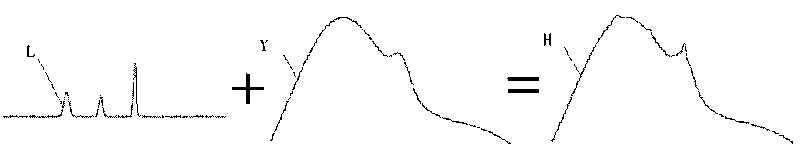
Multi-wavelength excitation-based fluorescence elimination method for Raman spectrum
A Raman spectroscopy and fluorescence elimination technology, applied in the fluorescence elimination field of Raman spectroscopy, can solve the problems such as fluorescence spectrum is not as stable as Raman spectrum, difficult to realize with micro-miniature Raman spectrometer, cannot guarantee the purity of Raman spectrum, etc. The steps are simple and easy to implement, the Raman signal is pure, and the effect is easy to popularize and apply.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
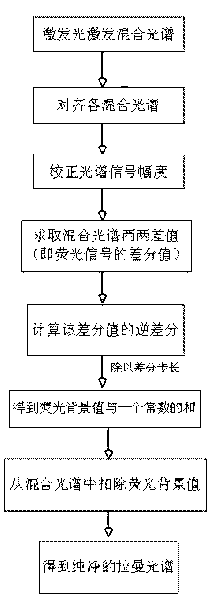
[0029] A fluorescence elimination method based on multi-wavelength excitation Raman spectroscopy. This method is to irradiate the same sample with multiple excitation lights of similar wavelengths sequentially generated by a laser light source semiconductor laser, and sequentially excite different fluorescence and Raman spectra. The mixed spectrum composed of Mann light; the array photosensitive spectrometer collects each mixed spectral signal, with the light intensity as the ordinate, the excitation light wavelength as the origin, and the frequency shift wavenumber as the abscissa, align each mixed spectrum, and normalize through the full spectrum integral value Then, the difference between each pair of mixed spectra is calculated, and the difference is the difference value of the fluorescence signal, and the difference step size is two mutual differences The difference between the wavelength of the excitation light of the subtracted mixed signal is calculated, and the inverse...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com