Laser propulsion device
A propulsion device and laser technology, applied in jet propulsion devices, rocket engine devices, machines/engines, etc., can solve problems such as small specific impulse ratio theoretical value, mass loss, etc., to improve actual specific impulse, prolong life, and avoid heat conduction Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
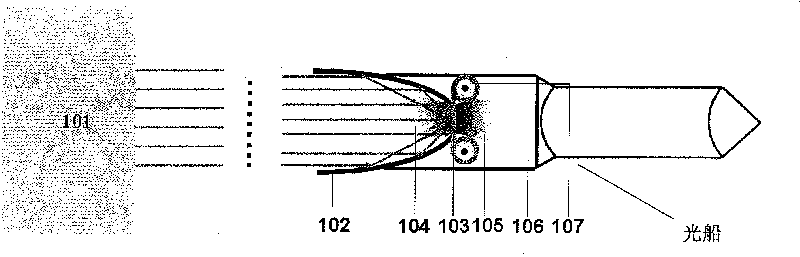
[0024] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a laser propulsion device according to an embodiment of a thin film propellant used in the present invention, the device includes a pulsed laser 101, a parabolic mirror 102, a combustion chamber 106 and a belt conveyor 107; wherein the belt conveyor is used for not Thin-film propellant 103 is provided intermittently, said thin-film propellant is located in the opening at the top of parabolic mirror 102, and is located at the focal point of parabolic mirror 102, so that said parabolic mirror can focus laser light onto the thin-film propellant. Preferably, the thickness of the thin film propellant is less than or equal to the ablation depth of the laser pulse, so that the laser light can pass through completely, so that the thin film propellant is substantially completely ablated when the laser is irradiated thereon; in addition, the thickness of the thin film propellant is small , The lateral heat conduction is also relatively low, s...
Embodiment 2
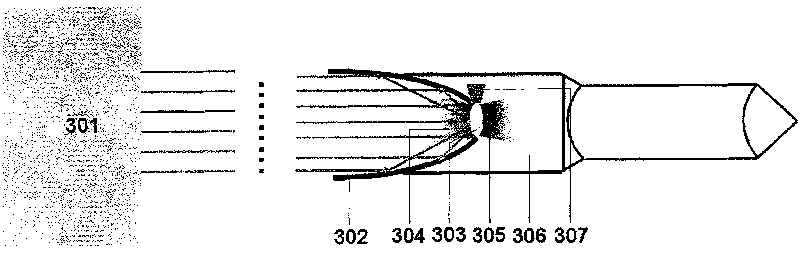
[0028] image 3 is a schematic diagram of a laser propulsion device according to one embodiment of the present invention employing solid particle or cluster propellants. Different from the laser propulsion device in Embodiment 1, this embodiment uses solid particle or cluster propellant 303 instead of film propellant 103 , and uses nozzle 307 instead of belt conveyor 107 . Such as image 3 As shown, solid particle or cluster propellant 303 is ejected using nozzle 307 . During the working process of the device, due to the low surface density of solid particles or clusters and the high absorption efficiency of laser light, no critical density surface will be formed, and the laser ablation will not be blocked, and the distance between particles is relatively large, so it will not be caused by Thermal diffusion results in energy loss that essentially converts the solid particle or cluster propellant into a plasma, resulting in a higher specific impulse. In addition, the injecti...
Embodiment 3
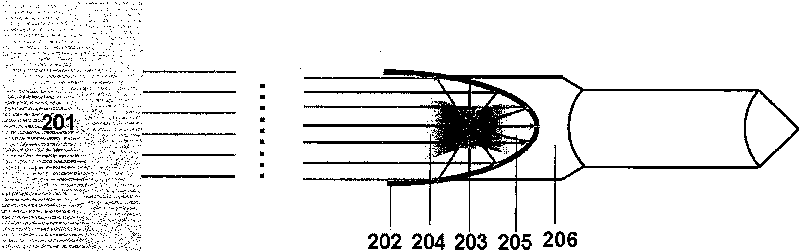
[0030] Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of a laser propulsion device according to an embodiment of the present invention using a disc conveyor. Different from the laser propulsion device of Embodiment 1, this embodiment uses a lightweight foam material propellant (not shown) instead of the film propellant 103 , and uses a disc conveyor 501 instead of the belt conveyor 107 . The thickness of the lightweight foam propellant is less than or equal to the ablation depth of the laser. During the working process of the device, the disc conveyor 501 continuously delivers the lightweight foam propellant to the opening, and when the laser irradiates the propellant, it is basically completely ablated and transformed into plasma to propel the lightship. In the present invention, the lightweight foam propellant may be a commercially available foam whose main component is polystyrene. In addition, the lightweight foam propellant can be either a pan conveyor or a figure 1 A belt conveyor ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com