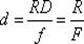Flatness error control method for single-point diamond turning method machining large-sized optical elements
A single-point diamond and optical element technology, used in metal processing mechanical parts, metal processing, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to guarantee surface accuracy, large flatness error, etc., to achieve reliable results, accurate detection and control , the effect of simple control principle
Inactive Publication Date: 2010-10-27
HARBIN INST OF TECH
View PDF5 Cites 21 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
In order to solve the problems that the existing SPDT method has large flatness errors and difficult to guarantee surface shape accuracy when processing large-size optical elements, the present invention provides a flatness error control method for processing large-size optical elements by single-point diamond milling
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
specific Embodiment approach 1
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
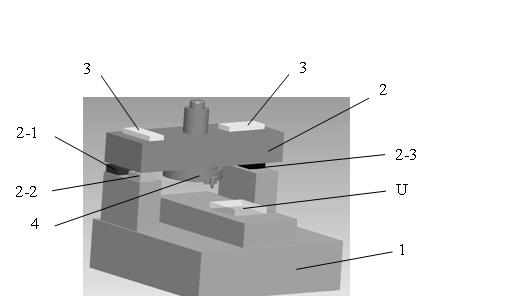
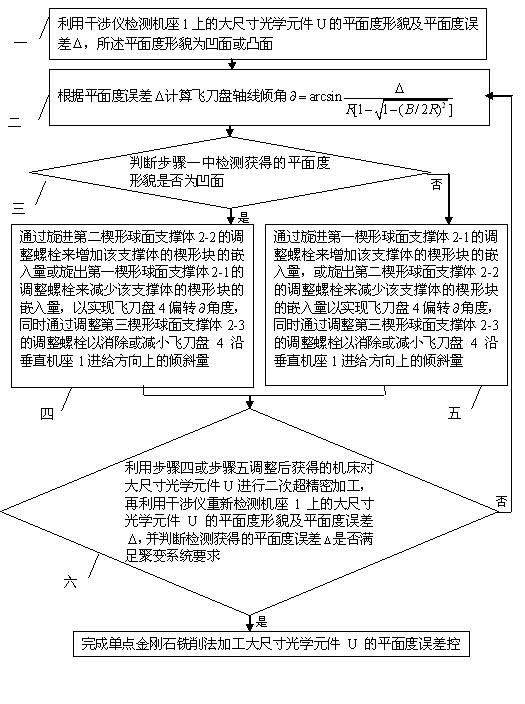
The invention relates to a flatness error control method for the single-point diamond turning method machining large-sized optical elements, which relates to the field of the ultraprecision machining of large-sized fragile optical elements. The invention solves the problems that: when the conventional SPDT method machines a large-sized optical element, the flatness error is high, and the surface figure precision can be hardly guaranteed. The flatness error control method first utilizes an interferometer to detect the flatness topography and the flatness error Delta of a large-sized optical element on a bed, the inclination angle of the axis of a fly-cutter head is then calculated according to the flatness error Delta, three wedged spherical supporting bodies are adjusted according to the detected flatness topography, so that the angle of the fly-cutter head can be deflected, the adjusted machine tool is finally utilized to carry out the secondary ultraprecision machining of the optical element, the interferometer is utilized again to redetect the flatness topography and the flatness error Delta, and when the flatness error Delta meets the requirement of a fusion system, flatness error control is fulfilled for the single-point diamond turning method machining the large-sized optical element. The invention is applicable to the machining of the surface figures of large-sized optical elements.
Description
technical field The invention relates to the field of ultra-precision machining of brittle optical elements, in particular to a flatness error control method for processing large-size optical elements by using a single-point diamond milling (SPDT) method. Background technique Human beings' heavy dependence on fossil energy is the main cause of environmental degradation, and it is urgent to find new alternative energy sources. Fusion energy is clean, pollution-free and almost inexhaustible. Using laser to control nuclear fusion to obtain energy is an ideal way to solve energy problems in the future. At present, all developed countries attach great importance to it. The laser output by the laser driver requires good beam quality, high enough laser energy and power density. To meet this requirement, a large number of electro-optical and nonlinear optical material components, such as KDP crystal, neodymium glass, K9 glass, Quartz glass etc. The common requirements of laser con...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): B23C3/00B23Q15/013B23Q15/26
Inventor 梁迎春陈明君李明全张龙江许乔张飞虎王键孙雅洲
Owner HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com