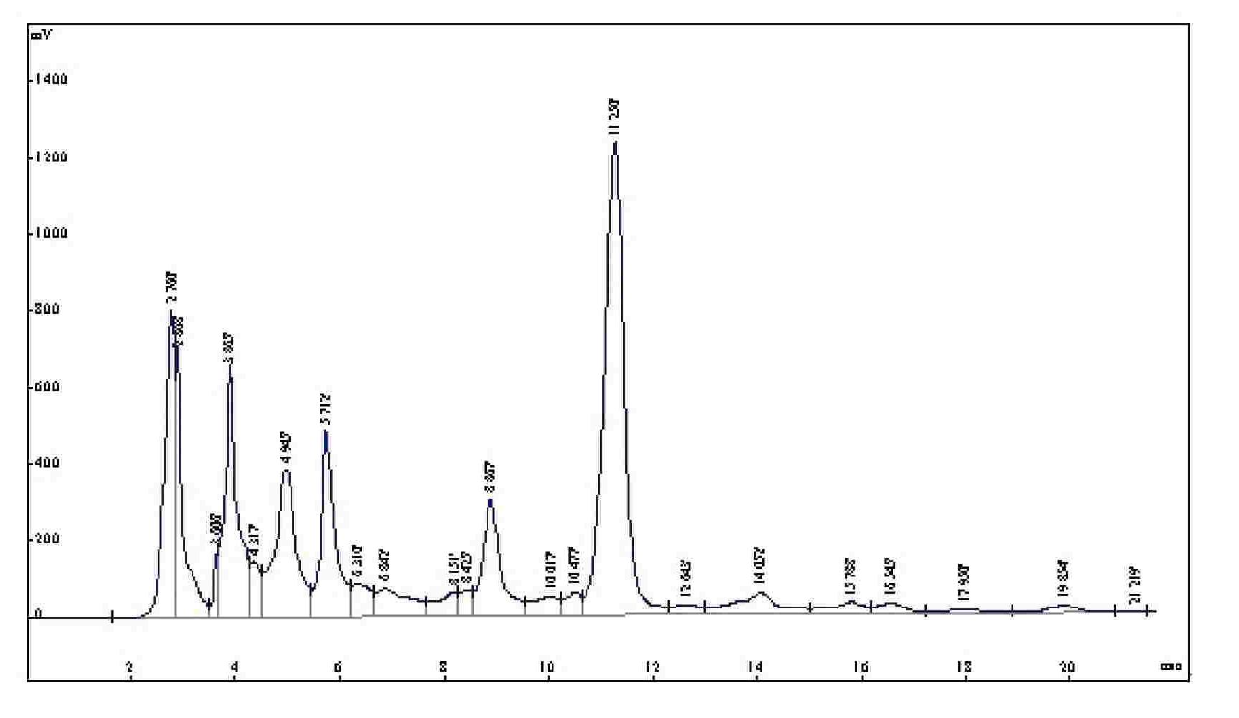
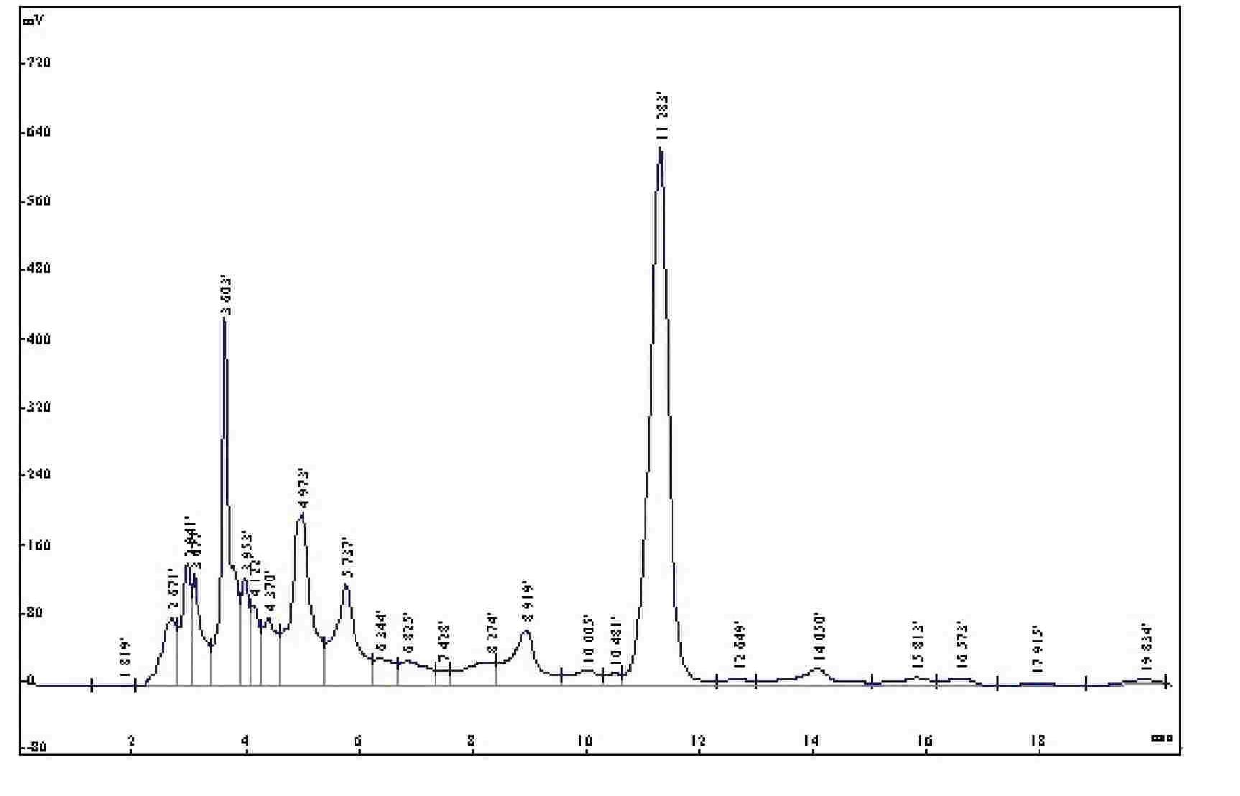
Method for preparing olive leaf extract
An olive leaf extract and olive leaf technology, applied in the preparation of sugar derivatives, chemical instruments and methods, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome processing, low extraction efficiency, heavy workload, etc., and achieve easy collection of samples , Low operating cost, less investment in equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The method for extracting oleuropein from olive leaves of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] (1) Extraction: Place fresh olive leaves in an atmospheric oven at 65°C overnight, weigh out 200g of dried olive leaves, cut them into pieces, add 3L 60% ethanol and 4g calcium carbonate, reflux and extract 3 times at 70°C, 2h each time , Combine the three extracts.
[0030] (2) Flocculation and sedimentation: Concentrate the extract to a specific gravity of 1.01~1.10, dilute 1.5 times with water, add 1% alum solids of the solution volume to be settled, stir for 30min, stand for 3~5h, centrifuge to obtain oleuropein as The brown clear solution of the main product;
[0031] (3) Extraction: Add 1L of petroleum ether with a boiling range of 60°C to 90°C to the supernatant obtained by centrifugation, shake well for extraction, stand still for layering, and separate; recover the petroleum ether from the petroleum ether phase and discard the residue ; The aqueous phase ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The method for extracting oleuropein from olive leaves of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0037] (1) Extraction: dry fresh olive leaves in the shade, weigh 500g of dried olive leaves, cut them into pieces, add 5L of 75% ethanol and 6g of calcium carbonate, reflux and extract 3 times at 70°C, 2h each time, and combine the three extracts .
[0038] (2) Flocculation and sedimentation: Concentrate the extract to a specific gravity of 1.01~1.10, dilute it by 1 time with water, add the 101 juice clarifier solution (configured as a 5% aqueous solution) of 3% of the solution volume to be settled, stir, stand for 3h, and centrifuge Separate to obtain a brown clear solution of oleuropein as the main product;
[0039] (3) Extraction: Add 2L of petroleum ether with a boiling range of 60°C to 90°C to the supernatant obtained by centrifugation, shake well for extraction, stand still for layering, and separate; recover the petroleum ether from the petroleum ether phase, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Take 5 kg of fresh olive leaves, dry them in a ventilated and cool place, and then blast them in an oven at 50°C for 3-20 hours. The measured water content is less than 5.0% and the oleuropein content is 1.89%. Take 1000g of dried leaves, break them into small pieces, add 10L of 95% ethanol aqueous solution, heat extraction at 70℃, time 2 hours, filter, add 8L of 95% ethanol solution for the second extraction, time 2 hours, filter, and add 6L of 95% ethanol for the third time The solution was extracted for 1 hour, and the filtrates were combined. Concentrate to a specific gravity of 1.10 at 50°C, dilute by 1 time with water, add 1% chitosan (1% solution with 1% acetic acid) of the solvent volume to be precipitated, stir for 30min, stand for 4h, centrifuge to remove the precipitate, Obtained orange-yellow clear solution.
[0045] The clarified solution was first extracted with petroleum ether (boiling range 60~90℃) once, the petroleum ether was recovered from the petroleum...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com