Demagnetization method and demagnetization circuit
A degaussing circuit and degaussing method technology, applied in the direction of circuits, magnetic objects, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of complex AC power lines and difficult control of the degaussing process, and achieve control of the degaussing magnetic field size and degaussing time, flexible degaussing magnetic field size and Degaussing time, easy to achieve effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
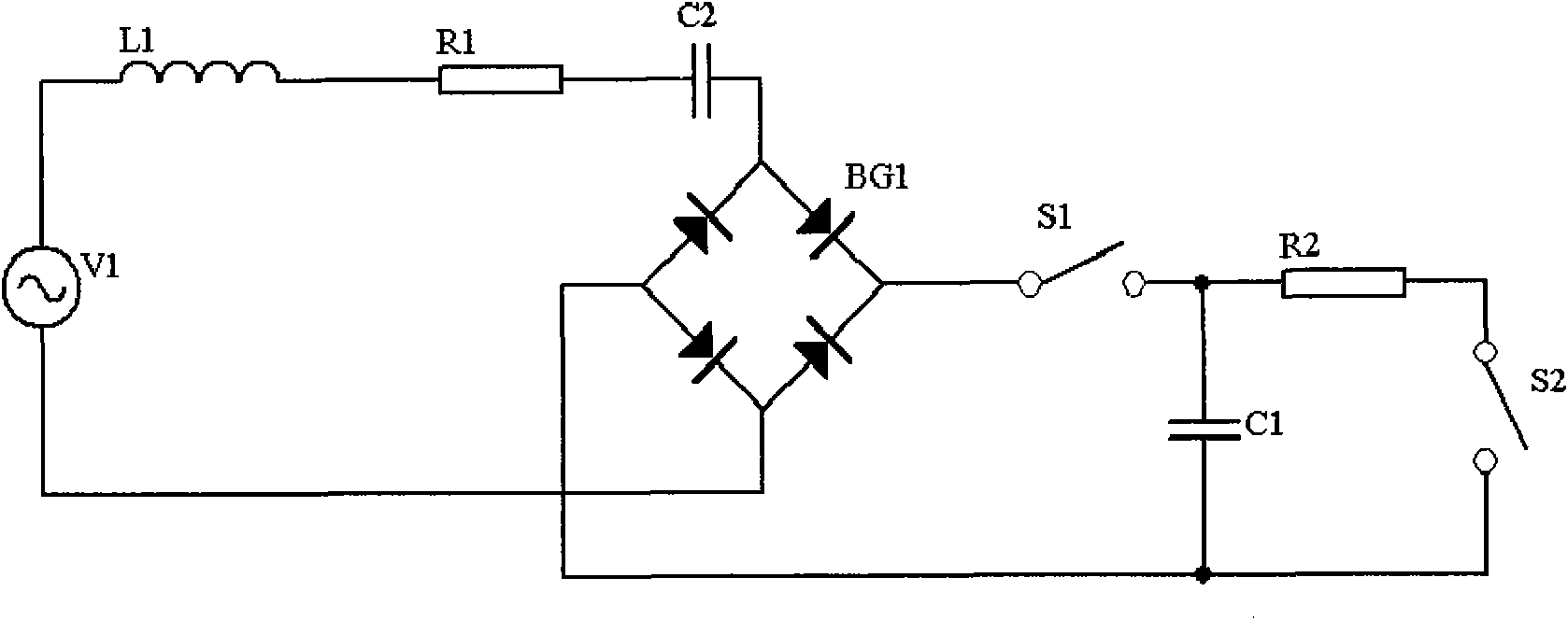
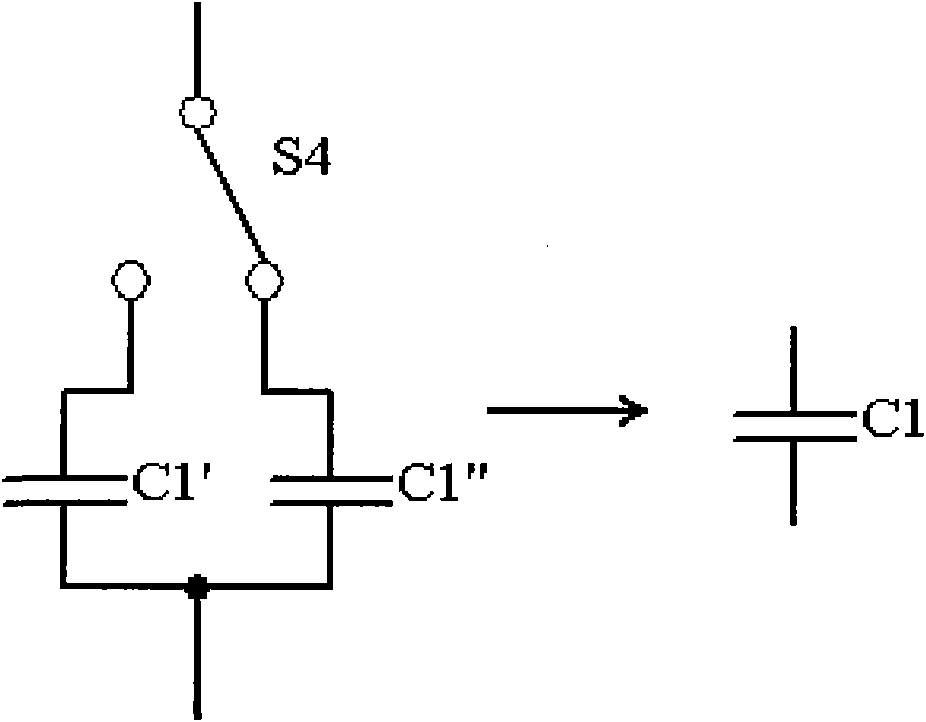
[0029] see figure 1 , The degaussing circuit of the present invention comprises an AC power supply V1, a magnetic field coil L1, a resistor R1, a resistor R2, a capacitor C1, a resonant capacitor C2, a diode bridge rectifier BG1, a switch S1 and a switch S2 connected together.
[0030] Wherein, the diode bridge rectifier stack BG1 may also be composed of four discrete diodes; the switch S1 and the switch S2 are mechanical switches, and may also be set as electronic switches.
[0031] The AC power supply V1 is 220V commercial power, one end is connected to the magnetic field coil L1, and the other end is connected to an AC terminal of the diode bridge rectifier BG1; the magnetic field coil is connected to the resistor R1 which acts as a current limiter, and the resistor R1 is connected to the resonant capacitor C2 to achieve resonance The capacitor C2 is then connected to another AC terminal of the diode bridge rectifier BG1, and the AC power supply V1, resistor R1, capacitor C...
Embodiment 2
[0044] see figure 2 , the difference from the first embodiment is that the current limiting resistor R1 is moved to the bridge arm of the diode bridge rectifier stack BG1, and four resistors R0 are respectively connected to the diodes, and all other components and positions remain unchanged.
[0045] In this way, the magnetic field coil L1 is directly connected to the resonant capacitor C2, and the current limiting function is realized by the four resistors R0 integrated into the diode bridge rectifier BG1. The degaussing principle and effect are the same as those in the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
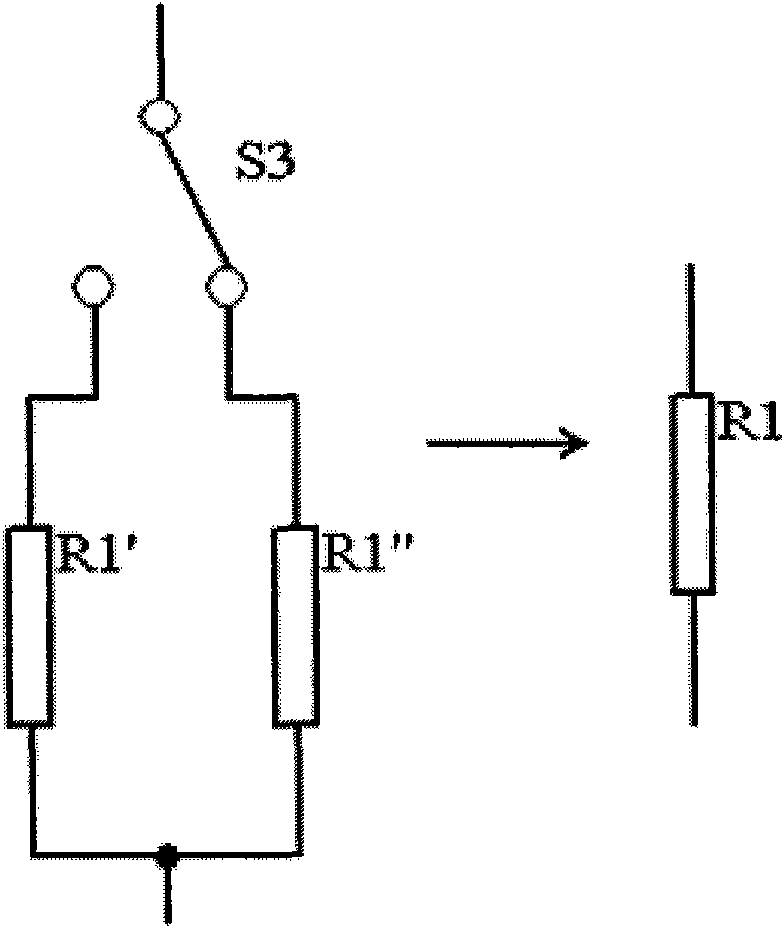
[0047] see image 3 , the difference from Example 1 is that the figure 1 The middle current-limiting resistor R1 is moved to the DC charging circuit, that is, the magnetic field coil L1 is directly connected to the resonant capacitor C2, one end of the current-limiting resistor R1 is connected to the DC terminal of the diode bridge rectifier BG1, and the other end is connected to the capacitor C1, and other components and positions remain constant.
[0048] Since the AC main circuit is connected to the DC charging circuit through the diode bridge rectifier BG1, and the current of the AC main circuit is controlled by the charging current of the DC charging circuit, moving the current limiting resistor R1 into the DC charging circuit can also play a role. To indirectly control the current of the AC main circuit, it has no effect on the principle and effect of degaussing.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com