Method for treating waste sludge in oil and natural gas exploration drilling operations
A technology of oil and gas, exploration and drilling, applied in the direction of biological sludge treatment, etc., can solve problems such as not adapting to energy-saving policies, consuming large solidification materials, soil environmental pollution, etc., to achieve the effect of retaining the value of cultivation and ensuring sustainable development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
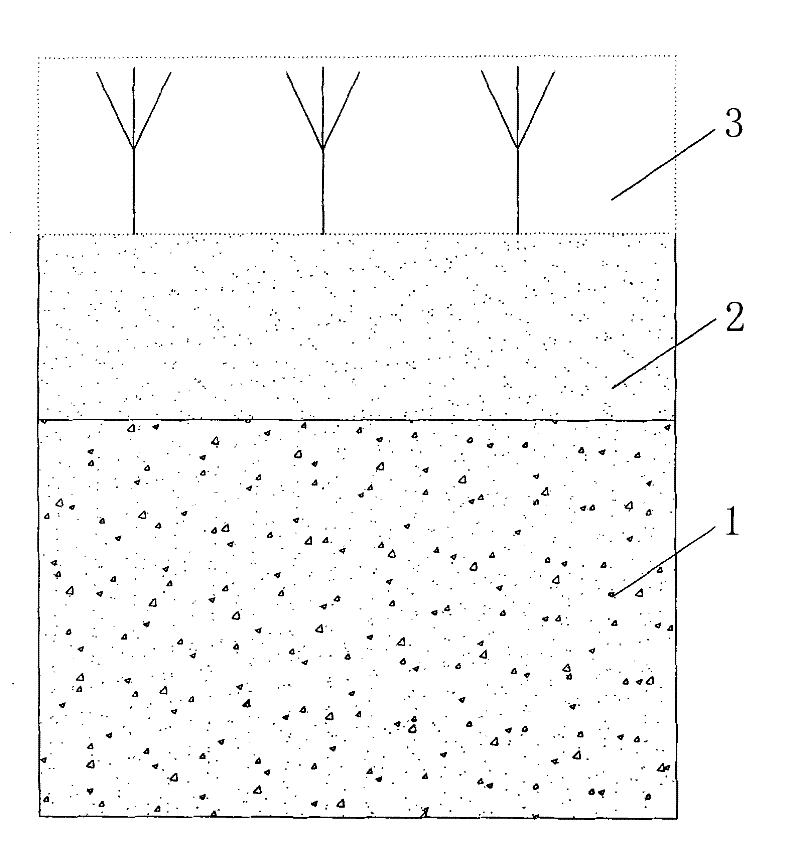
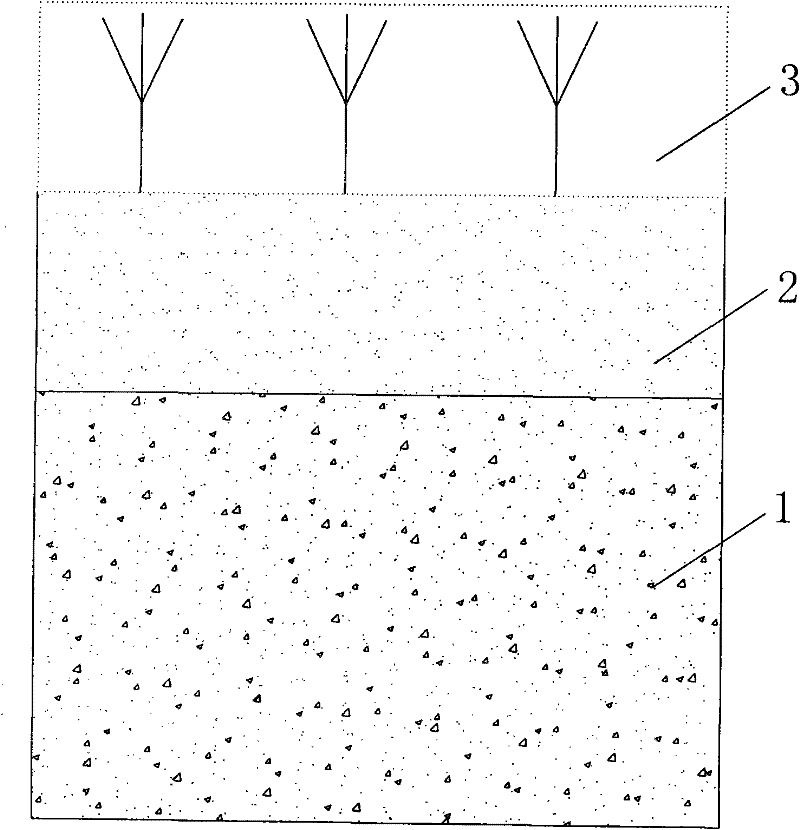
[0026] The method discloses a method for treating waste sludge in oil and gas exploration and drilling operations. The steps include:
[0027] a. Microbial treatment: add special microbial strains to the waste sludge in a weight ratio of 5:100 and mix evenly; and add natural soil to the waste sludge mixed with special microbial strains in a weight ratio of 2:1 In, mix evenly, thereby form microbial treatment layer 1; Described special-purpose microbial strain is Halomonas ventosae bacterium, Halomonas campisalis bacterium in Halomonas, and Bacillus megaterium (Bacillus megaterium) in Bacillus;
[0028] B, soil treatment: the microbial treatment layer 1 surface that forms in a step, covers the natural soil of 10-15cm, forms the soil treatment layer 2;
[0029] c. Plant treatment: On the surface of the soil treatment layer 2, plant leguminous and non-legume symbiotic nitrogen-fixing tree species, or plant herbaceous plants to form the plant treatment layer 3 .
Embodiment 2
[0031] As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, on the basis of Example 1, in step c, the leguminous and non-legume symbiotic nitrogen-fixing tree species are Leucaena or Alder. In the c step, the herb is miscanthus or clover. In the described a step, there are 4 strains of Halomonas ventosae bacteria, 1 strain of Halomonas campisalis bacteria, and 1 strain of Bacillus megaterium. In the step a, the added natural soil is air-dried and adjusted to a soil with a water content of 15-20% and a particle size of 0.5-1 cm. In step a, the water content of the microbial treatment layer 1 is 20-30%. In the step b, the natural soil is air-dried and adjusted to a soil with a water content of 15-20% and a particle size of 0.5-1 cm. The percentage of said water content is weight ratio. The COD mentioned in the present invention refers to the COD index in the waste sludge treatment in the field of drilling, that is, the chemical oxygen demand and the oil index.
Embodiment 3
[0033] The special microorganism that the present invention adopts belongs to Halomonas and Bacillus in classification, and 4 bacterial strains (C3-1, C7-2, C7-4 and C8-2) belong to Halomonas ventosae wherein; C5-2 belongs to Halomonas campisalis; C2-3 belongs to Bacillus megaterium. These strains have strong stress resistance (salt resistance 5%, pH 11.0 resistance), wide growth temperature range (15-37° C.), and good degradation effect on drilling waste mud components. These special bacteria are used to convert part of the complex substances in oil and gas exploration drilling waste mud into soil humus components, and partly degrade them into simple organic and inorganic compounds for use by other microorganisms in the soil and aboveground plants. Leucaena and alder planted are leguminous and non-legume symbiotic nitrogen-fixing tree species, transforming nitrogen in the atmosphere (N 2 ) to ammonia (NH 3 ) provides the nitrogen source required for plant growth, and also p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com