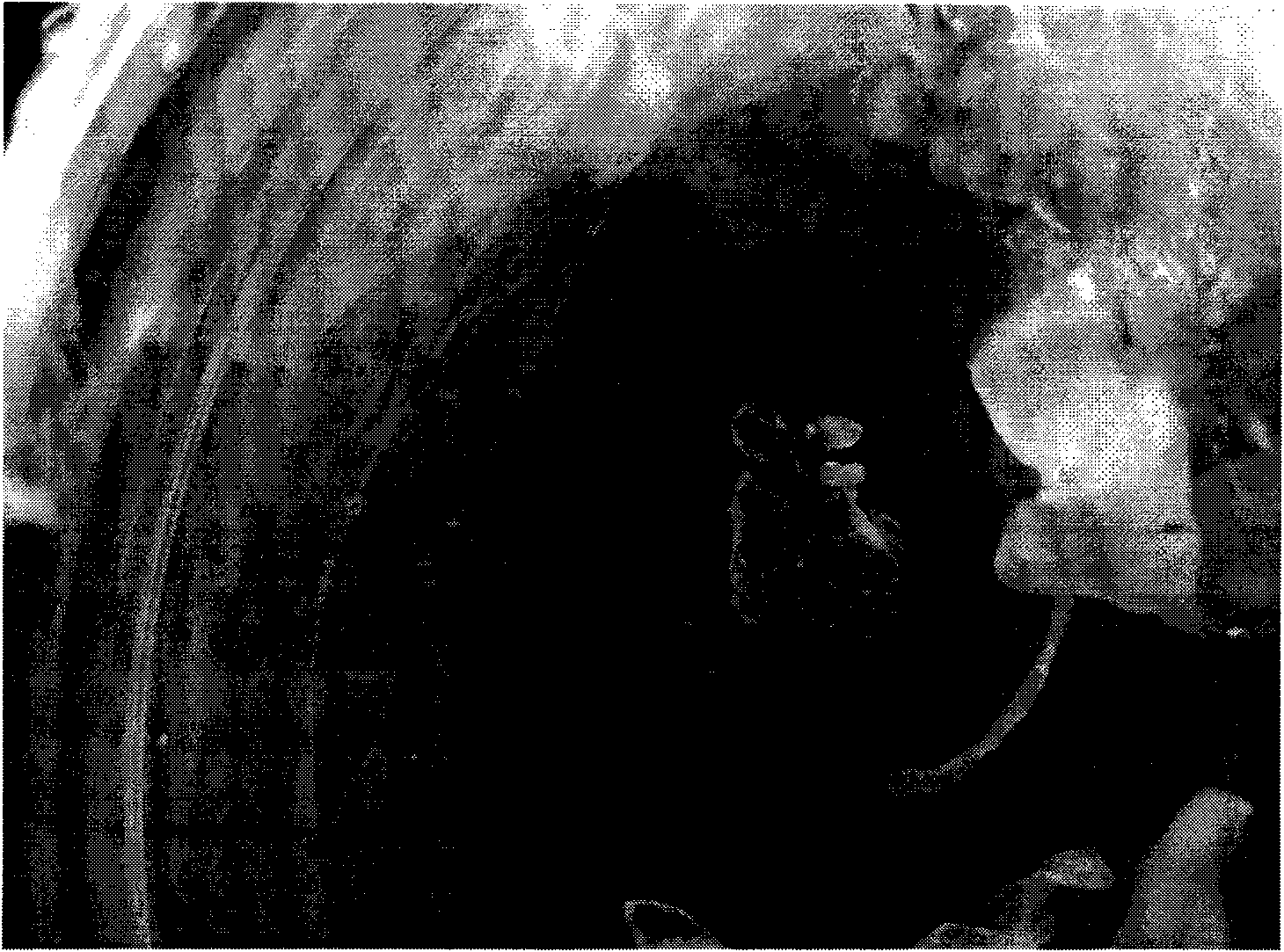Plant regeneration method of dianthus caryophyllus direct somatic embryo generating path and special culture medium
A somatic embryo and culture medium technology, applied in the field of special medium, can solve the problems of cumbersome ways to obtain callus and heavy workload, and achieve good proliferation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Test material selection, culture medium design and inoculation culture
[0039] 1. The source and treatment of test materials:
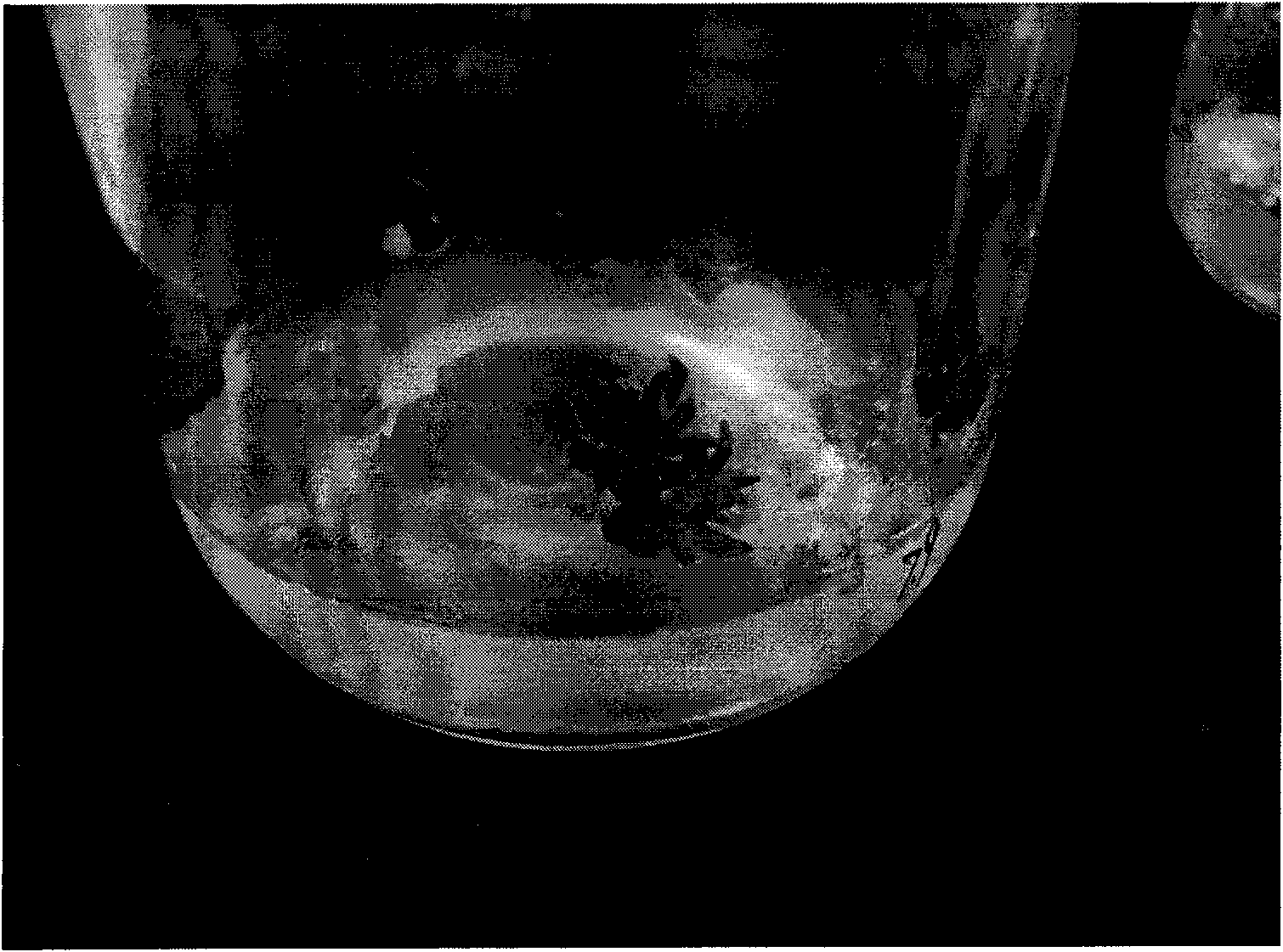
[0040]The test material of the present invention is selected from the flower buds of Carnation, collected from the flower test base of Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, and is a conventional commercially available Carnation variety (the in vitro cultured adult plant of Carnation of the present invention is not affected by varieties and its genotype constraints). The flower bud of carnation collected in the field is sterilized by conventional method (referring to: Li Mingjun compiles, plant tissue culture, China Agricultural Press, 1992 edition), the petal and the receptacle of the carnation flower bud after the disinfection are cut off on the ultra-clean workbench, The petals are separated from the receptacle, and the petals with the bases of the petals are cut into small pieces of 4 mm in length. These ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Effect of the size of flower buds on the callus induction rate of carnation
[0057] The size of carnation buds has a very important influence on the callus induction rate. In this experiment, callus induction was carried out by using carnation flower bracts of different sizes as explants. The size of carnation flower bracts is divided into 0.5~1.0cm, 1.0~1.5cm, 1.5~2.0cm. Different sizes of flower bracts have a very important effect on the induction of callus. The results showed that there was no significant difference in callus induction rate between flower buds with a size of 1.0-1.5 cm and 1.5-2.0 cm, but the callus induction rate was highest when the size of flower bracts was 1.0-1.5 cm. Therefore, flower buds with a size of 1.0-1.5 cm were selected to induce callus.
[0058] Table 2 Effects of flower buds of different sizes on somatic embryo induction of carnation callus
[0059] bract size
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Effects of Different Concentrations of 2,4-D and BA on Callus Induction of Carnation Flower Bracts
[0061] In plant tissue culture, 2,4-D is a widely used auxin growth regulator, and it is recognized as the most effective auxin for initiating cell dedifferentiation, forming callus or organogenesis . The most significant physiological function of cytokinin BA is to promote cell division.
[0062] Mixed use of auxin and cytokinin BA can regulate callus differentiation
[0063] After cultivating the flower bracts of carnation for about 1 week, a small amount of yellow-white callus can be seen in the swelling part of the incision. After about 1 month, two types of callus can be observed, one is white, translucent and more compact , the surface is shiny, and most of this callus can produce somatic embryos in subsequent subcultures. The other is green, loose and vigorously growing or water-soaked or browned. The state of this callus is difficult to adjust. It fa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com