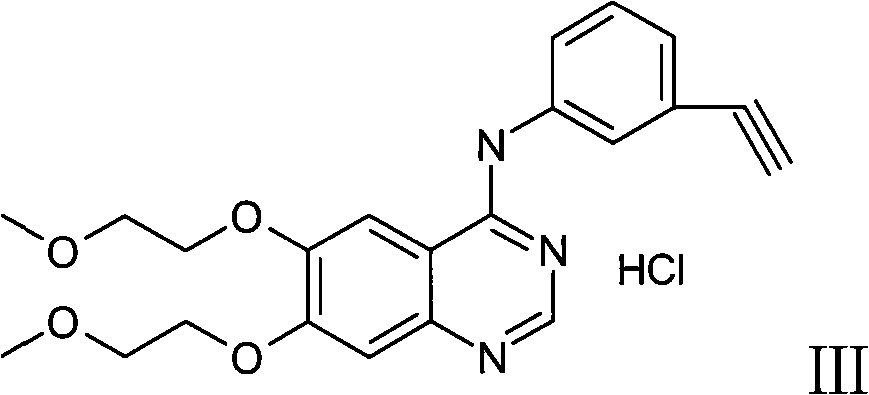
Medicament composition containing sorafenib, cMet inhibitors and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and application thereof
A technology of tyrosine kinase and sorafenib, which is applied to the pharmaceutical composition containing sorafenib, cMet inhibitor and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor and its application field, which can solve the problem of reducing drug dosage, interruption , Toxic and side effects and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing dosage, reducing side effects and improving curative effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 The combination of different ratios of PF-02341066, sorafenib and erlotinib synergistically promotes the death of Hep3B cells, see Table 2.
[0048] Table 2
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] In the experiment investigating the cell death of liver cancer cell line Hep3B caused by related compounds, it was found that when 1.0 μM PF-02341066, 1.5 μM sorafenib, 7.5 μM erlotinib or lower concentrations were used alone, there was almost no cell death, even if the above When any two of the three drugs were combined at lower concentrations, only 1.0 μM PF-02341066+1.0 μM sorafenib and 1.0 μM PF-02341066+5.0 μM erlotinib combined could cause about 20% cell death, while Another combination, namely 1.0 μM sorafenib + 5.0 μM erlotinib, had almost no cell death; but when these three drugs were combined at the lower concentrations mentioned above (1.0 μM +5.0μM erlotinib) produced an obvious synergistic effect, resulting in the death of about 50% of cancer cells; When rafe...
Embodiment 2
[0052]Example 2 The combination of different ratios of PF-02341066, sorafenib and erlotinib synergistically promotes the death of A549 cells, see Table 3.
[0053] table 3
[0054]
[0055]
[0056] In an experiment investigating the death of related compounds in lung cancer cell line A549, it was found that only about 10% of the cells were Even if any two of the above three drugs were combined at a lower concentration, no more than 15% of the cells died; but when the three drugs were combined at the above lower concentration (1.0 μ MPF-02341066 + Sorafenib+5.0μM erlotinib) produced a significant synergistic effect, resulting in the death of about 40% of cancer cells; when the above three drugs were combined in pairs at higher concentrations, there was only 1.5μMPF-02341066 +6.0μM Sorafenib can cause about 27% of cancer cells to die when used in combination, and the other two combinations, namely 1.5μM PF-02341066+7.5μM Erlotinib and 6.0μM Sorafenib+7.5μM Erlotinib only...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 The combination of different ratios of PF-02341066, sorafenib and erlotinib synergistically promotes the death of HCT116 cells, see Table 4.
[0058] Table 4
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] In an experiment investigating related compounds causing cell death in the colon cancer cell line HCT116, it was found that only about 10% of the cells were Even when any two of the above three drugs were combined at lower concentrations, only about 10% of the cells died; Sorafenib+5.0μM erlotinib) produced a significant synergistic effect, resulting in the death of about 44% of cancer cells; when the above three drugs were combined in pairs at higher concentrations, there was only 1.5μMPF-02341066 +6.0μM Sorafenib can cause about 25% of cancer cells to die when used in combination, and the other two combinations, namely 1.5μM PF-02341066+7.5μM Erlotinib and 6.0μM Sorafenib+7.5μM Erlotinib only Caused no more than 20% cell death, and when the three combined (1.5μMPF-0234...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com